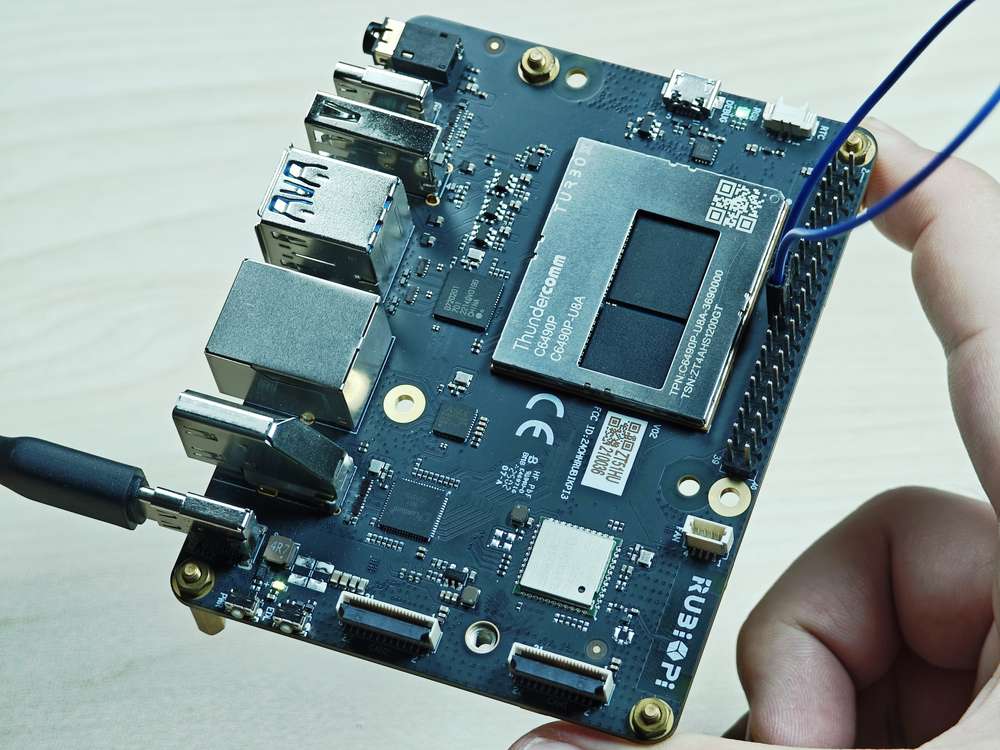
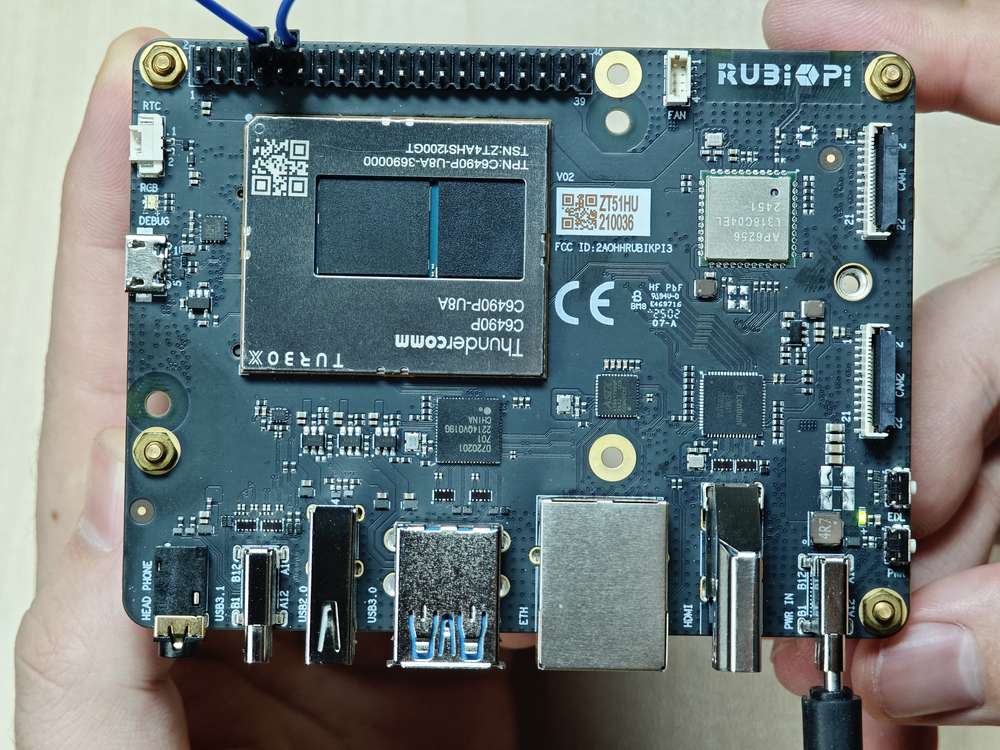
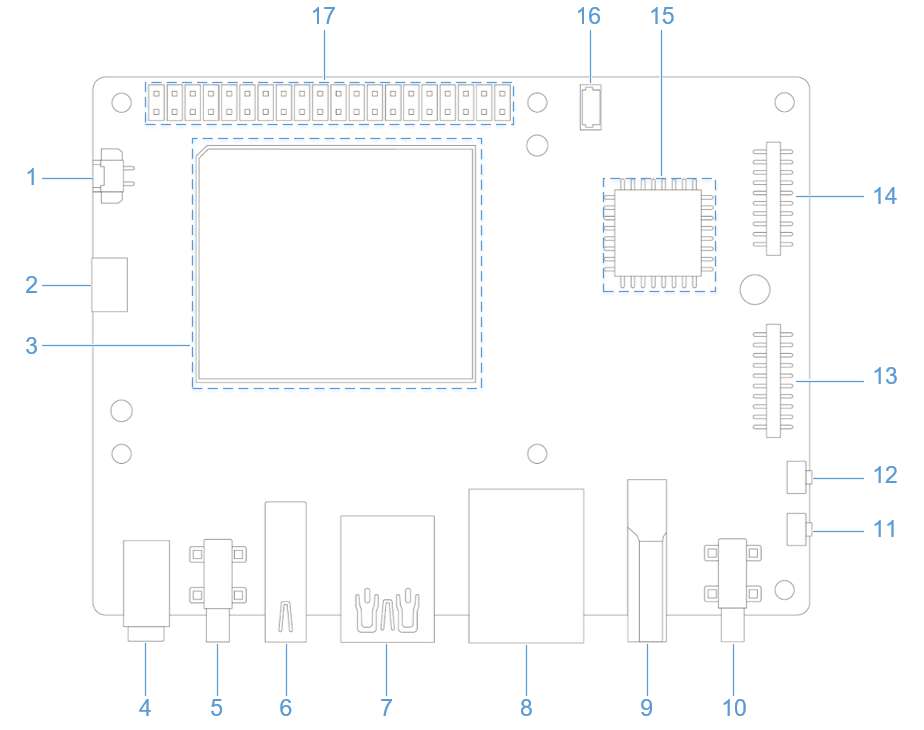
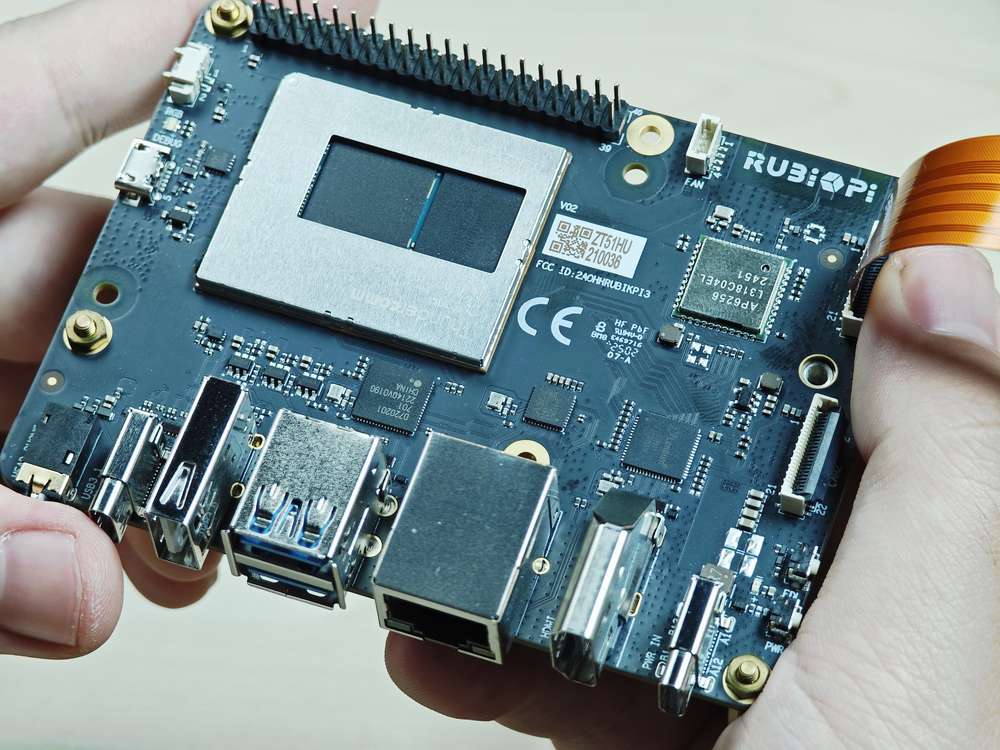
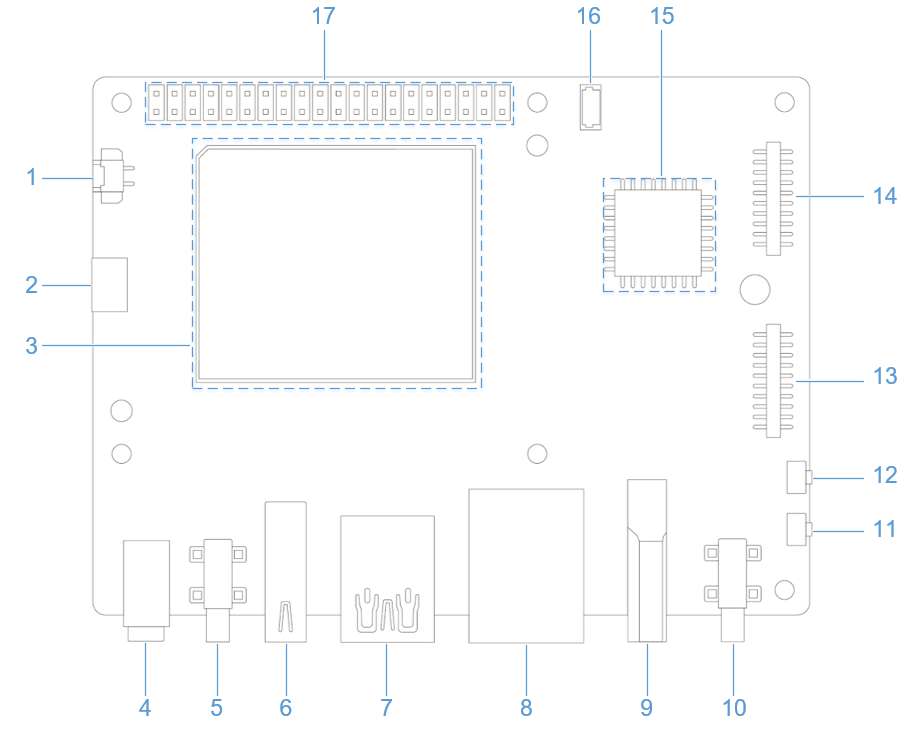
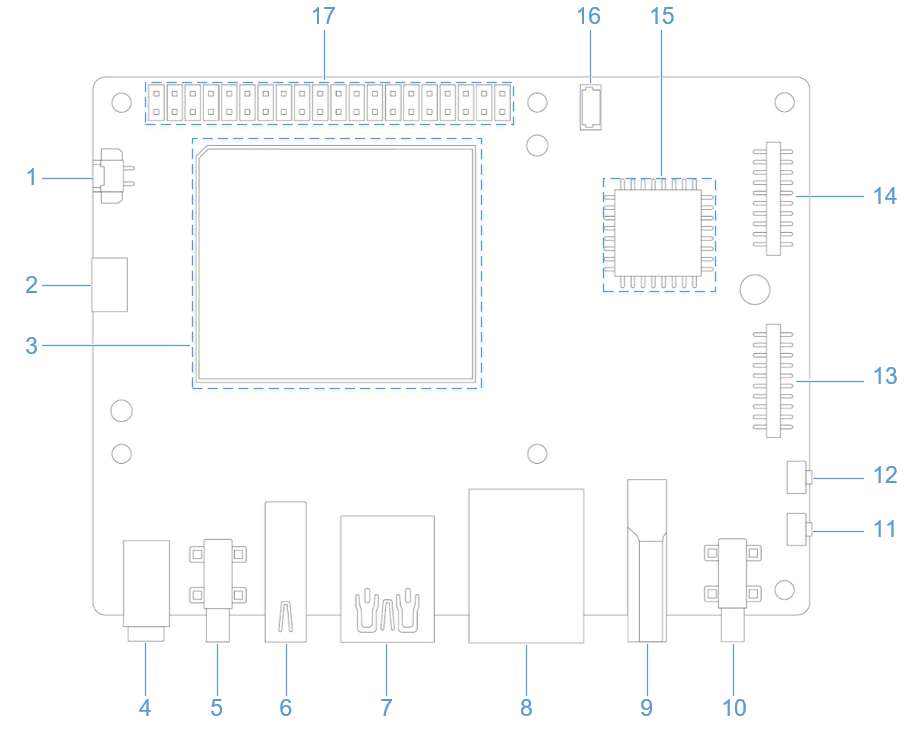
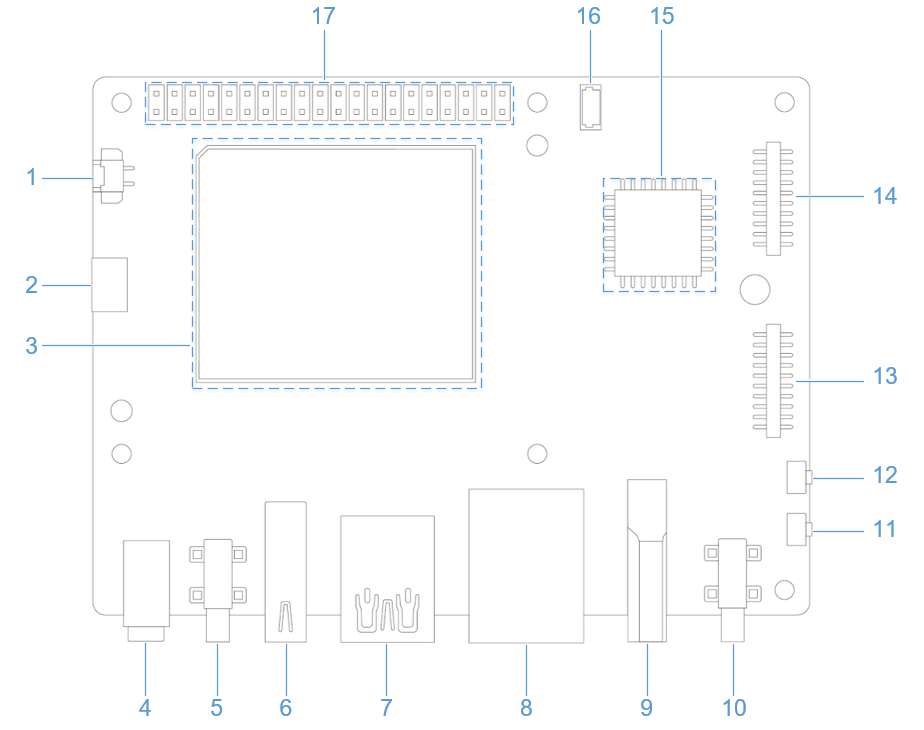
外设与接口
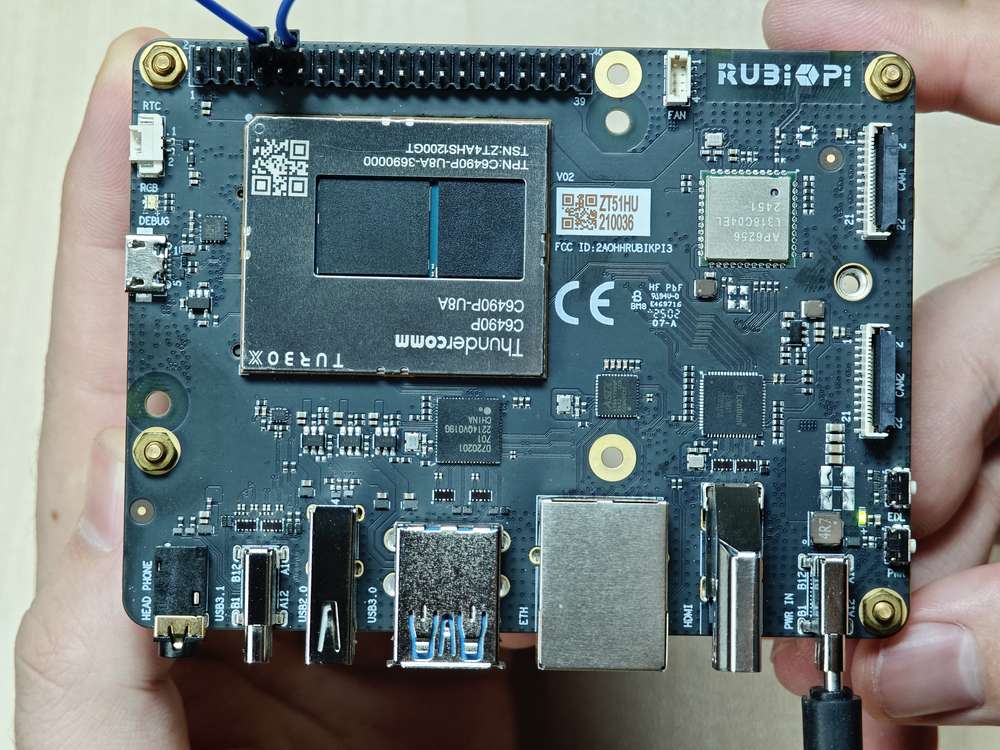
硬件资源图
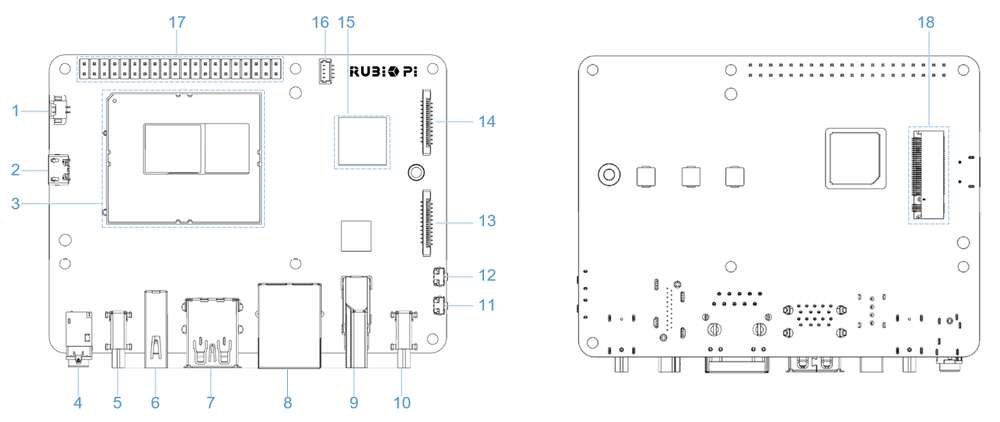
| 序号 | 接口 | 序号 | 接口 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | RTC 电池接口 | 10 | 电源 Type-C 接口 |
| 2 | Micro USB (UART 调试) | 11 | PWR 按键 |
| 3 | TurboX C6490P SOM | 12 | EDL 按键 |
| 4 | 3.5mm 耳机接口 | 13 | 摄像头接口 2 |
| 5 | USB Type-C with DP (USB 3.1) | 14 | 摄像头接口 1 |
| 6 | USB Type-A (USB 2.0) | 15 | Wi-Fi/蓝牙模块 |
| 7 | 2 x USB Type-A (USB 3.0) | 16 | 风扇接口 |
| 8 | 1000M 以太网 | 17 | 40-pin 连接器 |
| 9 | HDMI OUT | 18 | M.2 Key M 接口 |
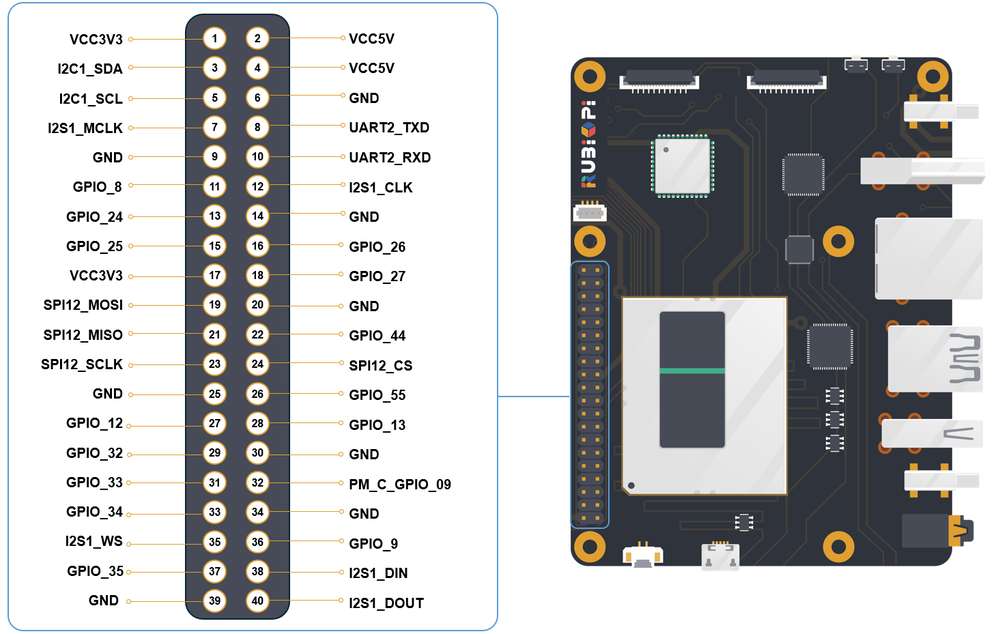
40 pin 连接器
GPIO
魔方派 3 适配了 WiringRP(基于高性能 GPIO 编程库 WiringPi),推荐使用 WiringRP 来对 GPIO 进行控制和编程。关于 WiringRP 详细信息可访问 https://github.com/rubikpi-ai/WiringRP 查看。
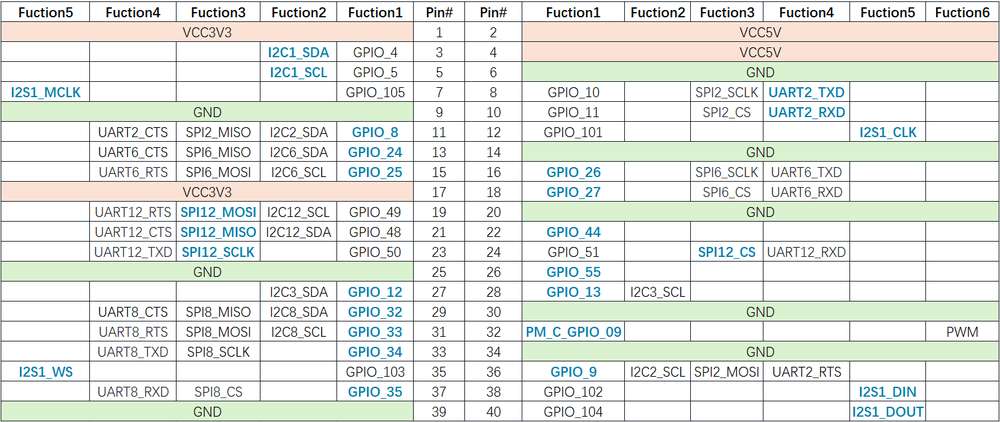
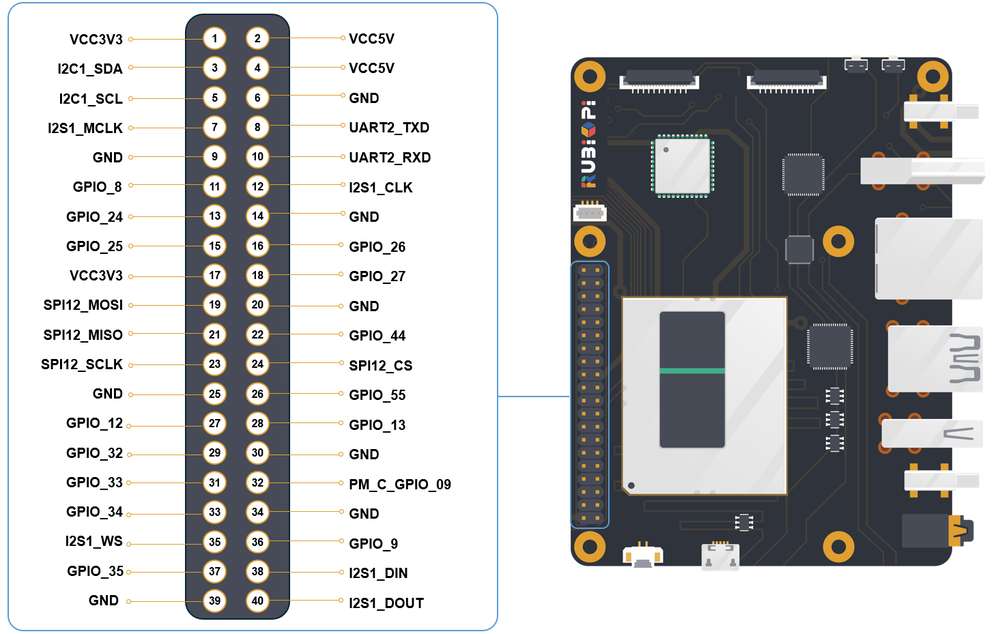
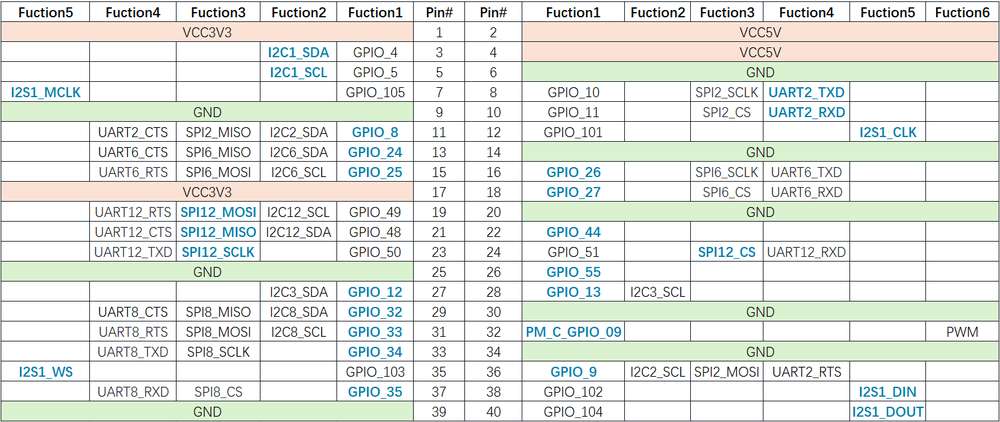
引脚分布
下图是 魔方派 3 40-pin 连接器的引脚默认功能,其中大部分引脚和树梅派 40-pin 连接器引脚的默认功能兼容。
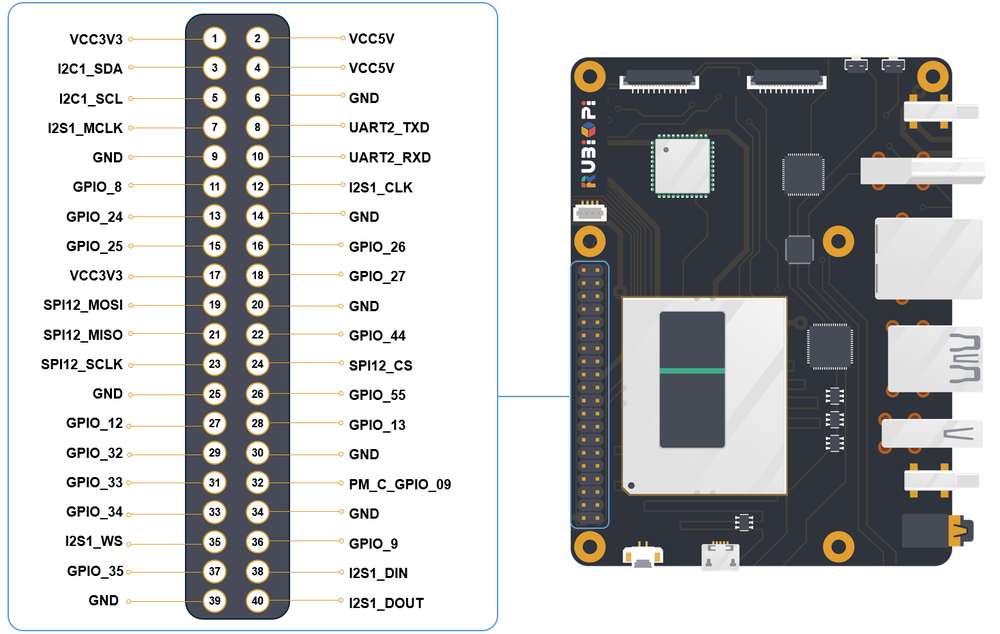
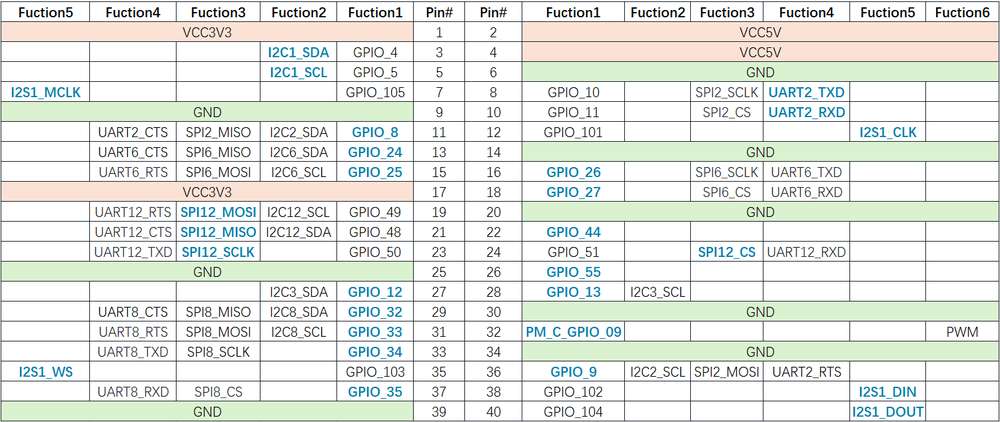
下表是 40-pin连接器支持的所有功能,图中蓝色字体表明默认功能。
使用 shell 命令控制
在 魔方派 3 中执行下面的步骤控制 GPIO。
-
使用 WiringRP 相关命令
-
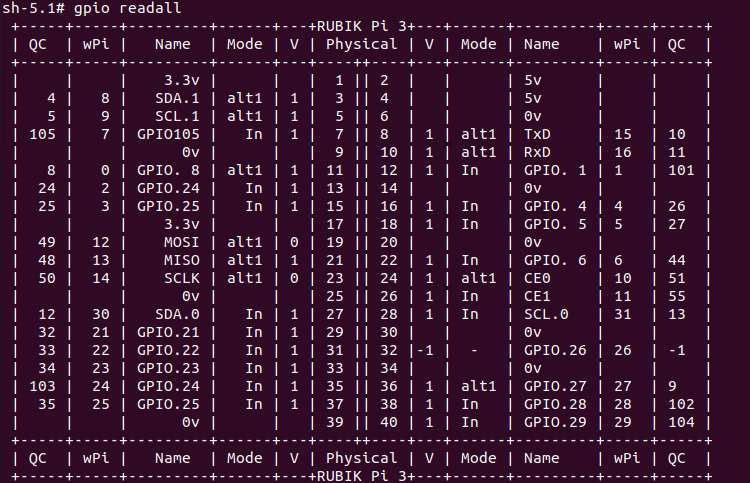
查看 GPIO 状态
gpio readall
-
设置 GPIO 模式
gpio mode 15 in # 将15号引脚模式置为输入
gpio pins # 查看更改之后的状态
gpio mode 15 out # 将15号引脚模式置为输出
gpio pins # 查看更改之后的状态 -
设置引脚电平
gpio write 15 1 # 将15号引脚置为高电平
gpio read 15 # 读取更改后引脚状态
gpio write 15 0 # 将15号引脚置为低电平
gpio read 15 # 读取更改后引脚状态
-
-
操作 /sys/class/gpio 下相关节点
GPIO 子系统的编号如下表。
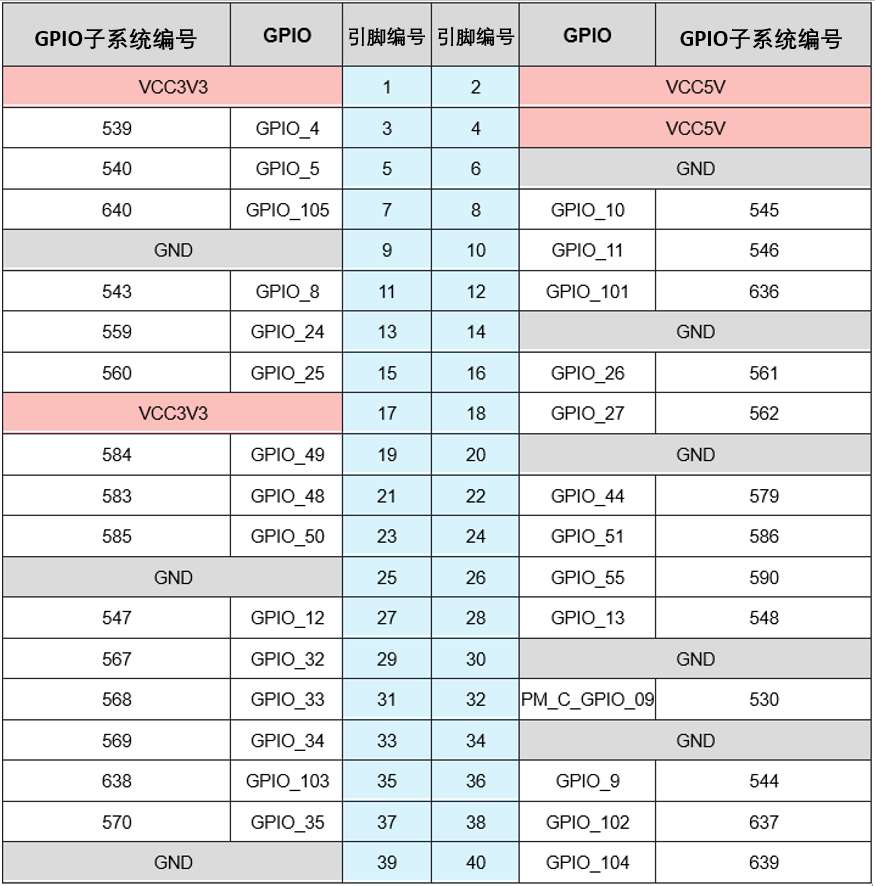
- 进入 /sys/class/gpio 目录:
cd /sys/class/gpio- 将要控制的 GPIO 导出,如控制 13 号引脚 GPIO_24:
echo 559 > export- 进入到 gpio559 目录设置 GPIO 属性:
cd gpio559
ls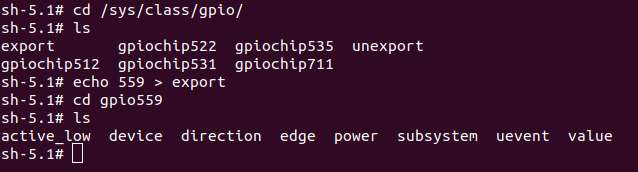
- direction(方向):
- 输入:in
- 输出:out
- value(值):
- 低电平:0
- 高电平:1
- edge (中断边沿):
- 上升沿触发:rising
- 下降沿触发:falling
- 双边沿触发:both
- 禁用中断:none
如设置 13 号引脚输出高电平:
echo out > direction
echo 1 > value取消导出 13 号引脚到用户空间:
echo 559 > unexport
使用 WiringRP (C) 控制
WiringRP 库中提供了一系列的 API 函数�,用更少的逻辑实现控制。
- 以下代码示例,将 13 号引脚设置为输出, 15 号引脚设置为输入,循环检测 15 号引脚的电平状态:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <wiringPi.h>
int main (void)
{
wiringPiSetup () ;
pinMode (13, OUTPUT) ;
pinMode (15, INPUT) ;
for (;;)
{
digitalWrite (13, HIGH) ; // On
printf("%d\n", digitalRead (15)); // On
delay (1000) ; // mS
digitalWrite (13, LOW) ; // Off
printf("%d\n", digitalRead (15)); // On
delay (1900) ;
}
return 0 ;
}
-
在 魔方派 3 中编译程序
adb push gpio.c /opt
adb shell
cd /opt
gcc gpio.c -o gpio -lwiringPi -
将 13 和 15 号引脚使用杜邦线短接,测试 GPIO 电平控制和电平读取情况,如下图所示:
注意注意引脚顺序,请勿将电源和地引脚短接,否则可能会造成板子损坏。
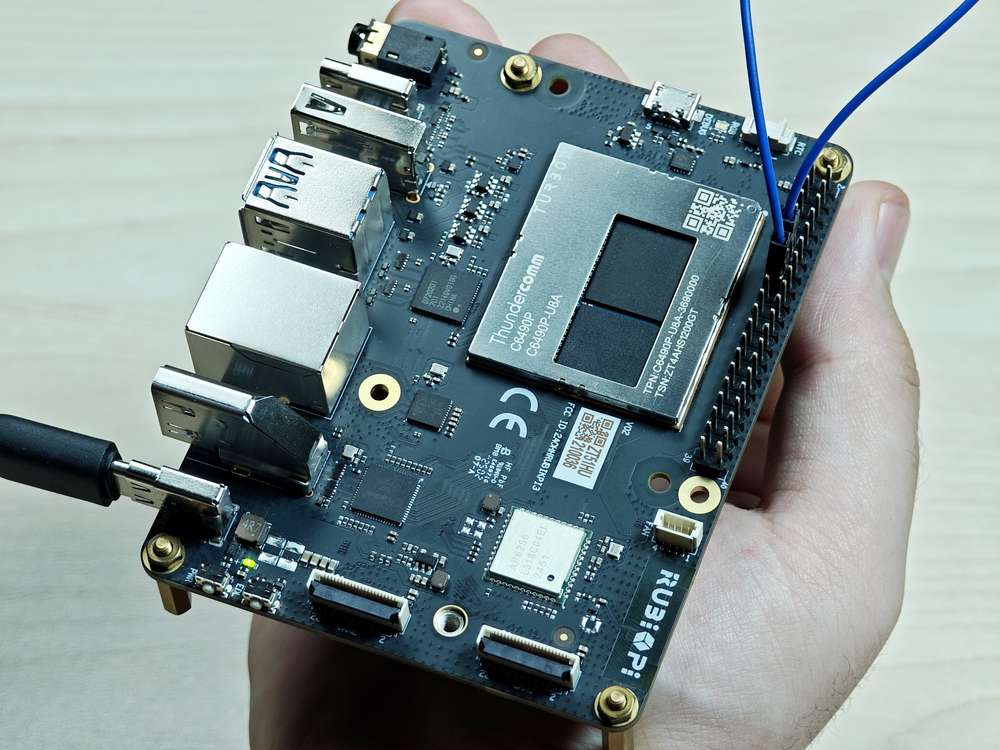
运行如下命令:
cd /opt
./gpio程序运行结果如下:
使用 WiringRP-Python 控制
WiringRP 库中提供了一系列的 API 函数,用更少的逻辑实现控制。
-
下方截取代码是使用 WiringRP 库操作 GPIO 的示例,其中将 13 号引脚设置为输出,15 号引脚设置为输入,循环检测 15 号引脚的电平状态。
import wiringpi
import time
wiringpi.wiringPiSetup()
wiringpi.pinMode(13, 1)
wiringpi.pinMode(15, 0)
wiringpi.digitalRead(15)
while True:
wiringpi.digitalWrite(13,1)
pin_level = wiringpi.digitalRead(15)
print(f"in_gpio level: {pin_level}")
time.sleep(1)
wiringpi.digitalWrite(13,0)
pin_level = wiringpi.digitalRead(15)
print(f"in_gpio level: {pin_level}")
time.sleep(1) -
将 gpio.py 传输到 魔方派 3 中,如使用 ADB 传输。
adb push gpio.py /opt -
将 13 和 15 号引脚使用杜邦线短接,测试 GPIO 电平控制和电平读取情况,如下图所示
注意注意引脚顺序,请勿将电源和地引脚短接,否则可能会造成板子损坏。
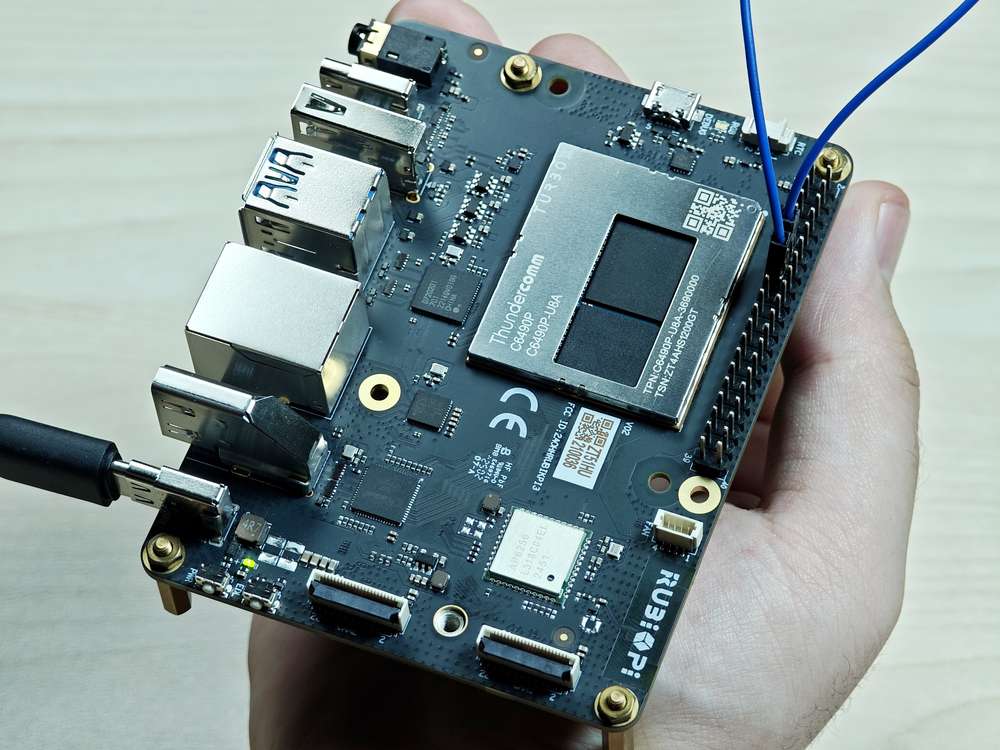
�运行如下命令:
cd /opt
python3 gpio.py程序运行结果如下:
使用 Python 程序控制
-
使用 Python 的 periphery 库控制 GPIO,需先在 魔方派 3 中使用下面命令安装 python-periphery:
pip3 install python-periphery -
下方截取代码是使用 periphery 库操作 GPIO 的示例,其中将 13 号引脚设置为输出,15 号引脚设置为输入,循环检测 15 号引脚的电平状态。
from periphery import GPIO
import time
out_gpio = GPIO(559, "out")
in_gpio = GPIO(560, "in")
try:
while True:
try:
out_gpio.write(True)
pin_level = in_gpio.read()
print(f"in_gpio level: {pin_level}")
out_gpio.write(False)
pin_level = in_gpio.read()
print(f"in_gpio level: {pin_level}")
time.sleep(1)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
out_gpio.write(False)
break
except IOError:
print("Error")
finally:
out_gpio.close()
in_gpio.close() -
将 gpio.py 传输到 魔方派 3 中,如使用 ADB 传输。
adb push gpio.py /opt -
将 13 和 15 号引脚使用杜邦线短接,测试 GPIO 电平控制和电平读取情况,如下图所示:
注意注意引脚顺序,请勿将电源和地引脚短接,否则可能会造成板子损坏。
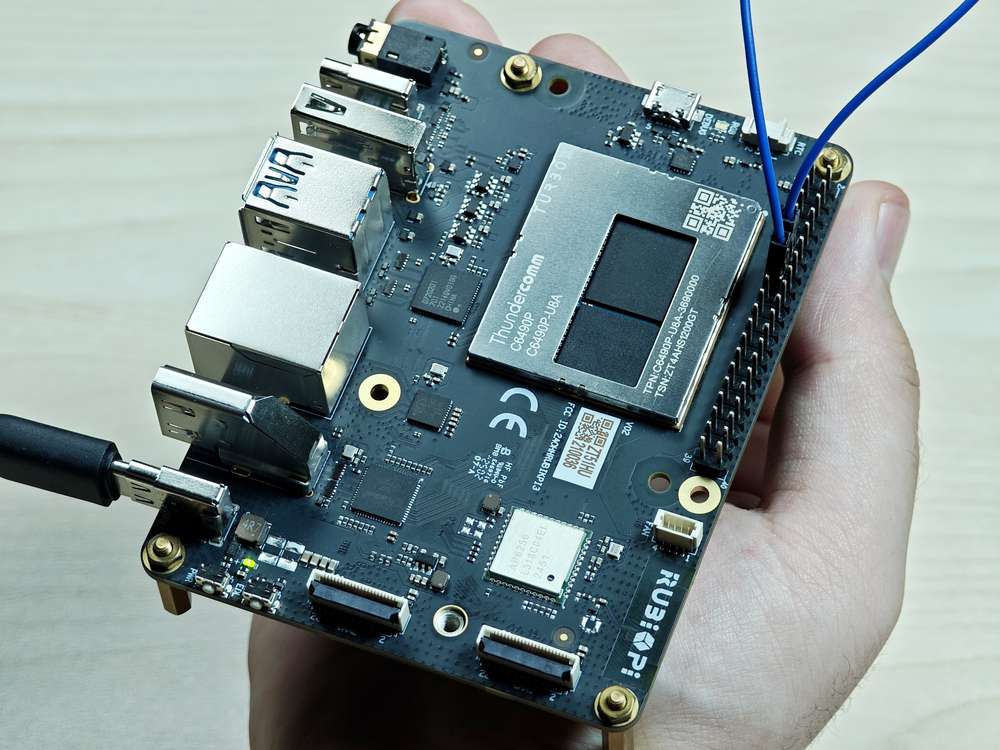
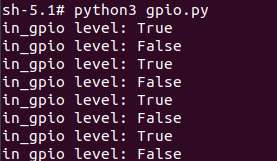
运行如下命令:
cd /opt
python3 gpio.py程序运行结果如下:
使用 C 语言程序控制
-
以下代码示例将 13 号引脚设置为输出,15 号引脚设置为输入,循环检测 15 号引脚的电平状态:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int out_gpio = 559;
int in_gpio = 560;
int main() {
char export_path[50] = {};
char export_command[100] = {};
snprintf(export_path, sizeof(export_path), "/sys/class/gpio/export");
snprintf(export_command, sizeof(export_command), "echo %d > %s ", out_gpio, export_path);
system(export_command);
snprintf(export_command, sizeof(export_command), "echo %d > %s ", in_gpio, export_path);
system(export_command);
char direction_path[50] = {};
snprintf(direction_path, sizeof(direction_path), "/sys/class/gpio/gpio%d/direction", out_gpio);
FILE *direction_file = fopen(direction_path, "w");
if (direction_file == NULL) {
perror("Failed to open GPIO direction file");
return -1;
}
fprintf(direction_file, "out");
fclose(direction_file);
snprintf(direction_path, sizeof(direction_path), "/sys/class/gpio/gpio%d/direction", in_gpio);
direction_file = fopen(direction_path, "w");
if (direction_file == NULL) {
perror("Failed to open GPIO direction file");
return -1;
}
fprintf(direction_file, "in");
fclose(direction_file);
char value_in_path[50] = {};
char value_out_path[50] = {};
char cat_command[100] = {};
snprintf(value_out_path, sizeof(value_out_path), "/sys/class/gpio/gpio%d/value", out_gpio);
snprintf(value_in_path, sizeof(value_in_path), "/sys/class/gpio/gpio%d/value", in_gpio);
snprintf(cat_command, sizeof(cat_command), "cat %s", value_in_path);
FILE *value_out_file = fopen(value_out_path, "w");
if (value_out_file == NULL) {
perror("Failed to open GPIO value file");
return -1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
fprintf(value_out_file, "1");
fflush(value_out_file);
system(cat_command);
sleep(1);
fprintf(value_out_file, "0");
fflush(value_out_file);
system(cat_command);
sleep(1);
}
fclose(value_out_file);
char unexport_path[50] = {};
char unexport_command[100] = {};
snprintf(unexport_path, sizeof(unexport_path), "/sys/class/gpio/unexport");
snprintf(unexport_command, sizeof(unexport_command), "echo %d > %s ", out_gpio, unexport_path);
system(unexport_command);
snprintf(unexport_command, sizeof(unexport_command), "echo %d > %s ", in_gpio, unexport_path);
system(unexport_command);
return 0;
} -
编译程序:
-
交叉编译,具体可参考 交叉编译工具使用方法章节:
aarch64-qcom-linux-gcc gpio.c -o gpio --sysroot=/home/zhy/qcom_sdk_meta/sysroots/armv8-2a-qcom-linux/若使用了交叉编译,需将 gpio 传输到 魔方派 3 中,如使用 ADB 传输:
adb push gpio /opt -
在 魔方派 3 中编译:
adb push gpio.c /opt
adb shell
cd /opt
gcc gpio.c -o gpio
-
-
将 13 和 15 号引脚使用杜邦线短接,测试 GPIO 电平控制和电平读取情况,如下图所示:
注意注意引脚顺序,请勿将电源和地引脚短接,否则可能会造成板子损坏。
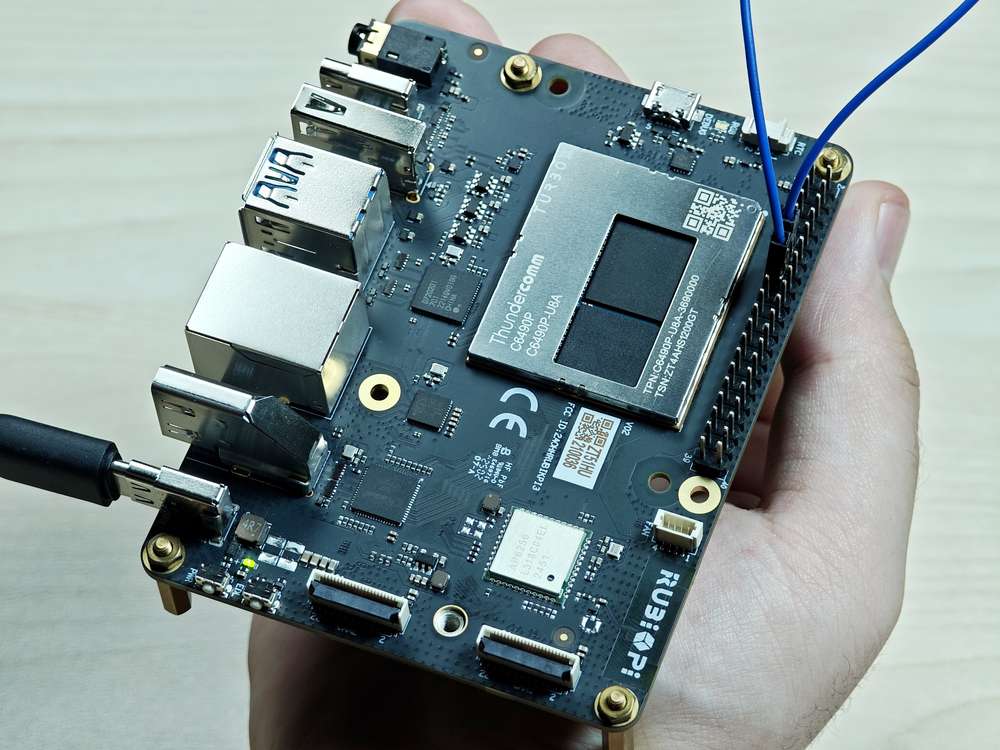
运行如下命令:
cd /opt
./gpio程序运行结果如下:
I2C
I2C 是飞利浦公司在 20 世纪 80 年代开发的一种双向 2 线制总线,用于实现高效的 IC 间控制总线。总线上的每个设备都有其唯一的地址(由飞利浦公司领导的 I2C 总机构注册)。I2C 核心支持多控制器模式,以及 10 位目标地址和 10 位可扩展地址。关于 I2C 的更多信息,请参阅 https://www.i2c-bus.org/fileadmin/ftp/i2c_bus_specification_1995.pdf。
魔方派 3 适配了 WiringRP(基于高性能 GPIO 编程库 WiringPi )。推荐使用 WiringRP 对 I2C 进行控制和编程。关于 WiringRP 详细信息可访问 https://github.com/rubikpi-ai/WiringRP 查看。
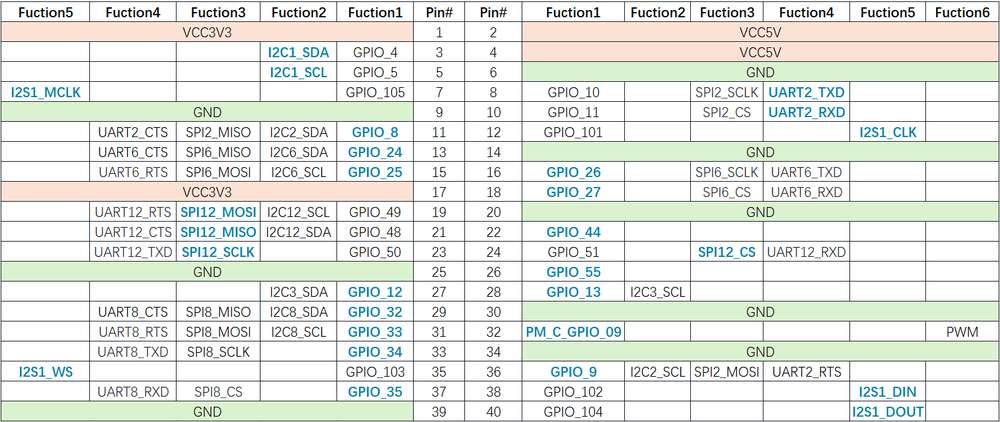
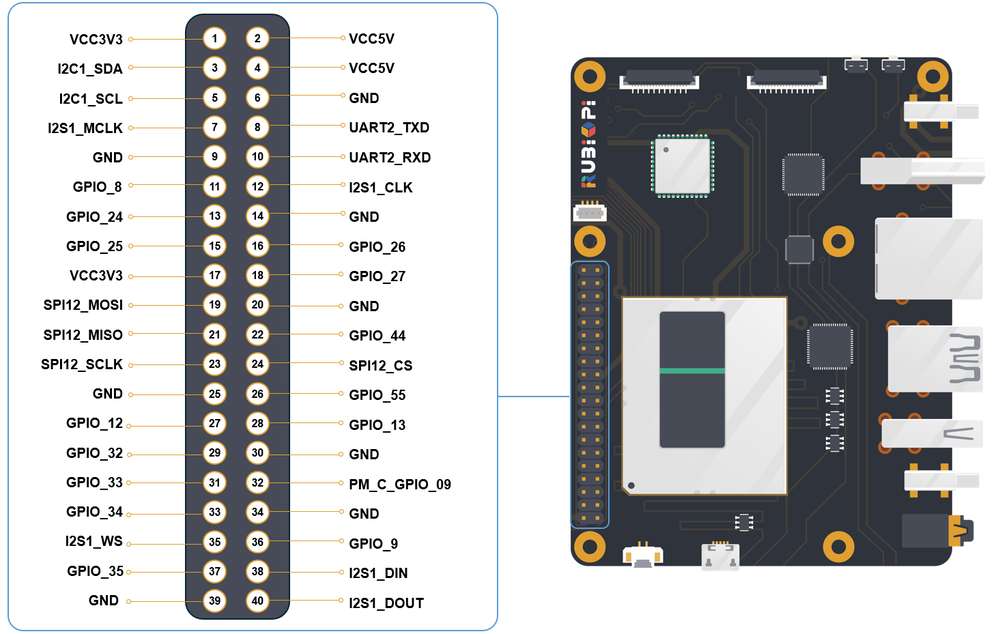
引脚分布
下图是 魔方派 3 40-pin 连接器的引脚默认功能,其中大部分引脚和树梅派 40-pin 连接器引脚的默认功能兼容。
3 号引脚和 5 号引脚默认已设置配为 I2C1。
下表是 40-pin 连接器支持的所有功能,图中蓝色字体表明默认功能。
使用 shell 命令测试
在 魔方派 3 中执行下面步骤控制 I2C 总线。
-
使用 WiringRP 相关命令:
./gpio -x ads1115:100:10 aread 100 #通过 I2C 总线读取 ADS1115 设备的模拟信号值 -
使用 i2cdetect 工具
-
查看 I2C1 接口上的设备:
i2cdetect -a -y -r 1 -
读取地址为 0x38 设备的全部寄存器:
i2cdump -f -y 1 0x38 -
向地址为 0x38 设备的 0x01 寄存器地址写入 0xaa:
i2cset -f -y 1 0x38 0x01 0xaa -
读取地址为 0x38 的设备,寄存器地址为0x01处的数值:
i2cget -f -y 1 0x38 0x01
-
使用 WiringRP (C) I2C 通信
WiringRP 库中提供了一系列的 API 函数,用更少的逻辑实现控制。
-
以下代码示例,I2C1 总线和地址为 0x38 的设备进行通信,向设备 0x01 地址处写入 0xaa:
#include <wiringPi.h>
#include <wiringPiI2C.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define I2C_ADDRESS 0x38
int main(void)
{
int fd;
if (wiringPiSetup() == -1) {
exit(1);
}
fd = wiringPiI2CSetup(1, I2C_ADDRESS);
if (fd == -1) {
exit(1);
}
unsigned char data[2];
if (read(fd, data, 2) != 2) {
exit(1);
}
wiringPiI2CWriteReg8(fd, 0x01, 0xaa) ;
close(fd);
return 0;
} -
在 魔方派 3 中编译程序
adb push gpio.c /opt
adb shell
cd /opt
gcc i2c.c -o i2c -lwiringPi -
将 3 和 5 号引脚连接 I2C 传感器,验证 I2C 总线通信,如下图所示
注意注意引脚顺序,请勿将电源和地引脚短接,否则可能会造成板子损坏。
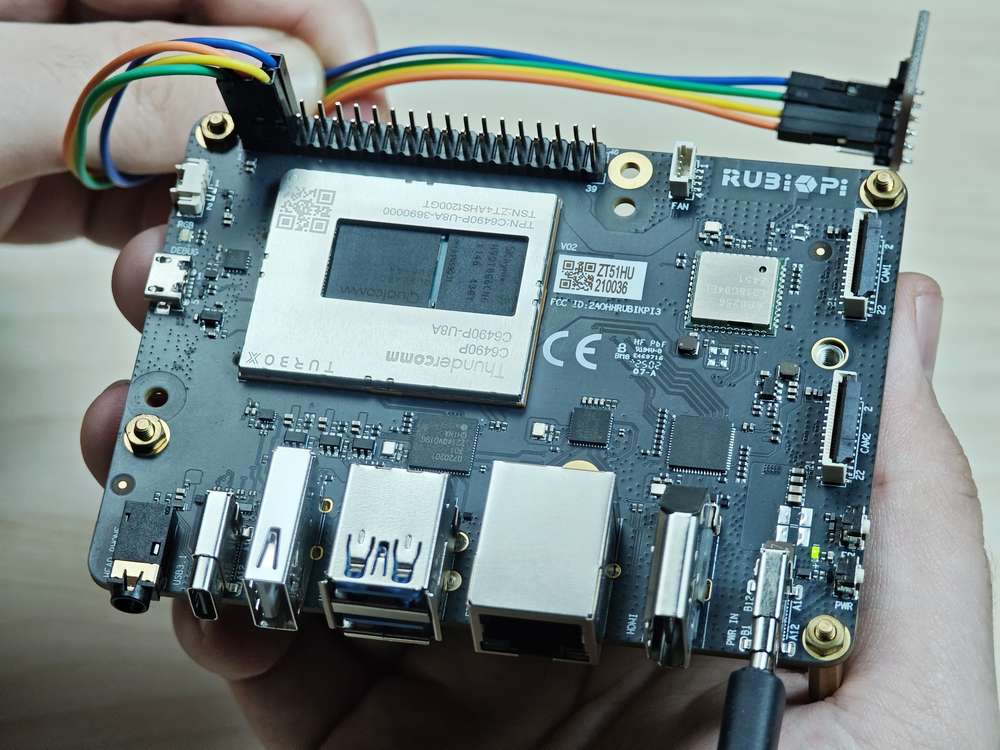

运行如下命令运行程序:
cd /opt
./i2c
使用 WiringRP-Python I2C 通信
WiringRP 库中提供了一系列的 API 函数,用更少的逻辑实现控制。
-
以下代码示例,使用 I2C1 总线和地址为 0x38 的设备进行通信,向设备 0x01 地址处写入 0xaa:
import wiringpi as wpi
wpi.wiringPiSetup()
fd=wpi.wiringPiI2CSetup(0x38, 1)
wpi.wiringPiI2CWriteReg8 (fd, 0x01, 0xaa) -
将 i2c.py 传输到 魔方派 3 中,如使用 ADB 传输。
adb push i2c.py /opt -
将 3 和 5 号引脚连接 I2C 传感器,验证 I2C 总线通信,如下图所示:
注意注意引脚顺序,请勿将电源和地引脚短接,否则可能会造成板子损坏。
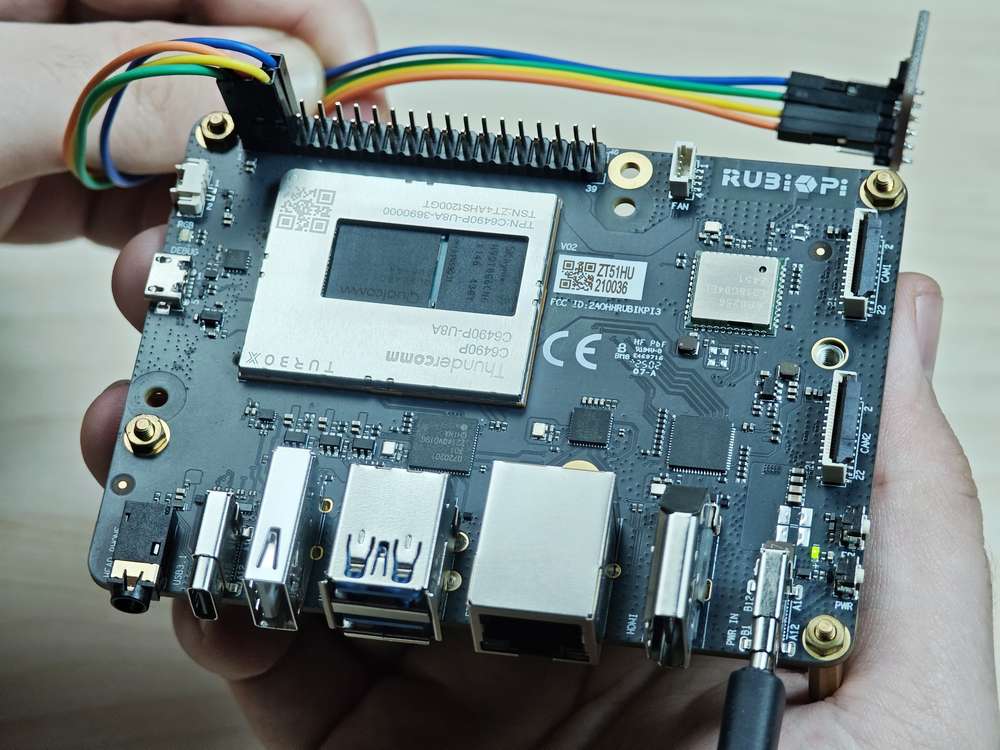

运行如下命令:
cd /opt
python3 i2c.py
使用 Python 程序 I2C 通信
-
使用 Python 的 smbus 库控制 I2C,需先在 魔方派 3 中使用下面命令安装 smbus 库:
pip3 install smbus -
以下代码示例,使用 I2C1 总线和地址为 0x38 的设备进行通信,向设备 0x01 地址处写入 0xaa:
import smbus
def main():
data = [0x01, 0xaa]
try:
i2c_bus = smbus.SMBus(1)
print("i2cdetect addr : ", end="")
for address in range(0x7F):
try:
i2c_bus.write_i2c_block_data(address, 0, data)
print("0x{:02X},".format(address), end="")
except OSError:
pass
print()
except Exception as e:
print(f"An error occurred: {e}")
finally:
if i2c_bus:
i2c_bus.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main() -
将 i2c.py 传输到 魔方派 3中,如果使用 ADB 传输,命令如下:
adb push i2c.py /opt -
将 3 和 5 号引脚连接 I2C 传感器,验证 I2C 总线通信,如下图所示:
注意注意引脚顺序,请勿将电源和地引脚短接,否则可能会造成板子损坏。
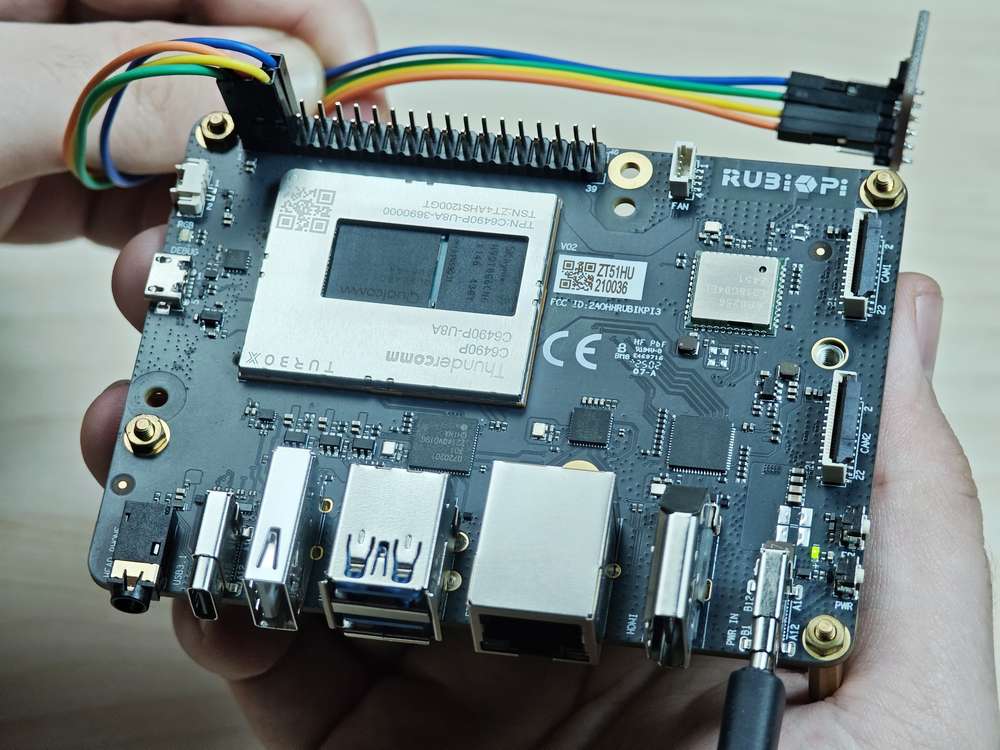

运行如下命令:
cd /opt
python3 i2c.py程序运行结果如下:
使用 C 语言程序 I2C 通信
-
以下代码示例,I2C1 总线和地址为 0x38 的设备进行通信,向设备 0x01 地址处写入 0xaa:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <linux/i2c-dev.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#define I2C_DEVICE_PATH "/dev/i2c-1"
int main() {
uint8_t data[2] = {0x01,0xaa};
const char *i2c_device = I2C_DEVICE_PATH;
int i2c_file;
if ((i2c_file = open(i2c_device, O_RDWR)) < 0) {
perror("Failed to open I2C device");
return -1;
}
ioctl(i2c_file, I2C_TENBIT, 0);
ioctl(i2c_file, I2C_RETRIES, 5);
printf("i2cdetect addr : ");
for (int x = 0; x < 0x7f; x++)
{
if (ioctl(i2c_file, I2C_SLAVE, x) < 0) {
perror("Failed to set I2C slave address");
close(i2c_file);
return -1;
}
if (write(i2c_file, data, 2) == 2)
{
printf("0x%x,", x);
}
}
close(i2c_file);
printf("\r\n");
return 0;
} -
编译程序:
-
交叉编译,具体可参考 交叉编译工具使用方法 章节:
aarch64-qcom-linux-gcc i2c.c -o i2c --sysroot=/home/zhy/qcom_sdk_meta/sysroots/armv8-2a-qcom-linux/若使用的交叉编译,需要将 i2c 传输到 魔方派 3 中,如果使用 ADB 传输,命令如下:
adb push i2c /opt -
在 魔方派 3 中编译
adb push i2c.c /opt
adb shell
cd /opt
gcc i2c.c -o i2c
-
-
将 3 和 5 号引脚连接 I2C 传感器,验证 I2C 总线通信,如下图所示:
注意注意引脚顺序,请勿将电源和地引脚短接,否则可能会造成板子损坏。
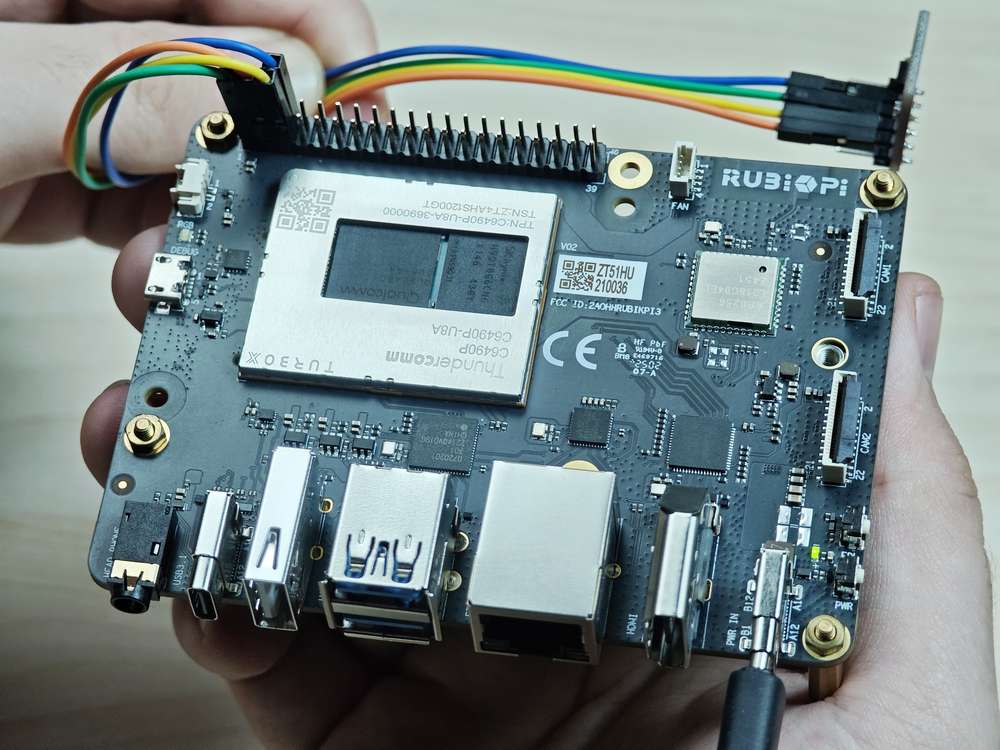

运行如下命令:
cd /opt
./i2c程序运行结果如下:
SPI
串行外设接口 (SPI) 是在全双工模式下工作的同步串行数据链路。SPI 又称为 4 线制串行总线。
魔方派 3 适配了 WiringRP(基于高性能 GPIO 编程库 WiringPi),推荐使用 WiringRP 对 SPI 进行控制和编程。关于 WiringRP 详细信息可访问 https://github.com/rubikpi-ai/WiringRP 查看。
引脚分布
下图是 魔方派 3 40-pin 连接器的引脚默认功能,其中大部分引脚和树梅派 40-pin 连接器引脚的默认功能兼容。
19 号、21 号、23 号、24 号引脚默认已设置配为 SPI。
下表是 40-pin 连接器支持的所有功能,图中蓝色字体表明默认功能。
使用 WiringRP (C) SPI 通信
WiringRP 库中提供了一系列的 API 函数,用更少的逻辑实现控制。
-
以下代码示例使用 SPI 总线进行数据收发通信:
#include <wiringPi.h>
#include <wiringPiSPI.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
int fd;
unsigned char send_data[64] = "hello world!";
unsigned char read_data[64];
if(wiringPiSetup() == -1)
exit(1);
fd = wiringPiSPISetup(0, 1000000);
if(fd < 0)
exit(2);
printf("\rtx_buffer: \n %s\n ", send_data);
// Send and receive data
if(wiringPiSPIDataRW(0, send_data, sizeof(send_data)) < 0)
exit(3);
printf("\rtx_buffer: \n %s\n ", send_data);
return 0;
} -
在 魔方派 3 中编译程序
adb push spi.c /opt
adb shell
cd /opt
gcc spi.c -o spi -lwiringPi -
将 19 号引脚和 21 号引脚使用杜邦线短接,验证 SPI 总线通信,如下图所示:
注意注意引脚顺序,请勿将电源和地引脚短接,否则可能会造成板子损坏。
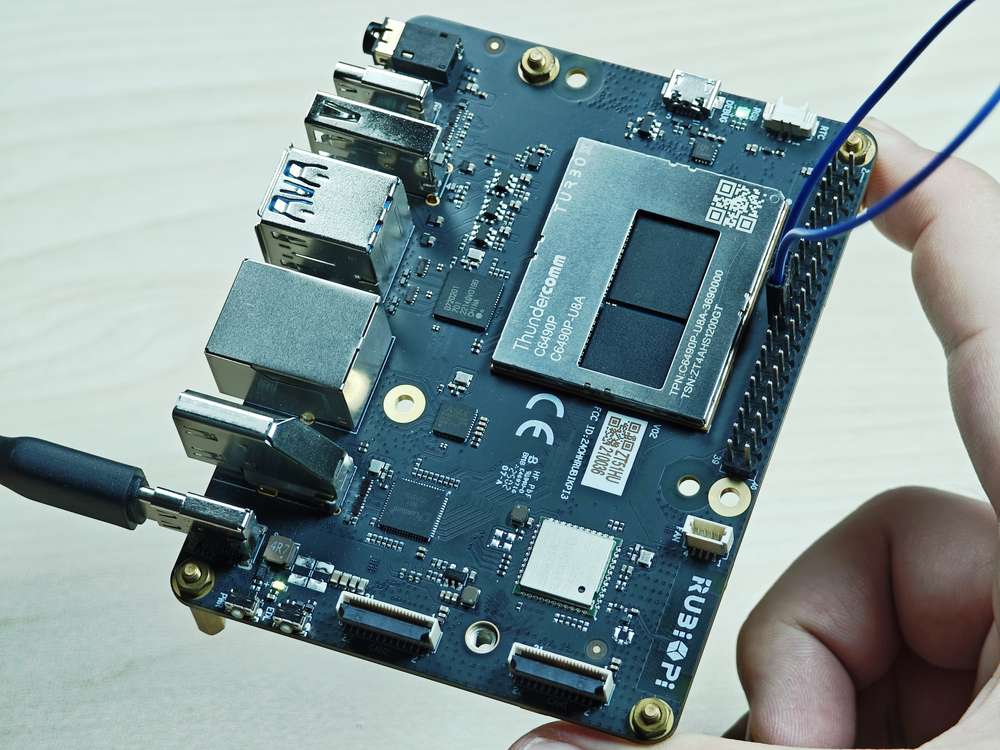

运行如下命令:
cd /opt
./spi程序执行结果如下:
使用 WiringRP-Python SPI通信
WiringRP 库中提供了一系列的 API 函数,用更少的逻辑实现控制。
-
以下代码示例使用 SPI 总线进行数据收发通信:
import wiringpi as wpi
wpi.wiringPiSetup()
wpi.wiringPiSPISetup(0, 8000000)
tx_buffer = bytes([72, 101, 108, 108, 111])
print("tx_buffer:\n\r ", tx_buffer)
retlen, rx_buffer = wpi.wiringPiSPIDataRW(0, tx_buffer)
print("rx_buffer:\n\r ", rx_buffer)
-
将 spi.py 传输到 魔方派 3 中,如使用 ADB 传输。
adb push spi.py /opt -
将 19 号引脚和 21 号引脚使用杜邦线短接,验证 SPI 总线通信,如下图所示:
注意注意引脚顺序,请勿将电源和地引脚短接,否则可能会造成板子损坏。
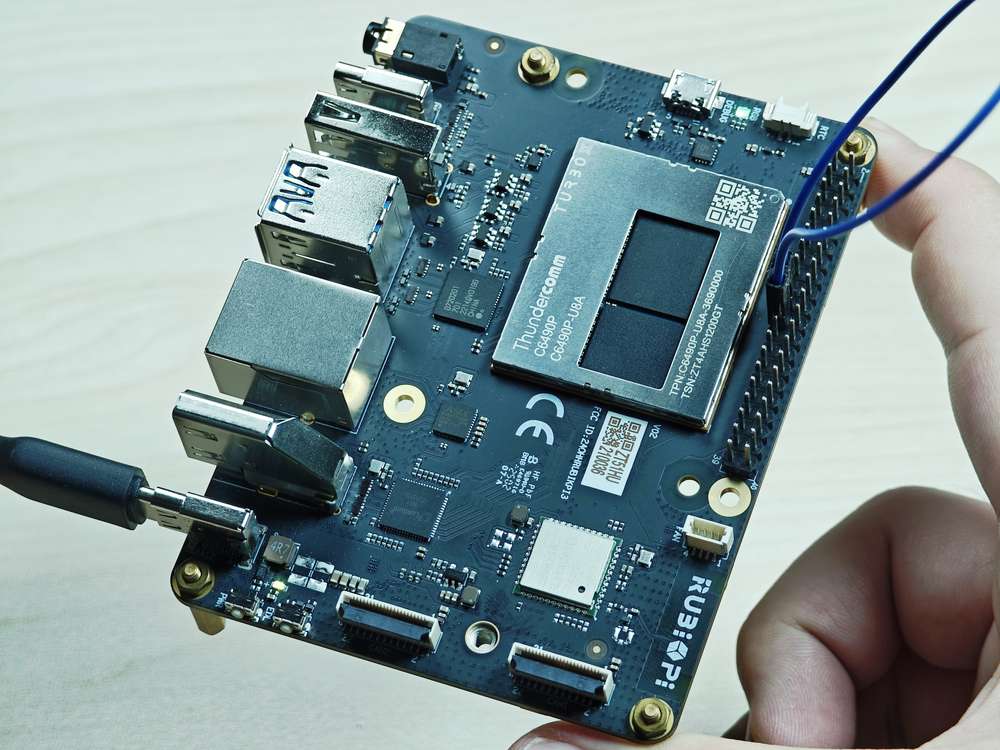

运行如下命令:
python3 spi.py程序执行结果如下:
使用 Python 程序 SPI 通信
-
使用 Python 的 spidev 库进行 SPI 通信,需先在 魔方派 3 中使用下面命令安装spidev 库:
pip3 install spidev -
以下代码示例使用 SPI 总线进行数据收发通信:
import spidev
def main():
tx_buffer = [ord(char) for char in "hello world!"]
rx_buffer = [0] * len(tx_buffer)
try:
spi = spidev.SpiDev()
spi.open(12, 0)
spi.max_speed_hz = 1000000
rx_buffer = spi.xfer2(tx_buffer[:])
print("tx_buffer:\n\r", ''.join(map(chr, tx_buffer)))
print("rx_buffer:\n\r", ''.join(map(chr, rx_buffer)))
except Exception as e:
print(f"An error occurred: {e}")
finally:
if spi:
spi.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main() -
将 spi.py 传输到 魔方派 3 中,如果使用 ADB 传输,命令如下:
adb push spi.py /opt -
将 19 号引脚和 21 号��引脚使用杜邦线短接,验证 SPI 总线通信,如下图所示:
注意注意引脚顺序,请勿将电源和地引脚短接,否则可能会造成板子损坏。
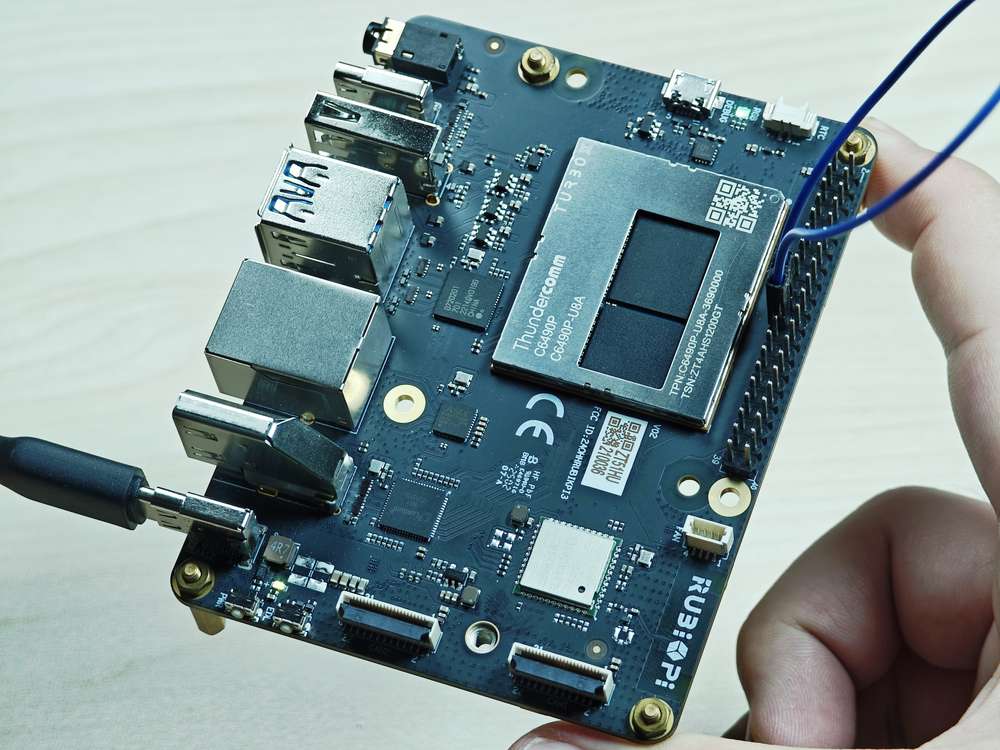

运行如下命令:
python3 spi.py程序执行结果如下:
使用 C 语言程序 SPI 通信
-
以下代码示例使用 SPI 总线进行数据收发通信:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <linux/spi/spidev.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#define SPI_DEVICE_PATH "/dev/spidev12.0"
int main() {
int spi_file;
uint8_t tx_buffer[50] = "hello world!";
uint8_t rx_buffer[50];
// Open the SPI device
if ((spi_file = open(SPI_DEVICE_PATH, O_RDWR)) < 0) {
perror("Failed to open SPI device");
return -1;
}
// Configure SPI mode and bits per word
uint8_t mode = SPI_MODE_0;
uint8_t bits = 8;
if (ioctl(spi_file, SPI_IOC_WR_MODE, &mode) < 0) {
perror("Failed to set SPI mode");
close(spi_file);
return -1;
}
if (ioctl(spi_file, SPI_IOC_WR_BITS_PER_WORD, &bits) < 0) {
perror("Failed to set SPI bits per word");
close(spi_file);
return -1;
}
// Perform SPI transfer
struct spi_ioc_transfer transfer = {
.tx_buf = (unsigned long)tx_buffer,
.rx_buf = (unsigned long)rx_buffer,
.len = sizeof(tx_buffer),
.delay_usecs = 0,
.speed_hz = 1000000, // SPI speed in Hz
.bits_per_word = 8,
};
if (ioctl(spi_file, SPI_IOC_MESSAGE(1), &transfer) < 0) {
perror("Failed to perform SPI transfer");
close(spi_file);
return -1;
}
/* Print tx_buffer and rx_buffer*/
printf("\rtx_buffer: \n %s\n ", tx_buffer);
printf("\rrx_buffer: \n %s\n ", rx_buffer);
// Close the SPI device
close(spi_file);
return 0;
} -
编译程序:
-
交叉编译,具体可参考 交叉编译工具使用方法章节:
aarch64-qcom-linux-gcc spi.c -o spi --sysroot=/home/zhy/qcom_sdk_meta/sysroots/armv8-2a-qcom-linux/若使用交叉编译,需要将 spi 传输到 魔方派 3 中,如果使用 ADB 传输,命令如下:
adb push spi /opt -
在 魔方派 3 中编译
adb push spi.c /opt
adb shell
cd /opt
gcc spi.c -o spi
-
-
将 19 号引脚和 21 号引脚使用杜邦线短接,验证 SPI 总线通信,如下图所示:
注意注意引脚顺序,请勿将电源和地引脚短接,否则可能会造成板子损坏。

运行如下命令:
cd /opt
./spi程序执行结果如下:
UART
魔方派 3 适配了 WiringRP(基于高性能 GPIO 编程库 WiringPi),推荐使用 WiringRP 对 UART 进行控制和编程。关于 WiringRP 详细信息可访问 https://github.com/rubikpi-ai/WiringRP 查看。
引脚分布
下图是 魔方派 3 40-pin 连接器的引脚默认功能,其中大部分引脚和树梅派 40-pin 连接器引脚的默认功能兼容。
8 号和 10 号引脚默认已设置配为 UART,设备节点为 /dev/ttyHS2。
下表是 40-pin 连接器支持的所有功能,图中蓝色字体表明默认功能。
使用 shell 命令测试
在 魔方派 3 中 使用下面命令控制串口通信
-
使用 stty 工具配置串口,如下将串口的输入速率和输出速率都设置为 115200,并关闭回显:
stty -F /dev/ttyHS2 ispeed 115200 ospeed 115200
stty -F /dev/ttyHS2 -echo -
在 魔方派 3 上开启两个终端,将 8 号引脚和 10 号引脚使用杜邦线短接,分别执行下面命令,接收端会回显发送端的内容:
注意�注意引脚顺序,请勿将电源和地引脚短接,否则可能会造成板子损坏。
echo "hello world!" > /dev/ttyHS2 # 发送端
cat /dev/ttyHS2 # 接收端
使用 WiringRP (C) UART通信
WiringRP 库中提供了一系列的 API 函数,用更少的逻辑实现控制。
-
以下代码示例使用 UART 进行数据收发通信:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <wiringPi.h>
#include <wiringSerial.h>
int main ()
{
int fd ;
int count ;
unsigned int nextTime ;
if ((fd = serialOpen ("/dev/ttyHS2", 115200)) < 0)
{
fprintf (stderr, "Unable to open serial device: %s\n", strerror (errno)) ;
return 1 ;
}
if (wiringPiSetup () == -1)
{
fprintf (stdout, "Unable to start wiringPi: %s\n", strerror (errno)) ;
return 1 ;
}
char tx_buffer[] = "hello world!\n";
for (count = 0 ; count < sizeof(tx_buffer) ; count++)
{
serialPutchar (fd, tx_buffer[count]) ;
delay (3) ;
printf ("%c", serialGetchar (fd)) ;
}
printf ("\n") ;
return 0 ;
} -
编译程序:
-
在 魔方派 3 中编译
adb push uart.c /opt
adb shell
cd /opt
gcc uart.c -o uart
-
-
将 8 号引脚和 10 号引脚使用杜邦线短接,验证串口通信,如下图所示:
注意注意引脚顺序,请勿将电源和地引脚短接,否则可能会造成板子损坏。
运行如下命令:
cd /opt
./uart程序执行结果如下:
使用 WiringRP-Python UART 通信
WiringRP 库中提供了一系列的 API 函数,用更少的逻辑实现控制。
-
以下代码示例使用 UART 进行数据收发通信:
import wiringpi
serial = wiringpi.serialOpen('/dev/ttyHS2', 115200)
wiringpi.serialPuts(serial, "hello world")
received_data = []
c = wiringpi.serialGetchar(serial);
received_data.append(chr(c))
cnt = wiringpi.serialDataAvail(serial);
for i in range(cnt):
c = wiringpi.serialGetchar(serial);
received_data.append(chr(c))
print("Received:", received_data)
wiringpi.serialClose(serial) -
将 uart.py 传输到 魔方派 3 中,如果使用 ADB 传输,命令如下:
adb push uart.py /opt -
将 8 号引脚和 10 号引脚使用杜邦线短接,验证串口通信,如下图所示:
注意注意引脚顺序,请勿将电源和地引脚短接,否则可能会造成板子损坏。
运行如下命令:
cd /opt
python3 uart.py
程序执行结果如下:
使用 Python 程序 UART 通信
-
使用 Python 的 serial 库进行 UART 通信,需先在 魔方派 3 中使用下面命令安装 serial 库:
pip3 install pyserial -
以下代码示例使用 UART 进行数据收发通信:
import serial
import time
with serial.Serial(
"/dev/ttyHS2",
baudrate=115200,
bytesize=serial.EIGHTBITS,
stopbits=serial.STOPBITS_ONE,
parity=serial.PARITY_NONE,
timeout=1,
) as uart3:
uart3.write(b"Hello World!\n")
buf = uart3.read(128)
print("Raw data:\n", buf)
data_strings = buf.decode("utf-8")
print("Read {:d} bytes, printed as string:\n {:s}".format(len(buf), data_strings)) -
将 uart.py 传输到 魔方派 3 中,如果使用 ADB 传输,命令如下:
adb push uart.py /opt -
将 8 号引脚和 10 号引脚使用杜邦线短接,验证串口通信,如下图所示
注意注意引脚顺序,请勿将电源和地引脚短接,否则可能会造成板子损坏。
运行如下命令:
python3 uart.py
程序执行结果如下:
使用 C 语言程序 UART 通信
-
以下代码示例使用 UART 进行数据收发通信:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
int serial_port_num = 2;
char serial_port[15];
sprintf(serial_port,"/dev/ttyHS%d",serial_port_num);
int serial_fd;
serial_fd = open(serial_port, O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY);
if (serial_fd == -1) {
perror("Failed to open serial port");
return 1;
}
struct termios tty;
memset(&tty, 0, sizeof(tty));
if (tcgetattr(serial_fd, &tty) != 0) {
perror("Error from tcgetattr");
return 1;
}
cfsetospeed(&tty, B9600);
cfsetispeed(&tty, B9600);
tty.c_cflag &= ~PARENB;
tty.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB;
tty.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE;
tty.c_cflag |= CS8;
if (tcsetattr(serial_fd, TCSANOW, &tty) != 0) {
perror("Error from tcsetattr");
return 1;
}
char tx_buffer[] = "hello world!\n";
ssize_t bytes_written = write(serial_fd, tx_buffer, sizeof(tx_buffer));
if (bytes_written < 0) {
perror("Error writing to serial port");
close(serial_fd);
return 1;
}
printf("\rtx_buffer: \n %s ", tx_buffer);
char rx_buffer[256];
int bytes_read = read(serial_fd, rx_buffer, sizeof(rx_buffer));
if (bytes_read > 0) {
rx_buffer[bytes_read] = '\0';
printf("\rrx_buffer: \n %s ", rx_buffer);
} else {
printf("No data received.\n");
}
close(serial_fd);
return 0;
} -
编译程序:
-
交叉编译,具体可参考交叉编译工具使用方法章节:
aarch64-qcom-linux-gcc uart.c -o uart --sysroot=/home/zhy/qcom_sdk_meta/sysroots/armv8-2a-qcom-linux/若使用交叉编译,需要将 uart 传输到 魔方派 3 中,如果使用 ADB 传输,命令如下:
adb push uart /opt -
在 魔方派 3 中编译
adb push uart.c /opt
adb shell
cd /opt
gcc uart.c -o uart
-
-
将 8 号引脚和 10 号引脚使用杜邦线短接,验证串口通信,如下图所示
注意注意引脚顺序,请勿将电源和地引脚短接,否则可能会造成板子损坏。
运行如下命令:
cd /opt
./uart程序执行结果如下:
USB
魔方派 3 拥有 4 个 USB 口:
-
两个 USB 3.0 口,只能作为主机模式使用,如下图 7。
-
一个 USB 2.0 口,可以作为主机或设备模式使用,如下图 6。
-
一个 USB 3.1 Gen 1 口,可以作为主机或设备模式(ADB),以及 DP 显示使用,如下图 5。
USB 2.0 Type-A 接口
USB 2.0 接口默认为主机模式,作为设备模式时需要手动执行命令切换,如下为一种切换方式,在 魔方派 3 中输入下面命令,将 魔方派 3 模拟为 U 盘:
cd /sys/kernel/config/usb_gadget/ #在串口终端登录,执行下面命令
mkdir g1
cd g1
mkdir functions/mass_storage.0
dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/test.iso bs=1M count=2048 #创建大小为2G的U盘空间
mkfs.ext4 /tmp/test.iso
echo "/tmp/test.iso" > functions/mass_storage.0/lun.0/file
mkdir configs/c.1
ln -s functions/mass_storage.0/ configs/c.1/f3
mount -t debugfs none /sys/kernel/debug/
echo device > /sys/kernel/debug/usb/8c00000.usb/qcom_usb2_0_mode #将USB切换为device模式
echo 8c00000.usb > UDC #连接USB线,U盘被识别 可在U盘内写入和写出文件
echo host > /sys/kernel/debug/usb/8c00000.usb/qcom_usb2_0_mode #拔掉USB线,切换为主机模式
USB 3.1 Type-C 接口
Type-C 接口可自动完成主机和设备模式的切换。
-
当 Type-C 接入 PC 时自动切换为设备模式。
-
接入 OTG 线时自动切换为主机模式。
-
接入 DP 显示器时,自动输出 DP 视频信号。
USB 调试
本节提供有关获取调试日志的各种方法的信息。调试方式有 regdumps 、调试 ftraces 、 configfs 节点等。在调试与进入/退出低功耗模式、SMMU 故障、无时钟访问相关的问题时,可通过上述日志查看事件和控制器状态的详细信息。
-
USB 2.0 Type-A 设备路径: /sys/devices/platform/soc@0/8c00000.usb/xhci-hcd.0.auto/usb1
-
USB 3.0 Type-A 设备路径:
-
/sys/devices/platform/soc@0/1c00000.pci/pci0000:00/0000:00:00.0/0000:01:00.0/usb2
-
/sys/devices/platform/soc@0/1c00000.pci/pci0000:00/0000:00:00.0/0000:01:00.0/usb3
-
-
USB 3.1 Type-C 设备路径:/sys/devices/platform/soc@0/a600000.usb
USB 跟踪
使用 debugfs 跟踪可以更加深入地了解 USB 线上发生的每一个事务。如需查看跟踪列表,可运行以下命令。
确保已挂载
debugfs。如果尚未挂载,可运行以下命令来挂载debugfs:
mount -t debugfs none /sys/kernel/debug
ls /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/dwc3
以下是可用于验证 xHCI/gadget 协议栈/USB Type-C 连接器系统软件接口 (UCSI) 中的数据传输的跟踪。
dwc3_alloc_request dwc3_event dwc3_gadget_generic_cmd enable
dwc3_complete_trb dwc3_free_request dwc3_gadget_giveback filter
dwc3_ctrl_req dwc3_gadget_ep_cmd dwc3_prepare_trb
dwc3_ep_dequeue dwc3_gadget_ep_disable dwc3_readl
dwc3_ep_queue dwc3_gadget_ep_enable dwc3_writel
要列出 xHCI/主机控制器驱动程序 (HCD) 中的跟踪数据,请运行以下命令。
ls /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/xhci-hcd
以下是可用于验证 xHCI/HCD 中数据传输的跟踪。
enable xhci_handle_cmd_config_ep
filter xhci_handle_cmd_disable_slot
xhci_add_endpoint xhci_handle_cmd_reset_dev
xhci_address_ctrl_ctx xhci_handle_cmd_reset_ep
xhci_address_ctx xhci_handle_cmd_set_deq
xhci_alloc_dev xhci_handle_cmd_set_deq_ep
xhci_alloc_virt_device xhci_handle_cmd_stop_ep
xhci_configure_endpoint xhci_handle_command
xhci_configure_endpoint_ctrl_ctx xhci_handle_event
xhci_dbc_alloc_request xhci_handle_port_status
xhci_dbc_free_request xhci_handle_transfer
xhci_dbc_gadget_ep_queue xhci_hub_status_data
xhci_dbc_giveback_request xhci_inc_deq
xhci_dbc_handle_event xhci_inc_enq
xhci_dbc_handle_transfer xhci_queue_trb
xhci_dbc_queue_request xhci_ring_alloc
xhci_dbg_address xhci_ring_ep_doorbell
xhci_dbg_cancel_urb xhci_ring_expansion
xhci_dbg_context_change xhci_ring_free
xhci_dbg_init xhci_ring_host_doorbell
xhci_dbg_quirks xhci_setup_addressable_virt_device
xhci_dbg_reset_ep xhci_setup_device
xhci_dbg_ring_expansion xhci_setup_device_slot
xhci_discover_or_reset_device xhci_stop_device
xhci_free_dev xhci_urb_dequeue
xhci_free_virt_device xhci_urb_enqueue
xhci_get_port_status xhci_urb_giveback
xhci_handle_cmd_addr_dev
请运行以下命令,以便列出 USB 视频类 (UVC) gadget 驱动程序的可用事件。
ls /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/gadget
随即显示以下输出。
enable usb_gadget_activate
filter usb_gadget_clear_selfpowered
usb_ep_alloc_request usb_gadget_connect
usb_ep_clear_halt usb_gadget_deactivate
usb_ep_dequeue usb_gadget_disconnect
usb_ep_disable usb_gadget_frame_number
usb_ep_enable usb_gadget_giveback_request
usb_ep_fifo_flush usb_gadget_set_remote_wakeup
usb_ep_fifo_status usb_gadget_set_selfpowered
usb_ep_free_request usb_gadget_vbus_connect
usb_ep_queue usb_gadget_vbus_disconnect
usb_ep_set_halt usb_gadget_vbus_draw
usb_ep_set_maxpacket_limit usb_gadget_wakeup
usb_ep_set_wedge
如需列出 UCSI 驱动程序中的可用事件,可运行以下命令。
ls /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/ucsi
随即显示以下输出。
enable ucsi_connector_change ucsi_register_port ucsi_run_command
filter ucsi_register_altmode ucsi_reset_ppm
USB 寄存器打印
USB debugfs 提供以下信息,下面以 Type-C 接口为例。
-
工作模式
cat /sys/kernel/debug/usb/a600000.usb/mode # Type-C 接口备注USB 2.0 Type-A 的工作模式
cat /sys/kernel/debug/usb/8c00000.usb/qcom_usb2_0_mode示例输出:
device -
设备模式下所有端点的状态和传输环形缓冲区 (TRB) 队列。
-
当前链路状态。
cat /sys/kernel/debug/usb/a600000.usb/link_state示例输出
Sleep -
列出处理器 (LSP) dump。
cat /sys/kernel/debug/usb/a600000.usb/lsp_dump示例输出:
GDBGLSP[0] = 0x40000000
GDBGLSP[1] = 0x00003a80
GDBGLSP[2] = 0x38200000
GDBGLSP[3] = 0x00802000
GDBGLSP[4] = 0x126f1000
GDBGLSP[5] = 0x3a800018
GDBGLSP[6] = 0x00000a80
GDBGLSP[7] = 0xfc03f14a
GDBGLSP[8] = 0x0b803fff
GDBGLSP[9] = 0x00000000
GDBGLSP[10] = 0x000000f8
GDBGLSP[11] = 0x000000f8
GDBGLSP[12] = 0x000000f8
GDBGLSP[13] = 0x000000f8
GDBGLSP[14] = 0x000000f8
GDBGLSP[15] = 0x000000f8
ls /sys/kernel/debug/usb/a600000.usb
示例输出:
ep0in ep11out ep14in ep1out ep4in ep6out ep9in regdump
ep0out ep12in ep14out ep2in ep4out ep7in ep9out testmode
ep10in ep12out ep15in ep2out ep5in ep7out link_state
ep10out ep13in ep15out ep3in ep5out ep8in lsp_dump
ep11in ep13out ep1in ep3out ep6in ep8out mode
regdump 命令提供以下寄存器的寄存器空间的当前状态:
-
设备模式的寄存器,例如 DCTL、DSTS 和 DCFG
-
全局寄存器,例如 GCTL 和 GSTS
cd /sys/kernel/debug/usb/a600000.usb
cat regdump
示例输出:
GSBUSCFG0 = 0x2222000e
GSBUSCFG1 = 0x00001700
GTXTHRCFG = 0x00000000
GRXTHRCFG = 0x00000000
GCTL = 0x00102000
GEVTEN = 0x00000000
GSTS = 0x7e800000
GUCTL1 = 0x810c1802
GSNPSID = 0x5533330a
GGPIO = 0x00000000
GUID = 0x00060500
GUCTL = 0x0d00c010
GBUSERRADDR0 = 0x00000000
GBUSERRADDR1 = 0x00000000
GPRTBIMAP0 = 0x00000000
GPRTBIMAP1 = 0x00000000
GHWPARAMS0 = 0x4020400a
GDBGFIFOSPACE = 0x00420000
GDBGLTSSM = 0x41090658
GDBGBMU = 0x20300000
GPRTBIMAP_HS0 = 0x00000000
GPRTBIMAP_HS1 = 0x00000000
GPRTBIMAP_FS0 = 0x00000000
GPRTBIMAP_FS1 = 0x00000000
GUCTL2 = 0x0198440d
VER_NUMBER = 0x00000000
VER_TYPE = 0x00000000
GUSB2PHYCFG(0) = 0x00002400
GUSB2I2CCTL(0) = 0x00000000
GUSB2PHYACC(0) = 0x00000000
GUSB3PIPECTL(0) = 0x030e0002
GTXFIFOSIZ(0) = 0x00000042
GRXFIFOSIZ(0) = 0x00000305
GEVNTADRLO(0) = 0xfffff000
GEVNTADRHI(0) = 0x0000000f
GEVNTSIZ(0) = 0x00001000
GEVNTCOUNT(0) = 0x00000000
GHWPARAMS8 = 0x000007ea
GUCTL3 = 0x00010000
GFLADJ = 0x8c80c8a0
DCFG = 0x00cc08b4
DCTL = 0x8cf00a00
DEVTEN = 0x00000257
DSTS = 0x008a5200
DGCMDPAR = 0x00000000
DGCMD = 0x00000000
DALEPENA = 0x0000000f
DEPCMDPAR2(0) = 0x00000000
DEPCMDPAR1(0) = 0xffffe000
DEPCMDPAR0(0) = 0x0000000f
DEPCMD(0) = 0x00000006
OCFG = 0x00000000
OCTL = 0x00000000
OEVT = 0x00000000
OEVTEN = 0x00000000
OSTS = 0x00000000
主机 sysfs 查询
要查看总线详细信息,请运行以下命令。
lsub
示例输出:
Bus 002 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0003 Linux Foundation 3.0 root hub
Bus 001 Device 002: ID 03f0:134a HP, Inc Optical Mouse
Bus 001 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub
要列出当前目录的内容,请运行以下命令。
cd /sys/bus/usb/devices/
ls
示例输出:
1-0:1.0 1-1 1-1:1.0 2-0:1.0 usb1 usb2
要查看有关 USB 设备的详细信息,请运行以下命令。
cat /sys/kernel/debug/usb/devices
示例输出:
T: Bus=01 Lev=00 Prnt=00 Port=00 Cnt=00 Dev#= 1 Spd=480 MxCh= 1
B: Alloc= 0/800 us ( 0%), #Int= 0, #Iso= 0
D: Ver= 2.00 Cls=09(hub ) Sub=00 Prot=01 MxPS=64 #Cfgs= 1
P: Vendor=1d6b ProdID=0002 Rev= 6.05
S: Manufacturer=Linux 6.5.0-rc4 xhci-hcd
S: Product=xHCI Host Controller
S: SerialNumber=xhci-hcd.0.auto
C:* #Ifs= 1 Cfg#= 1 Atr=e0 MxPwr= 0mA
I:* If#= 0 Alt= 0 #EPs= 1 Cls=09(hub ) Sub=00 Prot=00 Driver=hub
E: Ad=81(I) Atr=03(Int.) MxPS= 4 Ivl=256ms
T: Bus=01 Lev=01 Prnt=01 Port=00 Cnt=01 Dev#= 2 Spd=1.5 MxCh= 0
D: Ver= 2.00 Cls=00(>ifc ) Sub=00 Prot=00 MxPS= 8 #Cfgs= 1
P: Vendor=03f0 ProdID=134a Rev= 1.00
S: Manufacturer=PixArt
S: Product=HP USB Optical Mouse
C:* #Ifs= 1 Cfg#= 1 Atr=a0 MxPwr=100mA
I:* If#= 0 Alt= 0 #EPs= 1 Cls=03(HID ) Sub=01 Prot=02 Driver=usbhid
E: Ad=81(I) Atr=03(Int.) MxPS= 4 Ivl=10ms
T: Bus=02 Lev=00 Prnt=00 Port=00 Cnt=00 Dev#= 1 Spd=5000 MxCh= 1
B: Alloc= 0/800 us ( 0%), #Int= 0, #Iso= 0
D: Ver= 3.00 Cls=09(hub ) Sub=00 Prot=03 MxPS= 9 #Cfgs= 1
P: Vendor=1d6b ProdID=0003 Rev= 6.05
S: Manufacturer=Linux 6.5.0-rc4 xhci-hcd
S: Product=xHCI Host Controller
S: SerialNumber=xhci-hcd.0.auto
C:* #Ifs= 1 Cfg#= 1 Atr=e0 MxPwr= 0mA
I:* If#= 0 Alt= 0 #EPs= 1 Cls=09(hub ) Sub=00 Prot=00 Driver=hub
E: Ad=81(I) Atr=03(Int.) MxPS= 4 Ivl=256ms
��相机串行接口(CSI)
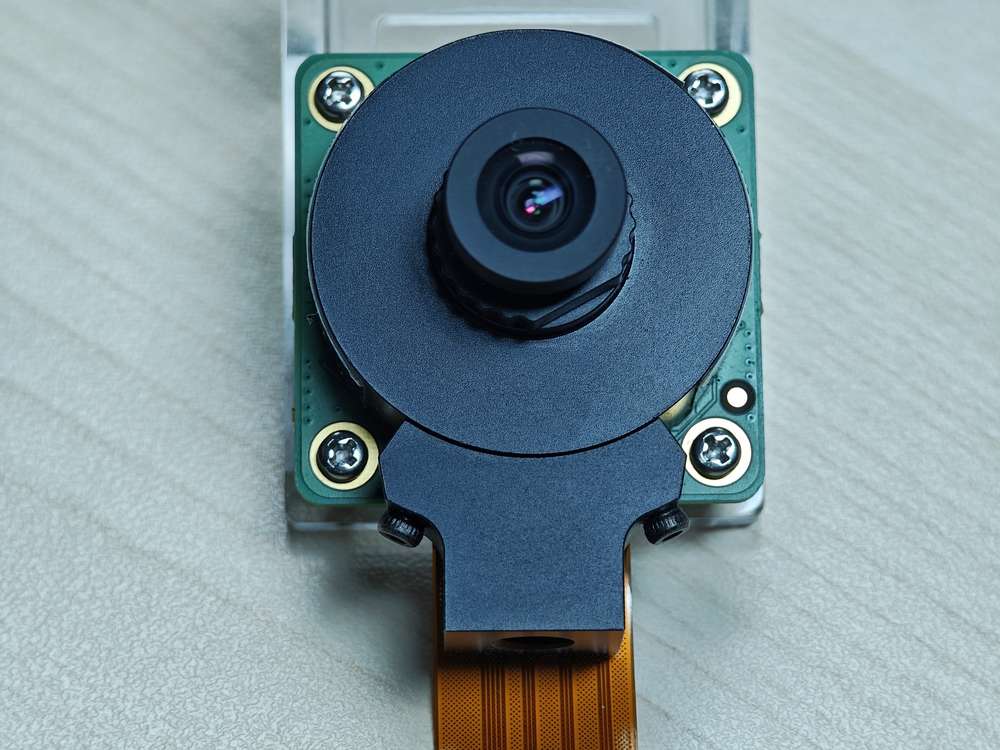
目前 魔方派 3 已经兼容树莓派官方的三款摄像头。下表显示了每个摄像头模块支持的分辨率:
| 分辨率 | 宽高比 | IMX477 | IMX708 | IMX219 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4056 x 3040 | 4:3 | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| 4608 x 2592 | 16:9 | 否 | 是 | 否 |
| 3280 x 2464 | 4:3 | 否 | 否 | 是 |
| 1920 x 1080 | 16:9 | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| 1632 x 1224 | 4:3 | 否 | 否 | 是 |
-
Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera(IMX477/M12 Mount)购买链接
在 魔方派 3 QIM 官方演示中,IMX477 摄像头使用了 WS1053516 镜头。

-
Raspberry Pi Camera Module 2 (IMX219) 购买链接
备注目前 魔方派 3 暂时只支持标准版 Module 2 摄像头,不支持广角(Wide)、夜光(NoIR)版本。
-
Raspberry Pi Camera Module 3 (IMX708) 购买链接
备注目前 魔方派 3 暂时只支持标准版 Module 3 摄像头,不支持广角(Wide)、夜光(NoIR)版本。当前软件版本暂不支持 Module 3 摄像头的 AF 自动对焦功能。
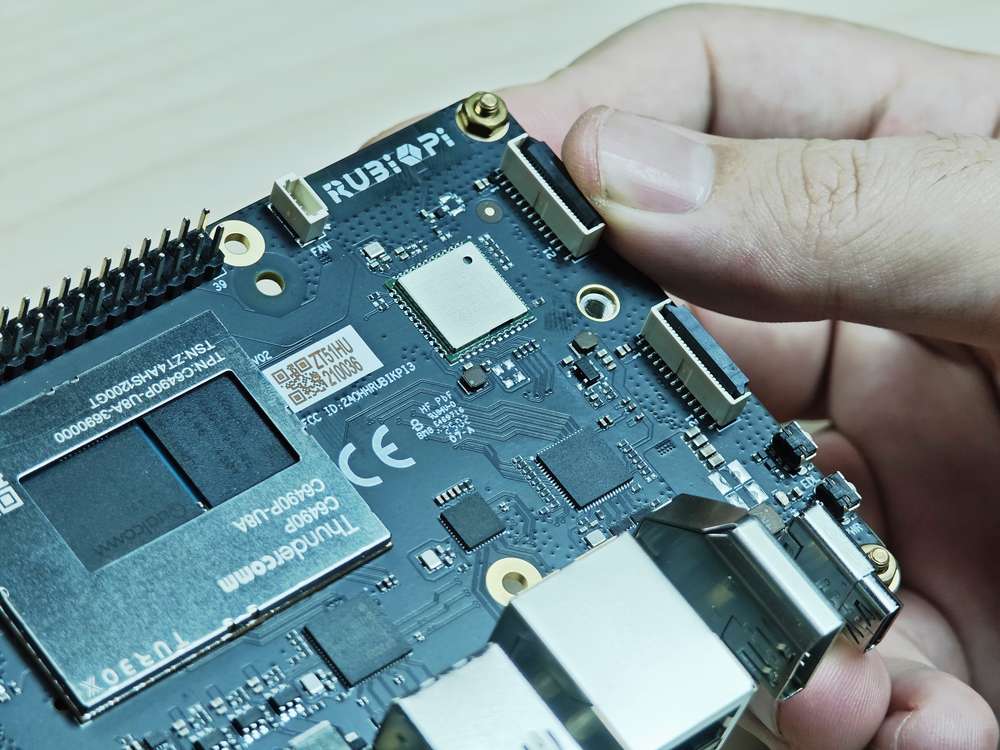
摄像头排线安装
魔方派 3 支持的摄像头 FPC 为 22 pin,0.5mm 间距,厚度 0.3±0.05mm。可以兼容 树莓派 5 同规格摄像头FPC。
严禁在板子未断电的情况下插拔摄像头,否则非常容易烧坏摄像头模组。

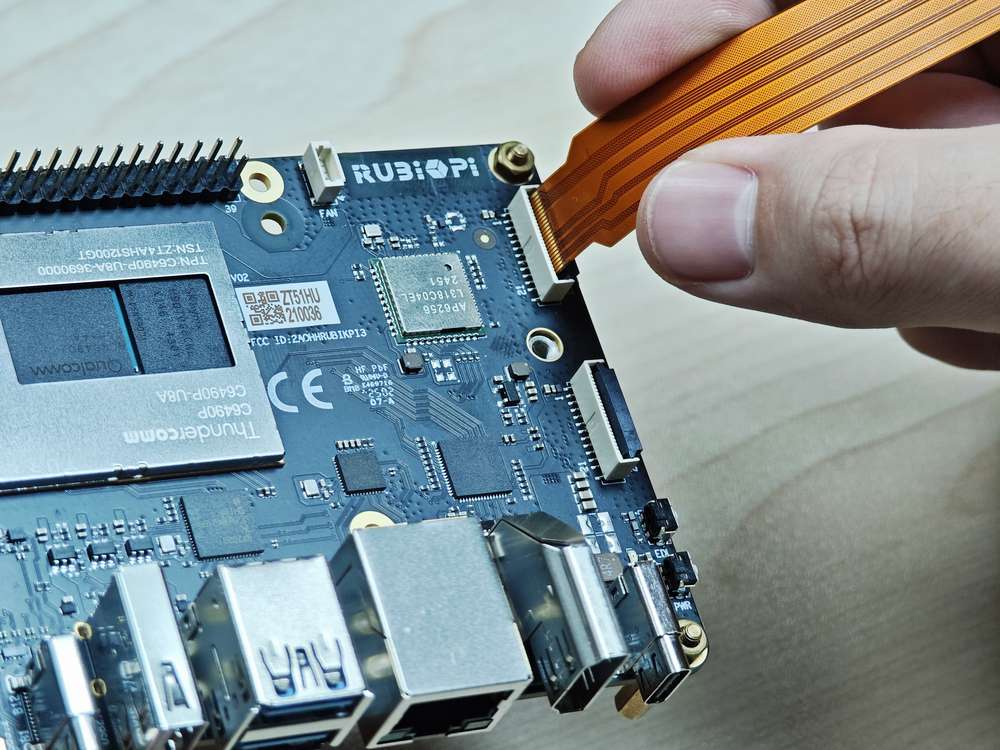
-
向上拉开连接器的锁扣部分:
-
插入 FPC,注意接触面朝向板内:

-
按下锁扣,确认 FPC 稳定没有松动:
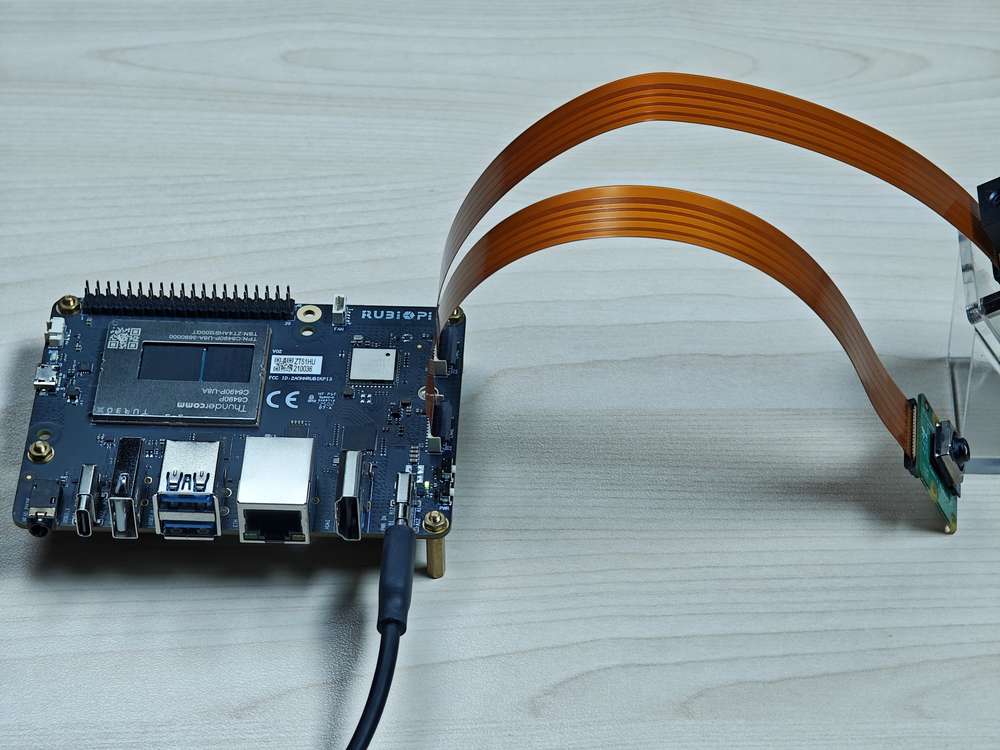
摄像头使用方法
在 魔方派 3 中可使用 gstreamer 命令对摄像头进行操作,操作前需输入下面命令对摄像头进行设置:
echo multiCameraLogicalXMLFile=kodiak_dc.xml > /var/cache/camera/camxoverridesettings.txt
echo enableNCSService=FALSE >> /var/cache/camera/camxoverridesettings.txt
可使用下面的命令关闭或打开摄像头相关的日志,执行完命令后重启设备生效。
默认值:
-
logWarningMask:0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF -
logCoreCfgMask:0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
echo logWarningMask=0x00 >> /var/cache/camera/camxoverridesettings.txt
echo logCoreCfgMask=0x00 >> /var/cache/camera/camxoverridesettings.txt
可将摄像头插入下图 13 和 14 处。
如下为实物连接图:
暂时无法支持两个 IMX708 4608x2592同时运行。
-
在 魔方派 3 中使用下面命令测试单个摄像头全屏预览:
export XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/dev/socket/weston
export WAYLAND_DISPLAY=wayland-1
setprop persist.overlay.use_c2d_blit 2
gst-launch-1.0 -e qtiqmmfsrc camera=0 name=camsrc ! video/x-raw\(memory:GBM\),format=NV12,width=1920,height=1080,framerate=30/1,compression=ubwc ! queue ! waylandsink fullscreen=true async=true预览结果如下图所示:

-
在 魔方派 3 中使用下面命令测试两摄像头并发预览:
# 终端1
export XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/dev/socket/weston
export WAYLAND_DISPLAY=wayland-1
setprop persist.overlay.use_c2d_blit 2
gst-launch-1.0 -e qtiqmmfsrc camera=0 name=camsrc ! video/x-raw\(memory:GBM\),format=NV12,width=1920,height=1080,framerate=30/1,compression=ubwc ! queue ! waylandsink sync=false x=0 y=0 width=960 height=540 enable-last-sample=false
# 终端2
export XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/dev/socket/weston
export WAYLAND_DISPLAY=wayland-1
setprop persist.overlay.use_c2d_blit 2
gst-launch-1.0 -e qtiqmmfsrc camera=1 name=camsrc ! video/x-raw\(memory:GBM\),format=NV12,width=1920,height=1080,framerate=30/1,compression=ubwc ! queue ! waylandsink sync=false x=960 y=540 width=960 height=540 enable-last-sample=false预览结果如下图所示:

-
在 魔方派 3 中使用下面命令测试两摄像头并发录像:
# 终端1:
echo multiCameraLogicalXMLFile=kodiak_dc.xml > /var/cache/camera/camxoverridesettings.txt
export XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/dev/socket/weston
export WAYLAND_DISPLAY=wayland-1
setprop persist.overlay.use_c2d_blit 2
gst-launch-1.0 -e qtiqmmfsrc camera=0 name=camsrc video_0::type=preview ! video/x-raw\(memory:GBM\),format=NV12,width=1920,height=1080,framerate=30/1,compression=ubwc,interlace-mode=progressive,colorimetry=bt601 ! queue ! v4l2h264enc capture-io-mode=5 output-io-mode=5 ! queue ! h264parse ! mp4mux ! queue ! filesink location="/opt/mux0.mp4"
# 终端2:
export XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/dev/socket/weston
export WAYLAND_DISPLAY=wayland-1
setprop persist.overlay.use_c2d_blit 2
gst-launch-1.0 -e qtiqmmfsrc camera=1 name=camsrc video_0::type=preview ! video/x-raw\(memory:GBM\),format=NV12,width=1920,height=1080,framerate=30/1,compression=ubwc,interlace-mode=progressive,colorimetry=bt601 ! queue ! v4l2h264enc capture-io-mode=5 output-io-mode=5 ! queue ! h264parse ! mp4mux ! queue ! filesink location="/opt/mux1.mp4"录制完成后在 /opt 目录下有录制的视频文件,如下图:
-
在 魔方派 3 中使用下面命令测试两摄像头并发录像加预览:
# 终端1
export XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/dev/socket/weston
export WAYLAND_DISPLAY=wayland-1
setprop persist.overlay.use_c2d_blit 2
gst-launch-1.0 -e qtiqmmfsrc camera=0 name=camsrc video_0::type=preview ! video/x-raw\(memory:GBM\),format=NV12,width=1920,height=1080,framerate=30/1,compression=ubwc,interlace-mode=progressive,colorimetry=bt601 ! queue ! v4l2h264enc capture-io-mode=5 output-io-mode=5 ! queue ! h264parse ! mp4mux ! queue ! filesink location="/opt/mux0.mp4" camsrc. ! video/x-raw\(memory:GBM\),format=NV12,width=1920,height=1080,framerate=30/1,compression=ubwc ! waylandsink sync=false x=0 y=0 width=960 height=540 enable-last-sample=false
# 终端2
export XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/dev/socket/weston
export WAYLAND_DISPLAY=wayland-1
setprop persist.overlay.use_c2d_blit 2
gst-launch-1.0 -e qtiqmmfsrc camera=1 name=camsrc video_0::type=preview ! video/x-raw\(memory:GBM\),format=NV12,width=1920,height=1080,framerate=30/1,compression=ubwc,interlace-mode=progressive,colorimetry=bt601 ! queue ! v4l2h264enc capture-io-mode=5 output-io-mode=5 ! queue ! h264parse ! mp4mux ! queue ! filesink location="/opt/mux1.mp4" camsrc. ! video/x-raw\(memory:GBM\),format=NV12,width=1920,height=1080,framerate=30/1,compression=ubwc ! waylandsink sync=false x=960 y=540 width=960 height=540 enable-last-sample=false录制完成后在 /opt 目录下有录制的视频文件:
预览结果如下:

-
在 魔方派 3 中使用下面命令测试摄像头拍照:
export XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/dev/socket/weston
export WAYLAND_DISPLAY=wayland-1
setprop persist.overlay.use_c2d_blit 2
gst-pipeline-app -e qtiqmmfsrc name=camsrc camera=0 ! "image/jpeg,width=1920,height=1080,framerate=30/1" ! multifilesink location=/opt/0_frame%d.jpg max-files=1执行上述命令后,会在终端输出如下 MENU,在 MENU 中输入 3,并按下 Enter 执行拍照指令。
##################################### MENU #####################################
============================== Pipeline Controls ==============================
(0) NULL : Set the pipeline into NULL state
(1) READY : Set the pipeline into READY state
(2) PAUSED : Set the pipeline into PAUSED state
(3) PLAYING : Set the pipeline into PLAYING state
==================================== Other ====================================
(p) Plugin Mode : Choose a plugin which to control
(q) Quit : Exit the application
Choose an option:
# 按下CTRL+C结束拍照拍照完成后在 /opt 目录下有对应的 jpg 文件:
摄像头故障排除
如果摄像头无法显示或捕捉图像,请检查以下内容:
-
检查摄像头模块连接。
请参阅 摄像头排线安装。
-
运行单流预览用例。
export XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/dev/socket/weston
export WAYLAND_DISPLAY=wayland-1
setprop persist.overlay.use_c2d_blit 2
gst-launch-1.0 -e qtiqmmfsrc camera=0 name=camsrc ! video/x-raw\(memory:GBM\),format=NV12,width=1920,height=1080,framerate=30/1,compression=ubwc ! queue ! waylandsink sync=false x=1000 y=1000 width=960 height=540 enable-last-sample=false -
使用以下命令收集日志。
journalctl -f > /opt/log.txt在日志中搜索 "probe success" 。Probe success 意味着摄像头模块已通电并响应 I2C 控制。如果特定传感器没有 "probe success" 日志,则可能是柔性电缆连接或摄像头模块的问题。
以下日志指示探测到一个 IMX477:
[ 80.645992] CAM_INFO: CAM-SENSOR: cam_sensor_driver_cmd: 939: Probe success,slot:7,slave_addr:0x34,sensor_id:0x477, is always on: 0 -
检查摄像头传感器驱动程序命令
使用
journalctl -f > /opt/log.txt命令收集日志并搜索 "cam_sensor_driver_cmd"。 "CAM_START_DEV Success" 表示摄像头传感器流式传输开始。"CAM_STOP_DEV Success" 表示摄像头传感器流式传输停止。例如:
start:
[ 81.172814] CAM_INFO: CAM-SENSOR: cam_sensor_driver_cmd: 1129: CAM_START_DEV Success, sensor_id:0x477,sensor_slave_addr:0x34
stop:
[ 88.905241] CAM_INFO: CAM-SENSOR: cam_sensor_driver_cmd: 1157: CAM_STOP_DEV Success, sensor_id:0x477,sensor_slave_addr:0x34 -
检查传感器流式传输。
启用 CSID SOF/EOF IRQ 日志,随后执行摄像头出流命令。
mount -o rw,remount /usr
mount -t debugfs none /sys/kernel/debug/
echo 0x8 > /sys/module/camera/parameters/debug_mdl
echo 3 >/sys/kernel/debug/camera_ife/ife_csid_debug
echo 1 > /sys/kernel/tracing/tracing_on
echo 1 > /sys/kernel/tracing/events/camera/cam_log_debug/enable
echo 2 > /sys/module/camera/parameters/debug_type
cat /sys/kernel/tracing/trace_pipe > trace.txt捕获的日志有助于提供有关 SOF 和 EOF 的详细信息。在日志 trace.txt 中搜索 "irq_status_ipp"。BIT12(0x1000)表示 SOF 数据包,BIT9(0x200)表示 EOF 数据包。日志如下所示:
<idle>-0 [000] d.h1. 19287.546764: cam_log_debug:
CAM_DBG: CAM-ISP: cam_ife_csid_irq: 4996: irq_status_ipp = 0x1110 cam-server-25604 [000] dNH.. 19287.561705: cam_log_debug:
CAM_DBG: CAM-ISP: cam_ife_csid_irq: 4996: irq_status_ipp = 0xee8
HDMI OUT
魔方派 3 的 HDMI 接口为下图 9。
魔方派 3 HDMI 参数信息:
-
HDMI 1.4
-
3840 x 2160 分辨率 @ 30 fps
-
DSI 0 to HDMI (LT9611)
-
支持 CEC
-
支持分辨率自适应
-
支持热插拔
DP 和 HDMI 可同时接显示器,并发显示。
CEC
HDMI CEC(Consumer Electronics Control,消费者电子控制)是 HDMI 标准中的一项功能,旨在通过单一的 HDMI 连接线实现多设备之间的互联与统一控制。具体来说,CEC 允许连接的设备通过专用的 CEC 引脚进行通信,从而实现例如通过一个遥控器控制多台设备的功能。
魔方派 3 集成了 cec-client 工具,将 HDMI 线连接到电视后,可使用下面命令查看电视是否支持 CEC:
echo 'scan' | cec-client -s -d 1
若支��持 CEC 将会有如下输出:
opening a connection to the CEC adapter...
requesting CEC bus information ...
CEC bus information
===================
device #0: TV
address: 0.0.0.0
active source: no
vendor: Sony
osd string: TV
CEC version: 1.4
power status: standby
language: eng
device #1: Recorder 1
address: 1.0.0.0
active source: no
vendor: Pulse Eight
osd string: CECTester
CEC version: 1.4
power status: on
language: eng
device #4: Playback 1
address: 3.0.0.0
active source: no
vendor: Sony
osd string: PlayStation 4
CEC version: 1.3a
power status: standby
language: ???
若电视支持 CEC 功能,可在 魔方派 3 中使用下面命令控制电视音量的加减:
echo 'volup' | cec-client -t p -s
echo 'voldown' | cec-client -t p -s
更多 cec-client 使用方法,可使用 -h 参数进行查看:
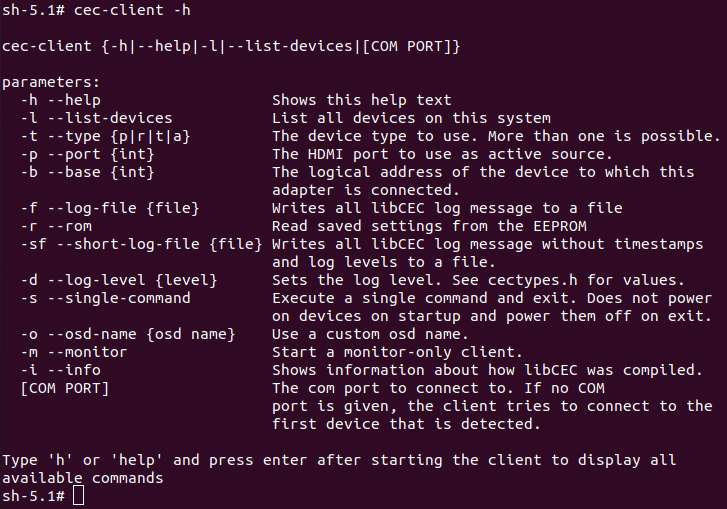
HDMI OUT 触摸屏
魔方派 3 默认支持 1024*600P 分辨率的 HDMI OUT 触摸屏,如下图所示:

上图中使用的屏幕为 7 寸 IPS 高清触摸屏幕。
HDMI OUT 调试
魔方派 3 使用的是 LT9611 这款 DSI-to-HDMI 桥接芯片。
下表列出 HDMI 桥接芯片所需的配置。
| 说明 | DTSI 节点 |
|---|---|
| 将 DSI-to-HDMI 桥接面板设置为 Primary | &sde_dsi { qcom, dsi-default-panel = <&dsi_ext_bridge_1080p>; |
| 为桥接芯片配置基准电源条目 | &sde_dsi { vddio-supply = <&vreg_18c_ip62>; vdda-9p9-supply = <&vreg_11oc_9p88>; vdda-9p9-supply = <&vreg_11oc_9p88>; |
| 为桥接芯片配置面板复位 GPIO | lt9611: lt,lt9611 { reset-options = <&tlmm 21 0>;} |
| 在外部桥接模式下配置 DSI 主机驱动程序以使用第三方 DSI-to-HDMI 桥接芯片 | qcom,mdss-dsi-ext-bridge-mode; |
获取 LT9611 日志
要获取 LT9611 日志,请运行以下命令:
dmesg | grep lt9611
查看 log,出现下面的字样代表 HDMI OUT 可以正常运行。
这段日志记录了 LT9611 芯片的初始化和 HDMI 连接过程,从固件版本检测到 CEC 初始化,芯片启动正常。
-
芯片的固件版本是 0xe2.17.02。这表示芯片初始化时,驱动成功读取了版本信息。
-
LT9611 的 CEC(消费电子控制)功能适配器成功注册。
-
CEC 初始化完成,表明 LT9611 的 CEC 模块已经可以正常工作。
-
芯片成功读取了 HPD(热插拔检测)状态,并且会有返回值,表示确认 HDMI 设备接入。
-
芯片检测到视频信号参数:水平分辨率 1920(像素),垂直分辨率 1080(像素),像素时钟频率 148500 kHz(148.5 MHz)。这对应的是 1080p 分辨率(全高清),60Hz 刷新率的典型配置。
[ 5.492765] lt9611 9-0039: LT9611 revision: 0xe2.17.02
[ 5.570258] lt9611 9-0039: CEC adapter registered
[ 5.582944] lt9611 9-0039: CEC init success
[ 8.233028] lt9611 9-0039: success to read hpd status: 13
[ 8.233044] lt9611_device_connect_status_notify: send msg[Hdmi Connection] ret[32]
[ 8.345015] lt9611 9-0039: hdisplay=1920, vdisplay=1080, clock=148500
[ 8.836662] lt9611 9-0039: video check: hactive_a=1920, hactive_b=1920, vactive=1080, v_total=1125, h_total_sysclk=401, mipi_video_format=170
获取 DSI 日志
我们也可以通过输出的 DSI 信息进行调试。DSI 指的是 Display Serial Interface(显示串行接口),通常与移动设备或嵌入式系统的显示驱动(如 MIPI DSI)相关。
这个命令用来查看与显示接口(DSI)相关的内核日志,通常用于调试显示驱动或硬件问题。
dmesg | grep dsi
输出结果示例:
[ 4.811430] i2c 9-0039: Fixed dependency cycle(s) with /soc@0/qcom,dsi-display-primary
[ 4.941131] dsi_phy ae94400.qcom,mdss_dsi_phy0: supply gdsc not found, using dummy regulator
[ 4.941385] [drm:dsi_pll_init [msm_drm]] [msm-dsi-info]: DSI_PLL_0: DSI pll label = dsi_pll_5nm
[ 4.941466] [drm:dsi_pll_init [msm_drm]] [msm-dsi-info]: DSI_PLL_0: PLL SSC enabled
[ 4.941513] dsi_pll_init: PLL base=00000000625eaee4
[ 4.941658] [drm:dsi_pll_clock_register_5nm [msm_drm]] [msm-dsi-info]: DSI_PLL_0: Registered clocks successfully
[ 4.941700] [drm:dsi_phy_driver_probe [msm_drm]] [msm-dsi-info]: DSI_0: Probe successful
[ 4.973185] [drm:dsi_ctrl_dev_probe [msm_drm]] [msm-dsi-info]: dsi-ctrl-0: Probe successful
[ 5.585113] [drm:dsi_display_bind [msm_drm]] [msm-dsi-info]: Successfully bind display panel 'qcom,mdss_dsi_ext_bridge_1080p '
[ 5.585154] msm_drm ae00000.qcom,mdss_mdp0: bound soc@0:qcom,dsi-display-primary (ops dsi_display_comp_ops [msm_drm])
[ 8.345467] [drm:dsi_display_set_mode [msm_drm]] [msm-dsi-info]: mdp_transfer_time=0, hactive=1920, vactive=1080, fps=60, clk_rate=0
[ 8.345740] [drm:dsi_ctrl_isr_configure [msm_drm]] [msm-dsi-info]: dsi-ctrl-0: IRQ 249 registered
获取显示面板信息
若要查看选定的显示面板,请运行以下命令:
cat /sys/kernel/debug/qcom,mdss_dsi_ext_bridge_2k60/dump_info
示例输出
name = qcom,mdss_dsi_ext_bridge_2k60
Resolution = 2560(80|48|32|1)x1440(33|3|5|1)@60fps 0 Hz
CTRL_0:
ctrl = dsi-ctrl-0
phy = dsi-phy-0
Panel = ext video mode dsi bridge
Clock master = dsi-ctrl-0
获取 DSI 时钟信息
若要检查 DSI 时钟信息,请运行以下命令:
cat /sys/kernel/debug/qcom,mdss_dsi_ext_bridge_2k60/dsi-ctrl-0/state_info
示例输出
Current State:
CTRL_ENGINE = ON
VIDEO_ENGINE = ON
COMMAND_ENGINE = OFF
Clock Info:
BYTE_CLK = 181274400, PIXEL_CLK = 241699200, ESC_CLK = 19200000
获取调压器信息
要检查调压器状态和电压,请运行以下命令:
cat /sys/kernel/debug/regulator/regulator_summary
获取接口信息
要检索调试 dump 输出(显示接口编号、VSync 计数、欠载计数和接口模式),请运行以下命令:
cat /sys/kernel/debug/dri/0/encoder*/status
示例输出
intf:1 vsync: 359036 underrun: 0 mode: video
intf:0 vsync: 0 underrun: 0 mode: video
获取常规 DPU 调试信息
常见的 DPU 调试信息说明如下:
检查 DPU 时钟速率:
cat /sys/kernel/debug/clk/clk_summary | grep disp_cc
将 DPU 设置为性能模式:
cd /sys/kernel/debug/dri/0/debug/core_perf/
echo 1 > perf_mode
DisplayPort
魔方派 3 拥有 1 个 USB Type-C 接口的 DisplayPort (DP),如下图 5。
DP 的参数如下:
-
3840 × 2160 分辨率 @ 60 fps
-
单流传输 (Single stream transport)
-
DisplayPort 和 USB 3.0 的并发功能
DP 和 HDMI 可同时接显示器,并发显示。
DP 调试
获取 DP 日志
输入下面命令开启日志打印权限。
echo 8 > /proc/sys/kernel/printk
echo ‘file dsi* +p’ > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
第一条命令中的
8表示日志�级别。Linux 内核用 0 到 8 表示日志的优先级,数值越小,优先级越高:
0 (KERN_EMERG): 系统紧急情况(比如崩溃)。
1 (KERN_ALERT): 需要立即处理的问题。
2 (KERN_CRIT): 严重错误。
3 (KERN_ERR): 一般错误。
4 (KERN_WARNING): 警告。
5 (KERN_NOTICE): 正常但值得注意的事件。
6 (KERN_INFO): 信息性消息。
7 (KERN_DEBUG): 调试信息。
8: 比调试还低的级别,可以打出全部级别。
而echo ‘file dsi* +p’ > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control则会显示
内核中所有文件名以 dsi* 开头的源文件(通常是 DSI 显示驱动相关的代码)里的调试信息。
这些调试信息会输出到内核日志,可以通过 dmesg 查看。通过下面的命令输出来调试 DP:
mount -t debugfs none /sys/kernel/debug
echo 'file dp_display.c +p' > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
echo 'file dp_aux.c +p' > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
echo 'file dp_link.c +p' > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
echo 'file dp_power.c +p' > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
echo 'file dp_ctrl.c +p' > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
echo 'file dp_parser.c +p' > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
打开全部的限制等级之后,我们就可以筛选 DP 的日志来进行进一步的验证,以下是 DP 正常启动之后,输出的日志:
hub 4-0:1.0: USB hub found
hub 4-0:1.0: 1 port detected
usb usb5: We don't know the algorithms for LPM for this host, disabling LPM.
hub 5-0:1.0: USB hub found
hub 5-0:1.0: 1 port detected
[drm:dp_power_clk_enable][msm-dp-info][3216]core:on link:off strm0:off strm1:off
[drm:dp_display_host_init][msm-dp-info][3216][OK]
[drm:dp_display_host_ready][msm-dp-info][2912][OK]
[drm:dp_panel_read_sink_caps][msm-dp-info][2912]fec_en=0, dsc_en=0, widebus_en=0
[drm:dp_link_process_request][msm-dp-info][2912]event: DP_LINK_STATUS_UPDATED
[drm:dp_power_clk_enable][msm-dp-info][2912]core:on link:on strm0:off strm1:off
[drm:dp_catalog_ctrl_fec_config][msm-dp-err][2912]no link
[drm:dp_ctrl_link_train][msm-dp-info][2912]link training #1 successful
[drm:dp_ctrl_link_train][msm-dp-info][2912]link training #2 successful
[drm:dp_link_process_request][msm-dp-info][2912]event: DP_LINK_STATUS_UPDATED
[drm:dp_catalog_ctrl_fec_config][msm-dp-err][2912]no link
[drm:dp_ctrl_link_train][msm-dp-info][2912]link training #1 successful
[drm:dp_ctrl_link_train][msm-dp-info][2912]link training #2 successful
[drm:dp_display_send_hpd_event][msm-dp-info][2912][name=DP-1]:[status=connected] [bpp=0] [pattern=0]
[drm:dp_display_send_hpd_event][msm-dp-info][2912]uevent success: 0
lt9611 9-0039: success to read hpd status: 8
lt9611_device_connect_status_notify: send msg[Hdmi Disconnect] ret[32]
lt9611 9-0039: success to read hpd status: 8
lt9611_device_connect_status_notify: send msg[Hdmi Disconnect] ret[32]
[drm:dp_power_clk_enable][msm-dp-info][577 ]core:on link:on strm0:on strm1:off
[drm:dp_catalog_ctrl_fec_config][msm-dp-err][577 ]no link
[drm:dp_ctrl_link_train][msm-dp-info][577 ]link training #1 successful
[drm:dp_ctrl_link_train][msm-dp-info][577 ]link training #2 successful
[drm:dp_panel_resolution_info][msm-dp-info][577 ]DP RESOLUTION: active(back|front|width|low)
[drm:dp_panel_resolution_info][msm-dp-info][577 ]1920(148|88|44|0)x1080(36|4|5|0)@60fps 24bpp 148500Khz 10LR 2Ln
以上正常启动流程的日志总结如下:
-
USB 初始化: 系统启动时检测到两个单端口 USB HUB,禁用 USB 5 的 LPM。
-
DP 准备: DP 控制器初始化,读取显示器能力,准备建立连接。
-
DP 链接训练: 通过多次链接训练,DP 与显示器建立稳定连接。
-
DP 连接确认: 系统确认 DP-1 已连接,通知用户空间。
-
HDMI 断开: LT9611 检测到 HDMI 断开,可能是用户操作或接口切换。
-
DP 输出: HDMI 断开后,DP 启用视频流,输出 1080p@60Hz 的画面。
Wi-Fi & 蓝牙
魔方派 3 上搭载了 AP6256 Wi-Fi 模块,支持 Wi-Fi 5 和蓝牙 5.2。
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi 是一种使用 IEEE 802.11 协议的无线网络技术。它允许智能手机、可穿戴设备、笔记本电脑、台式机和其他消费电子产品等电子设备在没有物理电缆的情况下连接到互联网。
工作频段
AP6256 Wi-Fi 模块支持 2.4 GHz、5 GHz 工作频段。
工作模式
Wi-Fi 软件在以下模式下运行:
| 模式 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| STA 模式 | 在 STA 模式下,设备连接到 Wi-Fi 网络中的接入点,并与网络中的其他设备进行通信。此模式是 Wi-Fi 连接中的无线设备的标准模式。 |
| 热点模式 | 热点模式使设备能够使用蜂窝链路 (LTE) 向 Wi-Fi 客户端提供回程 (Internet) 连接。该设备通过其轻量级热点接口建立此连接。在热点模式下,设备可以与连接到同一热点的其他 Wi-Fi 客户端通信,与热点设备通信,共享设备的 WAN 连接。 |
STA 模式
在 STA 模式(Station)下,设备可连接到一个已经存在的无线网络,以便访问网络资源或互联网。在 魔方派 3 中输入如下面命令进行连接:
-
扫描附近 Wi-Fi:
iw wlan0 scan | grep SSID -
连接 Wi-Fi:
wpa_passphrase <ssid> <passphrase> > /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf # 输入Wi-Fi账号和密码
systemctl restart wifi # 连接Wi-Fi连接好 Wi-Fi 后,下次开机会自动进行连接。
-
如想切换 Wi-Fi 可修改 /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf 文件,如下是一种修改方式:
ctrl_interface=/var/run/wpa_supplicant
update_config=1
pmf=1
network={
ssid="RUBIKPi"
psk="123456789"
}-
ssid 为无线网络名称
-
psk 为无线网络密码
按实际情况对文件进行修改。
-
-
修改完成后,输入下面命令进行连接:
killall -9 wpa_supplicant
wpa_supplicant -Dnl80211 -iwlan0 -c/etc/wpa_supplicant.conf -B
热点模式
无线接入热点模式即 AP 模式(Access Point),是一个无线网络的创建者,是网络的中心节点,一般家庭或办公室使用的无线网络路由器就是一个 AP,下面是 AP 的创建步骤:
-
开启 AP
-
创建或修改 /opt/hostapd.conf 文件:
ctrl_interface=/var/run/hostapd
driver=nl80211
ieee80211n=1
interface=wlan1
hw_mode=a
channel=36
beacon_int=100
dtim_period=1
ssid=RUBIKPi
auth_algs=1
ap_isolate=0
ignore_broadcast_ssid=0
wpa=2
wpa_key_mgmt=WPA-PSK
rsn_pairwise=CCMP
wpa_passphrase=123456789 -
执行下面命令开启 AP:
hostapd -B /opt/hostapd.conf # 设置软件AP
# 启动动态主机配置协议(DHCP)服务器
brctl addbr br0
brctl addif br0 wlan1
ifconfig br0 192.168.225.1 netmask 255.255.255.0 up
killall dnsmasq
dnsmasq --conf-file=/etc/dnsmasq.conf --dhcp-leasefile=/var/run/dnsmasq.leases --addn-hosts=/data/hosts --pid-file=/var/run/dnsmasq.pid -i br0 -I lo -z --dhcp-range=br0,192.168.225.20,192.168.225.60,255.255.255.0,43200 --dhcp-hostsfile=/data/dhcp_hosts --dhcp-option-force=6,192.168.225.1 --dhcp-script=/bin/dnsmasq_script.sh -
若要与 hostapd_cli 建立连接,可使用下面命令:
hostapd_cli -i wlan1 -p /var/run/hostapd
在
hostapd_cli控制台中监视 Wi-Fi STA 连接通知,例如AP-STA-CONNECTED、EAPOL-4WAY-HS-COMPLETED。示例输出
root@rubikpi:~# hostapd_cli -i wlanl -p /var/run/hostapd
hostapd_cli v2.11-devel
Copyright (c) 2004-2022, Jouni Malinen <j@wl.fi> and contributors
This software may be distributed under the terms of the BSD License.
See README for more details.
Interactive mode
> <3>AP-STA-CONNECTED aa: a4: fd: 8b: ec: 90
<3>EAPOL-4WAY-HS-COMPLETED aa: a4: fd: 8b:ec:90
> list_sta
aa: a4: fd: 8b:ec:90 -
若开启 AP 5G 模式前,未使用 STA 模式连接过 5G Wi-Fi,则需使用如下命令,查看环境中 5G channel 的配置。
iw dev wlan0 scan
在命令执行结果中通过 primary channel 字段确定当前已被激活 channel,如下所示,channel 字段为 36,将 36 写入 /opt/hostapd.conf 文件中的 channel 字段即可
HT operation:
* primary channel: 36
* secondary channel offset: above
* STA channel width: any
* RIFS: 0
* HT protection: nonmember
* non-GF present: 0
* OBSS non-GF present: 0
* dual beacon: 0
* dual CTS protection: 0
* STBC beacon: 0
* L-SIG TXOP Prot: 0
* PCO active: 0
* PCO phase: 0
-
验证 AP
要验证连接状态,请从其他设备连接到 AP。
例如,通过执行以下步骤从移动设备连接到 AP:
-
在移动设备上,转到 Wi-Fi settings。
-
等待 Wi-Fi STA 检测到 AP。
-
选择 AP 并输入在 魔方派 3 设备上为 AP 配置的相应
wpa_passphrase,然后进行连接。
> status
state=ENABLED
phy=phyR freq=2412
num_sta_non_erp=0
num_sta_no_short_slot_time=0
num_sta_no_short_preamble=0
olbc=0
num_sta_ht_no_gf=0 num_sta_no_ht=0
num_sta_ht_20_mhz=0
num_sta_ht40_intolerant=0
olbc_ht=0
ht_op_mode=0x0
hw_mode=g
country_code=US
country3=0x20
cac_time_seconds=0
cac_time_left_seconds=N/A
channel=1
edmg_enable=0 edmg_channel=0
secondary_channel=0
ieee80211n=1
ieee80211ac=0
ieee80211ax=0
ieee80211be=0
beacon_int=100
dtim_period=2
ht_caps_info=000c
ht_mcs_bitmask=ffff0000000000000000
supported_rates-02 04 0b 16 Oc 12 18 24 30 48 60 6c
max_txpower=30
bss[0]=wlan1
bssid[0]=00:03:7f:95:8e:8e
ssid [0]=QSoftAP
num_sta[0]=1
> |- 要验证连接,在 魔方派 3 设备的终端 中 ping 移动设备的 IP 地址。
以下输出表示 Wi-Fi 连接已成功建立,数据传输已开始:
sh-5.1# ping 192.168.1.42
PING 192.168.1.42 (192.168.1.42): 56 data bytes
64 bytes from 192.168.1.42: seq=0 ttl=64 time-11.175 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.1.42: seq=1 ttl=64 time=14.528 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.1.42: seq=2 ttl=64 time=29.735 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.1.42: seq=3 ttl=64 time=223.822 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.1.42: seq-4 ttl=64 time-23.675 ms
^C
192.168.1.42 ping statistics ---
7 packets transmitted, 5 packets received, 28% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 11.175/60.587/223.822 ms
sh-5.1#也可以在连接设备的 Settings 中验证 Wi-Fi 连接状态。例如,要获取连接到 魔方派 3 AP 的移动设备的 IP 地址,执行以下步骤:
-
导航至 Settings > Wi-Fi。
-
验证 AP 的 SSID。
-
-
关闭 AP:
要停止 AP,在终端 中执行以下操作:
-
通过执行以下步骤停止 hostapd:
-
要停止 hostapd 过程,可运行以下命令:
killall hostapd -
要禁用接口,可运行以下命令:
ifconfig wlan1 down
-
-
运行以下命令删除
ctrl_interface:rm -rf /var/run/hostapd/wlan1
Wi-Fi 热点成功停止。
-
蓝牙
蓝牙® 无线技术是一种短距离通信系统,可实现设备之间的无线数据交换。蓝牙技术的主要优势如下:
-
替代便携式和固定式电子设备的线缆
-
提供稳健、节能且经济高效的解决方案
-
促进解决方案及其应用的灵活性。
在 魔方派 3 中使用下面命令测试蓝牙 功能。
BlueZ 协议栈
通用访问配置文件(GAP)
通用访问配置文件(Generic Access Profile, GAP),保证不同的 Bluetooth 产品可以互相发现对方并建立连接,是所有其它蓝牙应用规范的基础。
bluetoothctl 是 BlueZ 套件的一部分,BlueZ 是 Linux 上的官方蓝牙协议栈。通过 bluetoothctl,用户可以以交互式的方式管理蓝牙设备,适用于桌面和嵌入式系统。
-
在终端输入如下命令启动
bluetoothctlbluetoothctl示例输出
sh-5.1# bluetoothctl
Agent registered uetoothd...
[CHG] Controller 22:22:F1:C1:99:C0 Pairable: yes- 进入
bluetoothctl交互模式后,提示符会变为[bluetooth]#,表示可以输入命令进行管理。
- 进入
-
输入
help命令查看帮助信息[bluetooth]# help
输出示例:
Menu main:
Available commands:
-------------------
advertise Advertise Options Submenu
monitor Advertisement Monitor Options Submenu
scan Scan Options Submenu
gatt Generic Attribute Submenu
admin Admin Policy Submenu
player Media Player Submenu
endpoint Media Endpoint Submenu
transport Media Transport Submenu
list List available controllers
show [ctrl] Controller information
select <ctrl> Select default controller
devices [Paired/Bonded/Trusted/Connected] List available devices, with an optional property as the filter
system-alias <name> Set controller alias
reset-alias Reset controller alias
power <on/off> Set controller power
pairable <on/off> Set controller pairable mode
discoverable <on/off> Set controller discoverable mode
discoverable-timeout [value] Set discoverable timeout
agent <on/off/capability> Enable/disable agent with given capability
default-agent Set agent as the default one
advertise <on/off/type> Enable/disable advertising with given type
set-alias <alias> Set device alias
scan <on/off/bredr/le> Scan for devices
info [dev] Device information
pair [dev] Pair with device
cancel-pairing [dev] Cancel pairing with device
trust [dev] Trust device
untrust [dev] Untrust device
block [dev] Block device
unblock [dev] Unblock device
remove <dev> Remove device
connect <dev> Connect device
disconnect [dev] Disconnect device
menu <name> Select submenu
version Display version
quit Quit program
exit Quit program
help Display help about this program
export Print environment variables
-
输入
show命令查看当前蓝牙控制器状态[bluetooth]# show
输出示例:
Controller 54:78:C9:D8:64:1F (public)
Name: rubikpi
Alias: rubikpi
Class: 0x00000000
Powered: no
Discoverable: no
DiscoverableTimeout: 0x000000b4
Pairable: yes
UUID: Message Notification Se.. (00001133-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: A/V Remote Control (0000110e-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: OBEX Object Push (00001105-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Message Access Server (00001132-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: PnP Information (00001200-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: IrMC Sync (00001104-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Headset (00001108-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: A/V Remote Control Target (0000110c-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Generic Attribute Profile (00001801-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Phonebook Access Server (0000112f-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Device Information (0000180a-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Audio Sink (0000110b-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Generic Access Profile (00001800-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Handsfree Audio Gateway (0000111f-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Audio Source (0000110a-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: OBEX File Transfer (00001106-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Handsfree (0000111e-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
Modalias: usb:v1D6Bp0246d0541
Discovering: no
Roles: central
Roles: peripheral
Advertising Features:
ActiveInstances: 0x00 (0)
SupportedInstances: 0x05 (5)
SupportedIncludes: tx-power
SupportedIncludes: appearance
SupportedIncludes: local-name
- 打开蓝牙
[bluetooth]# power on
- 关闭蓝牙
[bluetooth]# power off
- 开始扫描设备
[bluetooth]# scan on
- 停止扫描设备
[bluetooth]# scan off
- 配对设备
在配对远程设备之前,运行蓝牙查询扫描以确保远程设备可用。
[bluetooth]# pair XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
其中
XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX为目标设备的 MAC 地址,目标设备 MAC 地址可通过scan on命令获取。
- 信任设备
信任设备后,系统会自动接受来自该设备的连接请求。
[bluetooth]# trust XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
- 连接设备
[bluetooth]# connect XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
- 断开设备
[bluetooth]# disconnect XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
- 取消配对设备
[bluetooth]# remove XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
- 列出已配对设备
[bluetooth]# devices
- 日至检查
如果遇到问题,可以查看系统日志以获取更多信息。
sudo journalctl -u bluetooth
通用属性配置文件(GATT)
GATT 是一个服务框架,它使用 ATT 来发现服务,并在对等设备上读取和写入特征值。
要执行低功耗蓝牙 GATT 服务器或客户端功能,必须首先完成以下过程中的步骤。
- 为低功耗蓝牙 GATT 功能设置设备
- 通过运行以下命令打开蓝牙测试应用程序
bluetoothctl
用户可以通过 bluetoothctl 的主菜单选项执行一些 GATT 功能,例如连接和扫描。
示例输出
sh-5.1# bluetoothctl
Agent registered uetoothd...
[CHG] Controller 22:22:F1:C1:99:C0 Pairable: yes
- 运行下面命令,启用蓝牙:
power on
- 运行以下命令转至 GATT submenu:
menu gatt
示例输出
Menu gatt:
Available commands:
-------------------
list-attributes [dev/local] List attributes
select-attribute <attribute/UUID/local> [attribute/UUID] Select attribute
attribute-info [attribute/UUID] Select attribute
read [offset] Read attribute value
write <data=xx xx ...> [offset] [type] Write attribute value
acquire-write Acquire Write file descriptor
release-write Release Write file descriptor
acquire-notify Acquire Notify file descriptor
release-notify Release Notify file descriptor
notify <on/off> Notify attribute value
clone [dev/attribute/UUID] Clone a device or attribute
register-application [UUID ...] Register profile to connect
unregister-application Unregister profile
register-service <UUID> [handle] Register application service.
unregister-service <UUID/object> Unregister application service
register-includes <UUID> [handle] Register as Included service in.
unregister-includes <Service-UUID> <Inc-UUID> Unregister Included service.
register-characteristic <UUID> <Flags=read,write,notify...> [handle] Register application characteristic
unregister-characteristic <UUID/object> Unregister application characteristic
register-descriptor <UUID> <Flags=read,write...> [handle] Register application descriptor
unregister-descriptor <UUID/object> Unregister application descriptor
back Return to main menu
version Display version
quit Quit program
exit Quit program
help Display help about this program
export Print environment variables
2. 执行低功耗蓝牙 GATT 服务器功能
您可以使用 GATT submenu 选项和 bluetoothctl 命令执行低功耗蓝牙 GATT 服务器功能。
开始之前,请按照为低功耗蓝牙 GATT 功能设置设备中的说明设置设备。
��连接到远程设备
要连接到远程设备,请从 bluetoothctl 菜单运行以下命令:
connect <bt_address>
参数
<bt_address> 是远程设备的蓝牙地址。
要获取远程设备的蓝牙地址,请运行蓝牙低功耗 GATT 扫描。
示例
要使用 <bt_address> 6D:38:AF:C6:B5:62 连接到客户端,请运行以下命令:
connect 6D:38:AF:C6:B5:62
添加主要服务
要将主服务添加到 GATT 服务器,请从 menu gatt 菜单:运行以下命令
register-service <UUID> [handle]
示例
如果服务的 UUID 为 FF01 且句柄为 30,则运行以下命令:
register-service FF01 30
示例输出
[MyDeviceB:/service0001/char0008]# register-service FF01 30
[NEW] Primary Service (Handle 0x001e)
/org/bluez/app/service0
FF01
[/org/bluez/app/service0] Primary (yes/no): yes
添加一个特征
要向服务器的服务添加特征,请从 menu gatt 菜单运行以下命令:
register-characteristic <UUID> <Flags=read,write,notify...> [handle]
参数
<Flags> 是特征的标志值。有关具体值的信息,请参阅标志值。
示例
服务的 UUID 为 FF02,标志为 read,write,notify,句柄为 31。要添加特征,请运行以下命令:
register-characteristic FF02 read,write,notify 31
示例输出
[MyDeviceB]# register-characteristic FF02 read,write,notify 31
[NEW] Characteristic (Handle 0x001f)
/org/bluez/app/service0/chrc0
FF02
<egister-characteristic FF02 read,write,notify 31[/org/bluez/app/service0/chrc0] Enter value: 20
添加描述符号
要将描述符添加到服务器中的特征,请从 menu gatt 菜单运行以下命令:
register-descriptor <UUID> <Flags=read,write...> [handle]
参数
<Flags> 是描述符的标志值。有关具体值的信息,请参阅标志值。
示例
服务的 UUID 为 FF03,标志为 read,write,句柄为 33。要添加描述符,请运行以下命令:
register-descriptor FF03 read,write 33
示例输出
[MyDeviceB]# register-descriptor FF03 read,write 33
[NEW] Descriptor (Handle 0x0021)
/org/bluez/app/service0/chrc0/desc0
FF03
<egister-descriptor FF03 read,write 33[/org/bluez/app/service0/chrc0/desc0] Enter value: 21
添加包含的服务
开始之前,将所需服务添加为主要服务。
要将包含的服务添加到其他服务,请从 menu gatt 菜单运行以下命令:
register-includes <UUID> <UUID>
示例
考虑两个主要服务,其 UUID 分别为 FF01 和 1112。要将服务 1112 添加为服务 FF01 中包含的服务,请运行以下命令:
示例输出
[MyDeviceB]# register-includes FF01 1112
[NEW] Primary Service (Handle 0x001e)
/org/bluez/app/service0
FF01
[NEW] Primary Included Service (Handle 0x0000)
/org/bluez/app/service1
1112
Unknown
注册申请
要发布可用或�添加到服务器的服务,请从 menu gatt 菜单运行以下命令:
register-application [UUID]
示例
该服务的 UUID 是 FF01。要发布可用或添加到服务器的服务,请运行以下命令:
register-application FF01
示例输出
[MyDeviceB]# register-application FF01
[CHG] Secondary Service (Handle 0x0015)
/org/bluez/app/service2
1112
Unknown
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 0000110e-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 00001200-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 0000111f-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 0000110b-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 00001108-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 0000110c-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 00001800-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 0000110a-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 00001801-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 0000180a-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 0000111e-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 00001112-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Primary Service (Handle 0x0016)
/org/bluez/app/service1
FF01
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 0000110e-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 00001200-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 0000111f-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 0000110b-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 00001108-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 0000110c-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 00001800-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 0000110a-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 00001801-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 0000180a-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 0000ff01-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 0000111e-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 00001112-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
Application registered
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 0000110e-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 00001200-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 0000111f-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 0000110b-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 00001108-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 0000110c-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 00001800-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 0000110a-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 00001801-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 0000180a-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 0000ff01-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E UUIDs: 0000111e-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
开始广播
要启动 GATT 广播,请从 bluetoothctl 菜单运行以下命令:
advertise on
��示例输出
[MyDeviceB]# advertise on
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E SupportedInstances: 0x0f (15)
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E ActiveInstances: 0x01 (1)
Advertising object registered
Tx Power: off
Name: off
Appearance: off
Discoverable: on
断开对端设备的连接
要断开远程设备的连接,请从 bluetoothctl 菜单运行以下命令:
disconnect <bt_address>
参数
<bt_address> 是远程设备的蓝牙地址。
示例
要断开客户端与 <bt_address> 6D:38:AF:C6:B5:62 的连接,请运行以下命令:
disconnect 6D:38:AF:C6:B5:62
标志值
<Flags> 的值可以为:
| broadcast | authenticated-signed-writes | encrypt-authenticated-read | encrypt-authenticated-notify |
| read | extended-properties | encrypt-authenticated-write | secure-notify |
| write | reliable-write | secure-read | encrypt-indicate |
| write-without-response | writable-auxiliaries | secure-write | encrypt-authenticated-indicate |
| notify | encrypt-read | authorize | secure-indicate |
| indicate | encrypt-write | encrypt-notify |
- 执行低功耗蓝牙 GATT 客户端功能
您可以使用 GATT submenu 选项和 bluetoothctl 命令执行低功耗蓝牙 GATT 客户端功能。
连接到远程设备
要连接到远程设备,请从 bluetoothctl 菜单运行以下命令:
connect <bt_address>
参数
<bt_address> 是远程设备的蓝牙地址。
要获取远程设备的蓝牙地址,请运行蓝牙低功耗 GATT 扫描 。
示例
要使用 <bt_address> 6D:38:AF:C6:B5:62 连接到服务器设备,请运行以下命令:
connect 6D:38:AF:C6:B5:62
示例输出
[bluetooth]# connect 6D:38:AF:C6:B5:62
Attempting to connect to 6D:38:AF:C6:B5:62
[CHG] Device 6D:38:AF:C6:B5:62 Connected: yes
Connection successful
[NEW] Primary Service (Handle 0x0000)
/org/bluez/hci0/dev_6D_38_AF_C6_B5_62/service0001
00001801-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
Generic Attribute Profile
[NEW] Characteristic (Handle 0x0000)
/org/bluez/hci0/dev_6D_38_AF_C6_B5_62/service0001/char0002
00002a05-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
Service Changed
[NEW] Characteristic (Handle 0x0000)
/org/bluez/hci0/dev_6D_38_AF_C6_B5_62/service0001/char0004
00002b3a-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
Server Supported Features
[NEW] Characteristic (Handle 0x0000)
/org/bluez/hci0/dev_6D_38_AF_C6_B5_62/service0001/char0006
00002b29-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
Client Supported Features
[NEW] Characteristic (Handle 0x0000)
/org/bluez/hci0/dev_6D_38_AF_C6_B5_62/service0001/char0008
00002b2a-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
Database Hash
[CHG] Device 6D:38:AF:C6:B5:62 UUIDs: 00001800-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Device 6D:38:AF:C6:B5:62 UUIDs: 00001801-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Device 6D:38:AF:C6:B5:62 ServicesResolved: yes
启动低功耗蓝牙 GATT 扫描
请从 bluetoothctl 菜单中运行以下命令,以便启动低功耗蓝牙 GATT 扫描:
scan le
要获取扫描结果,远程设备必须使用任何蓝牙低功耗应用程序进行公布。
示例输出
[MyDeviceB]# scan le
Discovery started
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E Discovering: yes
[CHG] Device F8:7D:76:9D:9B:6B RSSI: -70
[NEW] Device A4:30:7A:EE:AF:EF [TV] MyDeviceA (43)
[NEW] Device 52:2F:07:6F:AA:93 52-2F-07-6F-AA-93
[CHG] Device A4:30:7A:EE:AF:EF ManufacturerData Key: 0x0075
[CHG] Device A4:30:7A:EE:AF:EF ManufacturerData Value:
42 04 01 01 e7 a4 30 7a ee af ef a6 30 7a ee af B..... 0z....0z....
ee 01 3b 00 00 00 00 00 ......
[CHG] Device A4:30:7A:EE:AF:EF Modalias: bluetooth:v04E8p8080d0000
[CHG] Device A4:30:7A:EE:AF:EF UUIDs: 0000110a-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Device A4:30:7A:EE:AF:EF UUIDs: 0000110b-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Device A4:30:7A:EE:AF:EF UUIDs: 0000110c-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Device A4:30:7A:EE:AF:EF UUIDs: 0000110e-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Device A4:30:7A:EE:AF:EF UUIDs: 00001112-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Device A4:30:7A:EE:AF:EF UUIDs: 0000111f-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Device A4:30:7A:EE:AF:EF UUIDs: 00001200-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Device A4:30:7A:EE:AF:EF ManufacturerData Key: 0x0075
[CHG] Device A4:30:7A:EE:AF:EF ManufacturerData Value:
42 04 01 01 e7 a4 30 7a ee af ef a6 30 7a ee af B..... 0z....0z....
ee 01 3b 00 00 00 00 00 ......
[CHG] Device A4:30:7A:EE:AF:EF ManufacturerData Key: 0xff19
[CHG] Device A4:30:7A:EE:AF:EF ManufacturerData Value:
00 75 00 09 01 00 00 00 06 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 .u..................
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ................
[CHG] Device F8:7D:76:9D:9B:6B RSSI: -60
[CHG] Device A4:30:7A:EE:AF:EF ManufacturerData Key: 0x0075
[CHG] Device A4:30:7A:EE:AF:EF ManufacturerData Value:
42 04 01 20 e7 20 0d 00 02 01 2b 01 01 00 01 00 B .. ..... .......
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ........
[CHG] Device A4:30:7A:EE:AF:EF ManufacturerData Key: 0xff19
[CHG] Device A4:30:7A:EE:AF:EF ManufacturerData Value:
00 75 00 09 01 00 00 00 06 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 .u.............
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 .......
[NEW] Device 4A:04:87:DF:CB:35 4A-04-87-DF-CB-35
[DEL] Device 52:2F:07:6F:AA:93 52-2F-07-6F-AA-93
停止蓝牙低功耗 GATT 扫描
请从 bluetoothctl 菜单中运行以下命令,以便停止蓝牙低功耗 GATT 扫描:
scan off
示例输出
[MyDeviceB]# scan off
Discovery stopped
[CHG] Device A4:30:7A:EE:AF:EF RSSI is nil
[CHG] Device F8:7D:76:9D:9B:6B RSSI is nil
[CHG] Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E Discovering: no
获取属性列表
要获取远程设备的属性列表,请从 menu gatt 菜单运行以下命令:
list-attributes <bt_address>
参数
<bt_address> 是远程设备的地址。
示例
要列出地址为 6D:38:AF:C6:B5:62 的远程设备的属性,请运行以下命令:
list-attributes 6D:38:AF:C6:B5:62
示例输出
[MyDeviceB]# list-attributes 6D:38:AF:C6:B5:62
Primary Service (Handle 0x0000)
/org/bluez/hci0/dev_6D_38_AF_C6_B5_62/service0001
00001801-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
Generic Attribute Profile
Characteristic (Handle 0x0000)
/org/bluez/hci0/dev_6D_38_AF_C6_B5_62/service0001/char0002
00002a05-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
Service Changed
Characteristic (Handle 0x0000)
/org/bluez/hci0/dev_6D_38_AF_C6_B5_62/service0001/char0004
00002b3a-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
Server Supported Features
Characteristic (Handle 0x0000)
/org/bluez/hci0/dev_6D_38_AF_C6_B5_62/service0001/char0006
00002b29-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
Client Supported Features
Characteristic (Handle 0x0000)
/org/bluez/hci0/dev_6D_38_AF_C6_B5_62/service0001/char0008
00002b2a-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
Database Hash
获取属性信息
要获取属性的信息,请从 menu gatt 菜单运行以下命令:
attribute-info <attribute/UUID>
参数
<attribute/UUID> UUID 或属性路径。
示例
要获取 UUID 00002b29-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb 的属性信息,请运行以下命令:
attribute-info 00002b29-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
示例输出
[MyDeviceB]# attribute-info 00002b29-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
Characteristic - Client Supported Features
UUID: 00002b29-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
Service: /org/bluez/hci0/dev_73_F4_3F_FA_0A_DF/service0001
Flags: read
Flags: write
MTU: 0x0205
选择一个属性
要使用 UUID 或路径选择属性,请从 menu gatt 菜单运行�以下命令:
select-attribute <attribute/UUID>
参数
<attribute/UUID> UUID 或属性路径。
示例
- 要使用 UUID
00006677-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb选择属性,请运行以下命令:
select-attribute 00006677-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
示例输出
Characteristic User Description
[MyDeviceB]# select-attribute 00006677-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
<lect-attribute 00006677-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb[MyDeviceB:/service0028/char0029/desc002c]#
[MyDeviceB:/service0028/char0029/desc002c]#
要使用属性路径 /org/bluez/hci0/dev_6C_5F_B9_ED_5B_48/service0001/char0002 选择属性,请运行以下命令:
select-attribute /org/bluez/hci0/dev_6C_5F_B9_ED_5B_48/service0001/char0002
示例输出
[MyDeviceB:/service0001/char0004]# ED_5B_48/service0001/char0002
[MyDeviceB:/service0001/char0002]#
读取特征值
要读取特征值,请从 menu gatt 菜单执行以下操作:
- 选择所需的属性。
- 通过运行以下命令读取所选属性:
read 0
示例输出
[MyDeviceB:/service0028/char0029]# read 0
Attempting to read /org/bluez/hci0/dev_64_8C_C7_03_C4_B0/service0028/char0029
[CHG] Attribute /org/bluez/hci0/dev_64_8C_C7_03_C4_B0/service0028/char0029 Value:
11
11
[MyDeviceB:/service0028/char0029]#
写入特征值
要写入特征值,请从 menu gatt 菜单执行以下操作:
- 选择所需的属性。
- 通过运行以下命令将值写入所选属性:
write "<value>"
参数
value 为待写入值。
示例
要将属性值写入 0x11,请运行以下命令:
write "0x11"
示例输出
[MyDeviceB:/service0028/char0029]# read 0b
Attempting to read /org/bluez/hci0/dev_64_8C_C7_03_C4_B0/service0028/char0029
[CHG] Attribute /org/bluez/hci0/dev_64_8C_C7_03_C4_B0/service0028/char0029 Value:
22
22
[MyDeviceB:/service0028/char0029]# write "0x11"
Attempting to write /org/bluez/hci0/dev_64_8C_C7_03_C4_B0/service0028/char0029
[MyDeviceB:/service0028/char0029]# read 0
Attempting to read /org/bluez/hci0/dev_64_8C_C7_03_C4_B0/service0028/char0029
[CHG] Attribute /org/bluez/hci0/dev_64_8C_C7_03_C4_B0/service0028/char0029 Value:
11
11
[MyDeviceB:/service0028/char0029]#
读取描述符值
要读取描述符值,请从 menu gatt 菜单执行以下操作:
- 选择所需的属性。
- 通过运行以下命令读取所选属性:
read 0
示例输出
[MyDeviceB]# select-attribute 00006677-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
<lect-attribute 00006677-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb[MyDeviceB:/service0028/char0029/desc002c]#
[MyDeviceB:/service0028/char0029/desc002c]#
[MyDeviceB:/service0028/char0029/desc002c]# read 0
Attempting to read /org/bluez/hci0/dev_55_B1_D2_67_7C_CD/service0028/char0029/desc002c
[CHG] Attribute /org/bluez/hci0/dev_55_B1_D2_67_7C_CD/service0028/char0029/desc002c Value:
00
00
[MyDeviceB:/service0028/char0029/desc002c]# write "0x11"
Attempting to write /org/bluez/hci0/dev_55_B1_D2_67_7C_CD/service0028/char0029/desc002c
[MyDeviceB:/service0028/char0829/desc002c]# read 0
Attempting to read /org/bluez/hci0/dev_55_B1_D2_67_7C_CD/service0028/char0029/desc002c
[CHG] Attribute /org/bluez/hci0/dev_55_B1_D2_67_7C_CD/service0028/char0029/desc002c Value:
11
11
[MyDeviceB:/service0028/char0029/desc002c]#
写入描述符值
要写入描述符值,请从 menu gatt 菜单执行以下操作:
- 选择所需的属性。
- 通过运行以下命令将值写入所选属性:
write "<value>"
参数
value 为待写入值。
示例
要将属性值写入 0x11,请运行以下命令:
write "0x11"
示例输出
[MyDeviceB]# select-attribute 00006677-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
<lect-attribute 00006677-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb[MyDeviceB:/service0028/char0029/desc002c]#
[MyDeviceB:/service0028/char0029/desc002c]#
[MyDeviceB:/service0028/char0029/desc002c]# read 0
Attempting to read /org/bluez/hci0/dev_55_B1_D2_67_7C_CD/service0028/char0029/desc002c
[CHG] Attribute /org/bluez/hci0/dev_55_B1_D2_67_7C_CD/service0028/char0029/desc002c Value:
00
00
[MyDeviceB:/service0028/char0029/desc002c]# write "0x11"
Attempting to write /org/bluez/hci0/dev_55_B1_D2_67_7C_CD/service0028/char0029/desc002c
[MyDeviceB:/service0028/char0829/desc002c]# read 0
Attempting to read /org/bluez/hci0/dev_55_B1_D2_67_7C_CD/service0028/char0029/desc002c
[CHG] Attribute /org/bluez/hci0/dev_55_B1_D2_67_7C_CD/service0028/char0029/desc002c Value:
11
11
[MyDeviceB:/service0028/char0029/desc002c]#
读取加密的特征值
要读取加密的特征值,请从 menu gatt 菜单执行以下操作:
- 选择所需的属性。
- 通过运行以下命令读取所选属性:
read 0
- 当提示确认读数时,输入 yes。
示例输出
[MyDeviceB:/service0028/char0029]# read 0
Attempting to read /org/bluez/hci0/dev_4F_A4_EC_0D_D2_F2/service0028/char0029
[DEL] Device 60:A3:37:5A:35:5F 60-A3-37-5A-35-5F
[NEW] Device 60:A3:37:5A:35:5F 60-A3-37-5A-35-5F
Request confirmation
[agent] Confirm passkey 161326 (yes/no): yes
[CHG] Attribute /org/bluez/hci0/dev_4F_A4_EC_0D_D2_F2/service0028/char0029 Value:
00
[CHG] Device D4:8A:39:78:27:41 Address: D4:8A:39:78:27:41
[CHG] Device D4:8A:39:78:27:41 AddressType: public
00
[CHG] Device D4:8A:39:78:27:41 Bonded: yes
[CHG] Device D4:8A:39:78:27:41 Paired: yes
[CHG] Device D4:8A:39:78:27:41 Class: 0x005a020c
[CHG] Device D4:8A:39:78:27:41 Icon: phone
写入加密的特征值
- 选择所需的属性。
- 通过运行以下命令将值写入所选属性:
write "<value>"
参数
value 为待写入值。
示例
要将属性值写入 0x11,请运行以下命令:
write "0x11"
- 当提示确认写入时,输入 yes。
打开属性通知
要打开某个属性的通知,请从 menu gatt 菜单执行以下操作:
- 选择所需的属性。
- 通过运行以下命令启用属性通知:
notify on
如果属性发生任何更改,所有用户均会收到通知。
示例输出
[MyDeviceB:/service0028/char0029]# notify on
[CHG] Attribute /org/bluez/hci0/dev_44_38_FB_67_B2_E2/service0028/char0029 Notifying: yes
Notify started
[CHG] Attribute /org/bluez/hci0/dev_44_38_FB_67_B2_E2/service0028/char0029 Value:
55 U
[CHG] Attribute /org/bluez/hci0/dev_44_38_FB_67_B2_E2/service0028/char0029 Value:
88 .
[CHG] Attribute /org/bluez/hci0/dev_44_38_FB_67_B2_E2/service0028/char0029 Value:
55 55 UU
[CHG] Device D4:8A:39:78:27:41 RSSI: -74
[CHG] Attribute /org/bluez/hci0/dev_44_38_FB_67_B2_E2/service0028/char0029 Value:
55 U
[CHG] Attribute /org/bluez/hci0/dev_44_38_FB_67_B2_E2/service0028/char0029 Value:
11 U
[CHG] Attribute /org/bluez/hci0/dev_44_38_FB_67_B2_E2/service0028/char0029 Value:
66 f
关闭属性通知
要关闭某个属性的通知,请从 menu gatt 菜单执行以下操作:
- 选择所需的属性。
- 通过运行以下命令禁用该属性的通知:
notify off
示例输出
[MyDeviceB:/service0028/char0029]# notify off
[CHG] Attribute /org/bluez/hci0/dev_44_38_FB_67_B2_E2/service0028/char0029 Notifying: no
Notify stopped
基于 GATT 配置文件的 Human Interface Device
HOGP(HID over GATT)是由 Bluetooth SIG 维护的蓝牙配置文件规范,通过低功耗蓝牙实现 HID 的配置文件并作为与计算器之间的接口,消除 HID 中对电线或物理连接的需求。
HOGP 定义低功耗蓝牙无线通信设备如何使用 GATT 通过低功耗蓝牙协议栈支持 HID 服务。
-
设置 HOGP 功能的设备
-
前提条件
- 将 DUT 和远程设备放置在蓝牙附近。
-
步骤
- 在终端通过运行以下命令打开蓝牙测试应用程序:
bluetoothctl用户可以通过 bluetoothctl 的主菜单选项执行一些 GATT 功能,例如连接和扫描。
示例输出
sh-5.1# bluetoothctl
Agent registered uetoothd...
[CHG] Controller 22:22:F1:C1:99:C0 Pairable: yes- 运行以下命令,启用蓝牙:
power on -
示例输出
[bluetooth]# power on
[CHG] Controller 22:22:F1:C1:99:C0 Class: 0x007c0000
Changing power on succeeded
[CHG] Controller 22:22:F1:C1:99:C0 Powered: yes
关于 HOGP 功能,请参阅执行蓝牙 HOGP 功能。
- 执行蓝牙 HOGP 功能
可以使用 bluetoothctl 选项和 evtest 工具执行 HOGP 功能。
连接远程设备
要连接远程设备,请从 bluetoothctl 菜单运行以下命令:
connect <bt_address>
参数
<bt_address> 是远程设备的蓝牙地址。
示例
要使用 <bt_address> 30:73:00:41:22:49 连接到已配对的远程设备,请运行以下命令:
connect 30:73:00:41:22:49
示例输出
[bluetooth]# connect 30:73:00:41:22:49
Attempting to connect to 30:73:00:41:22:49
[CHG] Device 30:73:00:41:22:49 Connected: yes
[CHG] Device 30:73:00:41:22:49 Modalias: usb:v04E8p7021d0001
[CHG] Device 30:73:00:41:22:49 UUIDs: 00001000-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Device 30:73:00:41:22:49 UUIDs: 00001124-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Device 30:73:00:41:22:49 UUIDs: 00001200-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Device 30:73:00:41:22:49 ServicesResolved: yes
[CHG] Device 30:73:00:41:22:49 WakeAllowed: yes
Connection successful
验证 HOGP 功能
evtest 工具是一个用于验证 HOGP 功能的开源工具。它监视和查询输入设备(例如鼠标或键盘)的设备事件。
evtest 工具在用户编译时不可用。要验证 HOGP 功能,请从开源编译该工具并将其推送到 DUT(被测设备)。
示例:
要验证蓝牙无线鼠标的功能,请执行以下操作:
-
打开蓝牙无线鼠标。
-
在蓝牙无线鼠标的 DUT 上运行低能耗扫描 。
-
将 DUT 连接至蓝牙无线鼠标。
-
在 SSH 中运行 evtest 工具。
-
从屏幕上显示的已连接输入设备列表中选择蓝牙无线鼠标。
-
使用鼠标执行不同的操作,例如单击、滚动、拖动和移动。
-
验证屏幕上打印的每个操作的事件。
断开对端设备的连接
要断开远程设备的连接,请从 bluetoothctl 菜单运行以下命令:
disconnect <bt_address>
参数
<bt_address> 是远程设备的蓝牙地址。
示例
要断开与 <bt_address> 30:73:00:41:22:49 配对的远程设备,请运行以下命令:
disconnect 30:73:00:41:22:49
示例输出
[bluetooth]# connect 17:1A:35:8D:A2:A4
Attempting to connect to 17:1A:35:8D:A2:A4
[CHG] Device 17:1A:35:8D:A2:A4 Connected: yes
[CHG] Device 17:1A:35:8D:A2:A4 UUIDs: 0000110b-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Device 17:1A:35:8D:A2:A4 UUIDs: 0000110c-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Device 17:1A:35:8D:A2:A4 UUIDs: 0000110e-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Device 17:1A:35:8D:A2:A4 ServicesResolved: yes
[CHG] Device 17:1A:35:8D:A2:A4 Bonded: yes
[CHG] Device 17:1A:35:8D:A2:A4 Paired: yes
[NEW] Endpoint /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep1
[NEW] Endpoint /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep2
[NEW] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep1/fd0
Connection successful
[CHG] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep1/fd0 State: active
[CHG] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep1/fd0 Volume: 0x0040 (64)
[CHG] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep1/fd0 State: idle
[CHG] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep1/fd0 Volume: 0x0044 (68)
[CHG] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep1/fd0 Volume: 0x0040 (64)
[MySoundbar]#
高级音频分发配置文件
A2DP 定义了如何通过蓝牙连接将多媒体音频从一台设备传输至另一台设备。这种机制也称为蓝牙音频流。
要执行 A2DP 的发送或接收功能,必须首先完成以下过程中的步骤。
- 设置设备的 A2DP 功能
前提条件
- 将 DUT 和远程设备放置在蓝牙附近。
步骤
- 通过运行以下命令打开蓝牙测试应用程序:
bluetoothctl
示例输出
sh-5.1# bluetoothctl
Agent registered uetoothd...
[CHG] Controller 22:22:F1:C1:99:C0 Pairable: yes
- 根据需要转至 Transport submenu 或 Player submenu。
- 请从
bluetoothctl运行以下命令,以便转至 Transport submenu。
menu transport
示例输出
[bluetooth]# menu transport
Menu transport:
Available commands:
-------------------
list List available transports
show <transport> Transport information
acquire <transport> Acquire Transport
release <transport> Release Transport
send <transport> <filename> Send contents of a file
receive <transport> [filename] Get/Set file to receive
volume <transport> [value] Get/Set transport volume
back Return to main menu
version Display version
quit Quit program
exit Quit program
help Display help about this program
export Print environment variables
要在源中执行 Transport submenu 功能,请参阅执行蓝牙 A2DP 发送功能。 要在接收端中执行 Transport submenu 功能,请参阅执行蓝牙 A2DP 接收端功能。
- 请从 bluetoothctl 运行以下命令,以便转至 Player submenu。
menu player
示例输出
[bluetooth]# menu player
Menu player:
Available commands:
-------------------
list List available players
show [player] Player information
select <player> Select default player
play [item] Start playback
pause Pause playback
stop Stop playback
next Jump to next item
previous Jump to previous item
fast-forward Fast forward playback
rewind Rewind playback
equalizer <on/off> Enable/Disable equalizer
repeat <singletrack/alltrack/group/off> Set repeat mode
shuffle <alltracks/group/off> Set shuffle mode
scan <alltracks/group/off> Set scan mode
change-folder <item> Change current folder
list-items [start] [end] List items of current folder
search <string> Search items containing string
queue <item> Add item to playlist queue
show-item <item> Show item information
back Return to main menu
version Display version
quit Quit program
exit Quit program
help Display help about this program
export Print environment variables
要在接收端中执行 Player submenu 功能,请参阅执行蓝牙 A2DP 接收端功能。
-
执行蓝牙 A2DP 发送功能 用户可以使用
bluetoothctl菜单、menu transport子菜单和paplay命令执行蓝牙 A2DP 发送功能。 -
执行蓝牙 A2DP 接收端功能 用户可以使用
bluetoothctl菜单、menu transport子菜单和menu player子菜单执行蓝牙 A2DP 接收端功能。
- 执行蓝牙 A2DP 发送功能
用户可以使用 bluetoothctl 菜单、 menu transport 子菜单和 paplay 命令执行蓝牙 A2DP 发送功能。
开始之前,请设置设备并转至设置设备的 A2DP 功能中所述的所需菜单。
连接远程设备
要以 A2DP 发送端角色连接远程设备,请从 bluetoothctl 菜单运行以下命令:
connect <bt_address>
参数
<bt_address> 是远程设备的蓝牙地址。
示例
要使用 <bt_address> 17:1A:35:8D:A2:A4 连接到已配对的远程设备,请运行以下命令:
connect 17:1A:35:8D:A2:A4
示例输出
[bluetooth]# connect 17:1A:35:8D:A2:A4
Attempting to connect to 17:1A:35:8D:A2:A4
[CHG] Device 17:1A:35:8D:A2:A4 Connected: yes
[CHG] Device 17:1A:35:8D:A2:A4 UUIDs: 0000110b-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Device 17:1A:35:8D:A2:A4 UUIDs: 0000110c-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Device 17:1A:35:8D:A2:A4 UUIDs: 0000110e-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Device 17:1A:35:8D:A2:A4 ServicesResolved: yes
[CHG] Device 17:1A:35:8D:A2:A4 Bonded: yes
[CHG] Device 17:1A:35:8D:A2:A4 Paired: yes
[NEW] Endpoint /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep1
[NEW] Endpoint /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep2
[NEW] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep1/fd0
Connection successful
[CHG] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep1/fd0 State: active
[CHG] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep1/fd0 Volume: 0x0040 (64)
[CHG] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep1/fd0 State: idle
[CHG] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep1/fd0 Volume: 0x0044 (68)
[CHG] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep1/fd0 Volume: 0x0040 (64)
[MySoundbar]#
列出可用的传输
要列出可用的传输,请从 menu transport 子菜单运行以下命令:
list
示例输出
[MySoundbar]# list
Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep1/fd0
获取有关 Codec 功能的信息
要获取有关传输 codec 功能的信息,请从 menu transport 子菜单运行以下命令:
show <transport>
参数
<transport> 为传输路径。
示例
要获取有关 <transport> /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep1/fd0 codec 功能的信息,请运行以下命令:
show /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep1/fd0
示例输出
[MySoundbar]# show /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep1/fd0
Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep1/fd0
UUID: 0000110a-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
Codec: 0x00 (0)
Configuration: 0x21 (33)
Configuration: 0x15 (21)
Configuration: 0x02 (2)
Configuration: 0x35 (53)
Device: /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4
State: idle
Volume: 0x0040 (64)
设置绝对音量
确保 DUT 和远程设备支持
setabsvolume功能。
要设置传输的绝对音量,请从 menu transport 子菜单运行以下命令:
volume <transport> [value]
参数
-
<transport>为传输路径。 -
[value]是音量大小。
示例
要将 <transport> /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep1/fd0 的绝对音量设置为 50,可运行以下命令:
volume /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep1/fd0 50
示例输出
[MySoundbar]# volume /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep1/fd0 50
Changing Volume succeeded
[CHG] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep1/fd0 Volume: 0x0032 (50)
[MySoundbar]# volume /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep1/fd0 10
Changing Volume succeeded
播放音频文件
DUT 不支持音频播放器。使用
paplay命令播放音乐。仅支持 PCM 音频样本。
要播放 DUT 中的歌曲,请执行以下操作:
-
运行 SSH。
-
通过运行以下命令播放 WAV 文��件:
paplay <audio_filepath> -v
参数
<audio_filepath> 是 WAV 文件的文件路径。
示例
要播放 /tmp/pcmtest.wav 处的 WAV 文件,请运行以下命令:
paplay /tmp/pcmtest.wav -v
示例输出
sh-5.1# paplay /tmp/pcmtest.wav -v
Opening a playback stream with sample specification 's16le 2ch 44100Hz' and channel map 'front-left,front-right'.
Connection established.
Strean successfully created.
Buffer metrics: maxlength=4194304, tlength=352800, prebuf=349276, minreq=3528
Using sample spec 's16le 2ch 44100Hz', channel map 'front-left,front-right'.
Connected to device bluez_sink.20_19_D8_36_90_40.a2dp_sink (index: 4, suspended: no).
Stream started.
Time: 4.427 sec; Latency: 2042656 usec.
获取接收端列表
要在连接多个设备时获取接收端列表,请在 SSH中运行以下命令:
pactl list sinks short
示例输出
sh-5.1# pactl list sinks short
0 low-latency0 module-pal-card.c s16le 2ch 48000Hz SUSPENDED
1 deep-buffer0 module-pal-card.c s16le 2ch 48000Hz SUSPENDED
2 offload0 module-pal-card.c s16le 2ch 48000Hz SUSPENDED
3 voip-rx0 module-pal-card.c s16le 2ch 48000Hz SUSPENDED
4 bluez_sink.20_19_D8_36_90_40.a2dp_sink module-bluez5-device.c s16le 2ch 44100Hz SUSPENDED
在特定接收端上播放音频
要在连接多个设备时在特定接收端上播放音频,请在 SSH中运行以下命令:
paplay <audio_filepath> --device=<device_name> -v
参数
-
<audio_filepath>是 WAV 文件的文件路径。 -
<device_name>是接收端名称。
示例
要在 bluez_sink.20_19_D8_36_90_40.a2dp_sink 接收端上播放 pcmtest.wav,请运行以下命令:
paplay pcmtest.wav --device=bluez_sink.20_19_D8_36_90_40.a2dp_sink -v
示例输出
sh-5.1# paplay pcmtest.wav --device=bluez_sink.20_19_D8_36_90_40.a2dp_sink -v
Opening a playback stream with sample specification 's16le 2ch 44100Hz' and channel map 'front-left,front-right'.
Connection established.
Stream successfully created.
Buffer metrics: maxlength=4194304, tlength=352800, prebuf=349276, minreq=3528
Using sample spec 's16le 2ch 44100Hz', channel map 'front-left,front-right'.
Connected to device bluez_sink.20_19_D8_36_90_40.a2dp_sink (index: 4, suspended: no).
Stream started.
Time: 2.925 sec; Latency: 2062081 usec.
断开对端设备的连接
要断开远程设备的连接,请从 bluetoothctl 菜单运行以下命令:
disconnect <bt_address>
参数
<bt_address> 是远程设备的蓝牙地址。
示例
要断开与 <bt_address> 17:1A:35:8D:A2:A4 配对的远程设备,请运行以下命令:
disconnect 17:1A:35:8D:A2:A4
示例输出
[MySoundbar]# disconnect 17:1A:35:8D:A2:A4
Attempting to disconnect from 17:1A:35:8D:A2:A4
[DEL] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep1/fd2
[DEL] Endpoint /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep1
[DEL] Endpoint /org/bluez/hci0/dev_17_1A_35_8D_A2_A4/sep2
[CHG] Device 17:1A:35:8D:A2:A4 ServicesResolved: no
Successful disconnected
[CHG] Device 17:1A:35:8D:A2:A4 Connected: no
- 执行蓝牙 A2DP 接收端功能
用户可以使用 bluetoothctl 菜单、 menu transport 子菜单和 menu player 子菜单执行蓝牙 A2DP 接收端功能。
开始之前,请设置设备并转至设置设备的 A2DP 功能中所述的所需菜单。
连接远程设备
要连接远程设备,请从 bluetoothctl 菜��单运行以下命令:
connect <bt_address>
参数
<bt_address> 是远程设备的蓝牙地址。
示例
要使用 <bt_address> D4:8A:39:78:27:41 连接到已配对的远程设备,请运行以下命令:
connect D4:8A:39:78:27:41
示例输出
[bluetooth]# connect D4:8A:39:78:27:41
Attempting to connect to D4:8A:39:78:27:41
[CHG] Device D4:8A:39:78:27:41 Connected: yes
[NEW] Endpoint /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep1
[NEW] Endpoint /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep2
[NEW] Endpoint /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep3
[NEW] Endpoint /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep4
[NEW] Endpoint /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep5
[NEW] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep1/fd2
Connection successful
[NEW] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 [default]
[CHG] Device D4:8A:39:78:27:41 ServicesResolved: yes
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 Repeat: off
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 Shuffle: off
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 Status: stopped
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 Title: Not Provided
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 TrackNumber: 0x00000001 (1)
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 NumberOfTracks: 0x00000001 (1)
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 Duration: 0x00000000 (0)
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 Album:
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 Artist:
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 Genre:
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 Position: 0x00000000 (0)
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 Position: 0x00000000 (0)
[CHG] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep1/fd2 Volume: 0x004d (77)
[CHG] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep1/fd2 State: pending
[CHG] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep1/fd2 State: active
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 Status: playing
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 Position: 0x00000000 (0)
[CHG] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep1/fd2 State: idle
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 Position: 0x00000000 (0)
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 Status: stopped
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 Position: 0x00000000 (0)
[MyDeviceB]#
列出可用的传输
要列出可用的传输,请从 menu transport 子菜单运行以下命令:
list
示例输出
[MyDeviceB]# list
Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep1/fd2
获取有关 codec 功能的信息
要获取有关传输 codec 功能的信息,请从 menu transport 子菜单运行以下命令:
show <transport>
参数
<transport> 为传输路径。
示例
要获取有关 <transport> /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep1/fd2 codec 功能的信息,请运行以下命令:
show /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep1/fd2
示例输出
[MyDeviceB]# show /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep1/fd2
Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep1/fd2
UUID: 0000110b-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
Codec: 0x00 (0)
Configuration: 0x21 (33)
Configuration: 0x15 (21)
Configuration: 0x02 (2)
Configuration: 0x35 (53)
Device: /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41
State: active
Volume: 0x007f (127)
设置绝对音量
确保 DUT 和远程设备支持
setabsvolume功能。
要设置传输的绝对音量,请从 menu transport 子菜单运行以下命令:
volume <transport> [value]
参数
-
<transport>为传输路径。 -
[value]是音量大小。
示例
要将 <transport> /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep1/fd2 的绝对音量设置为 0,可运行以下命令:
volume /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep1/fd2 0
示例输出
<me /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep1/fd2 0
Changing Volume succeeded
[CHG] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep1/fd2 Volume: 0x0000 (0)
<me /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep1/fd2 100
Changing Volume succeeded
[CHG] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep1/fd2 Volume: 0x0064 (100)
< /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep1/fd2 50
Changing Volume succeeded
播放音频文件
要播放音频文件,请从 menu player 子菜单运行以下命令:
play [item]
示例输出
[MyDeviceB]# play
Attempting to play
Play successful
[CHG] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep1/fd2 State: pending
[CHG] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep1/fd2 State: active
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 Position: 0x000cc8b9 (837817)
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 Status: playing
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 Position: 0x000cc932 (837938)
[MyDeviceB]#
暂停播放
请从 menu player 子菜单运行以下命令,以便暂停播放:
pause
示例输出
[MyDeviceB]# pause
Attempting to pause
Pause successful
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 Position: 0x000cc888 (837768)
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 Status: paused
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 Position: 0x000cc888 (837768)
[CHG] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep1/fd2 State: idle
[MyDeviceB]#
停止播放
请从 menu player 子菜单中运行以下命令,以便停止播放:
stop
示例输出
[MyDeviceB]# stop
Attempting to stop
Stop successful
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 Position: 0x00000000 (0)
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 Status: stopped
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 Position: 0x00000000 (0)
[CHG] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep1/fd2 State: idle
播放下一个音频文件
要播放下一个音频文件,请从 menu player 子菜单运行以下命令:
next
示例输出
[MyDeviceB]# next
Attempting to jump to next
Next successful
播放上一个音频文件
要播放上一个音频文件,请从 menu player 子菜单运行以下命令:
previous
示例输出
[MyDeviceB]# previous
Attempting to jump to previous
Previous successful
快进播放
要快进播放,请从 menu player 子菜单运行以下命令:
fast-forward
示例输出
[MyDeviceB]# fast-forward
Fast forward playback
FastForward successful
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 Status: forward-seek
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 Position: 0x00000000 (0)
断开对端设备的连接
要断开远程设备的连接,请从 bluetoothctl 菜单运行以下命令:
disconnect <bt_address>
参数
<bt_address> 是远程设备的蓝牙地址。
示例
要断开与 <bt_address> D4:8A:39:78:27:41 配对的远程设备,请运行以下命令:
disconnect D4:8A:39:78:27:41
示例输出
[MyDeviceB]# disconnect D4:8A:39:78:27:41
Attempting to disconnect from D4:8A:39:78:27:41
[DEL] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/player0 [default]
[DEL] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep1/fd1
[DEL] Endpoint /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep1
[DEL] Endpoint /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep2
[DEL] Endpoint /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep3
[DEL] Endpoint /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep4
[DEL] Endpoint /org/bluez/hci0/dev_D4_8A_39_78_27_41/sep5
[CHG] Device D4:8A:39:78:27:41 ServicesResolved: no
Successful disconnected
[CHG] Device D4:8A:39:78:27:41 Connected: no
其他播放器功能
menu player 子菜单提供其他功能,使用户能够:
-
随机播放曲目
-
快退音频文件
-
重复播放单个曲目、所有曲目或播放列表
-
打开或关闭均衡器
-
搜索曲目
免提配置文件
HFP 定义音频网关设备如何连接至免提设备以实现远程控制和音频连接等功能。
要执行 HFP 客户端或音频网关功能,用户必须首先完成以下过程中的步骤。
- 设置设备的 HFP 功能
前提条件
- 将 DUT 和远程设备放置在蓝牙附近。
配置 DUT 的 HFP 客户端功能
在为 HFP 功能进行初始设备设置后,请对 HFP 客户端执行以下操作:
- 通过在 SSH 中运行以下命令来验证 ofono 服务的状态:
systemctl status ofono
- 在文本编辑器中打开 /etc/pulse/ 目录中的脉冲配置文件 system.pa。
- 将 headset=ofono 添加至文件中的以下行:
Load module bluetooth discover
load-module module-bluetooth-discover headset=ofono
该文件必须如下所示:
### Load module bluetooth discover
load-module module-bluetooth-discover headset=ofono
### Load module bluetooth policy
load-module module-bluetooth-policy
sh-5.1#
- 保存该文件。
- 通过运行以下命令重新加载守护进程:
systemctl daemon-reload
- 通过运行以下命令重新启动 PulseAudio:
systemctl restart pulseaudio
- 重新加载守护程序并重新启动 PulseAudio 后,system.pa 配置文件中的更改会在系统中反映。使用 DBUS 在 PulseAudio 和 ofono 之间建立连接。
- 通过在 SSH 中运行以下命令来运行 bluetoothctl:
bluetoothctl
- 通过从 bluetoothctl 菜单运行以下命令来验证是否列出了免提客户端设备的 UUID:
show
示例输出
[bluetooth]# show
Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E (public)
Name: qcm6490
Alias: qcm6490
Class: 0x002c0000
Powered: yes
Discoverable: no
DiscoverableTimeout: 0x000000b4
Pairable: yes
UUID: A/V Remote Control (e000110e-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: PnP Information (e0001200-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Audio Source (e000110a-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Audio Sink (e000110b-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: A/V Remote Control Target (0000110c-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Generic Access Profile (e0001800-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Generic Attribute Profile (00001801-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Device Information (0000180a-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Handsfree (e000111e-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
Modalias: usb:v1D6Bp0246d0541
Discovering: no
Roles: central
Roles: peripheral
Advertising Features:
ActiveInstances: 0x00 (0)
SupportedInstances: 0x10 (16)
SupportedIncludes: tx-power
SupportedIncludes: appearance
SupportedIncludes: local-name
SupportedSecondaryChannels: 1M
SupportedSecondaryChannels: 2M
SupportedSecondaryChannels: Coded
[bluetooth]#
免提音频网关和耳机 UUID 未列出。仅列出从 PulseAudio 配置的免提客户端 UUID。
- 在 SSH 中运行以下命令打开 ofono/test 菜单:
ls -rt /usr/lib/ofono/test
ofono/test 应用程序仅在 qcom-multimedia-test-image 中可用。要在用户版本上运行 ofono/test 应用程序,用户必须对其进行编译。
示例输出
sh-5.1# ls -rt /usr/lib/ofono/test
unlock-pin set-ddr hangup-call
test-stk-menu set-context-property hangup-all
test-ss-control-cs set-cbs-topics hangup-active
test-ss-control-cf set-call-forwarding get-tech-preference
test-ss-control-cb send-vcard get-serving-cell-info
test-ss send-vcal get-operators
test-sms send-ussd get-icon
test-smart-messaging send-sms enter-pin
test-serving-cell-info scan-for-operators enable-throttling
test-push-notification reset-pin enable-modem
test-phonebook remove-contexts enable-gprs
test-network-registration release-and-swap enable-cbs
test-modem release-and-answer display-icon
test-message-waiting reject-calls disable-throttling
test-gnss register-operator disable-modem
test-cbs register-auto disable-gprs
test-call-settings receive-sms disable-call-forwarding
test-call-forwarding process-context-settings dial-number
test-call-barring private-chat deactivate-context
test-advice-of-charge online-modem deactivate-all
swap-calls offline-modem create-multiparty
set-use-sms-reports monitor-ofono create-mms-context
set-umts-band lockdown-modem create-internet-context
set-tty lock-pin change-pin
set-tech-preference list-operators cdma-set-credentials
set-speaker-volume list-modems cdma-list-call
set-sms-smsc list-messages cdma-hangup
set-sms-bearer list-contexts cdma-dial-number
set-sms-alphabet list-calls cdma-connman-enable
set-roaming-allowed list-applications cdma-connman-disable
set-msisdn list-allowed-access-points cancel-ussd
set-mms-details initiate-ussd cancel-sms
set-mic-volume ims-unregister backtrace
set-lte-property ims-register answer-calls
set-gsm-band hold-and-answer activate-context
set-fast-dormancy hangup-multiparty
sh-5.1#
关于 HFP 客户端功能,请参阅执行蓝牙 HFP 客户端功能。
配置 DUT 的 HFP 音频网关功能
在为 HFP 功能进行初始设备设置后,请对 HFP 音频网关执行以下操作:
- 通过在 SSH 中运行以下命令来运行
bluetoothctl:
bluetoothctl
- 通过从
bluetoothctl菜单运行以下命令来验证是否列出了免提音频网关和耳机的 UUID:
show
示例输出
[bluetooth]# show
Controller 22:22:9B:2C:79:1E (public)
Name: qcm6490
Alias: qcm6490
Class: 0x006c0000
Powered: yes
Discoverable: no
DiscoverableTimeout: 0x000000b4
Pairable: yes
UUID: A/V Remote Control (0000110a-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: PnP Information (00001200-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Handsfree Audio Gateway (0000111f-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Audio Sink (0000110b-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Headset (00001108-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: A/V Remote Control Target (0000110c-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Generic Access Profile (00001800-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Audio Source (0000110a-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Generic Attribute Profile (00001801-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Device Information (0000180a-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Handsfree (0000111e-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
Modalias: usb:v1D6Bp0246d0541
Discovering: no
Roles: central
Roles: peripheral
Advertising Features:
ActiveInstances: 0x00 (0)
SupportedInstances: 0x10 (16)
SupportedIncludes: tx-power
SupportedIncludes: appearance
SupportedIncludes: local-name
SupportedSecondaryChannels: 1M
SupportedSecondaryChannels: 2M
SupportedSecondaryChannels: Coded
[bluetooth]# |
关于 HFP 音频网关功能,请参阅执行蓝牙 HFP 音频网关功能。
-
执行蓝牙 HFP 客户端功能 可以使用
bluetoothctl菜单和ofono/test工具执行 HFP 客户端功能。 -
执行蓝牙 HFP 音频网关功能 用户可以使用
bluetoothctl菜单和paplay命令执行 HFP 音频网关功能。
- 执行蓝牙 HFP 客户端功能
可以使用 bluetoothctl 菜单和 ofono/test 工具执行 HFP 客户端功能。
开始之前,请设置您的设备,并且配置 DUT 以实现 HFP 客户端功能。
连接远程设备
要连接远程设备,请从 bluetoothctl 菜单运行以下命令:
connect <bt_address>
参数
<bt_address> 是远程设备的蓝牙地址。
示例
要使用 <bt_address> F8:7D:76:9D:9B:6B 连接到已配对的远程设备,请运行以下命令:
connect F8:7D:76:9D:9B:6B
示例输出
[bluetooth]# connect F8:7D:76:9D:9B:6B
Attempting to connect to F8:7D:76:9D:9B:6B
(CHG) Device F8:7D:76:9D:9B:6B Connected: yes
[NEW] Endpoint /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/sep3
[NEW] Endpoint /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/sep4
[NEW] Endpoint /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/sep5
[NEW] Endpoint /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/sep6
(NEW) Endpoint /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/sep1
(NEW) Endpoint /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/sep2
[NEW] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/sep1/fd0
Connection successful
[NEW] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/player0 [default]
[NEW] Item /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/player0/Filesystem /Filesystem
[NEW) Item /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/player0/NowPlaying /NowPlaying
[CHG) Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/player0 Type: Audio
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/player0 Subtype: None
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/player0 Status: stopped
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/player0 Browsable: yes
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/player0 Searchable: yes
[CHG) Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/player0 Playlist: /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/player0/NowPlaying
(CHG) Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/player0 Name: Music
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/player0 Repeat: off
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/player0 Shuffle: off
[NEW] Folder /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/player0
[CHG] Device F8:7D:76:9D:9B:6B ServicesResolved: yes
(CHG) Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/player0 Duration: 0x00000000 (0)
(CHG) Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/player0 Genre:
[CHG] Player /org/blwez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/player0 Title:
[CHG] Player /org/blwez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/player0 Item: /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/player@/NowPlaying/item18446749073709551615
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/player0 TrackNumber: 0x00000000 (0)
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/player0 Artist:
(CHG) Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/player0 NumberOfTracks: 0x00000000 (0)
[CHG) Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/player0 Album:
[NEW] Item /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/player0/NowPlaying/item18446744073709551615 <unknown>
[CHG] Player /org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/player0 Position: 0x00000000 (0)
[MyDeviceA]#
拨打电话号码
要拨打电话号码,请从 ofono/test 菜单运行以下命令:
./dial-number <phone_number>
参数
<phone_number> 是您打算拨打的电话号码。
示例输出
sh-5.1# ./dial-number 7123456789
Using modem /hfp/org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B
/hfp/org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/voicecall01
sh-5.1#
接听来电
要接听来电,请从 ofono/test 菜单运行以下命令:
./answer-calls
示例输出
sh-5.1# ./answer-calls
[ /hfp/org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B ]
[ /hfp/org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/voicecall01 ] incoming
sh-5.1# |
如果您正在通话,则会听到回声。这是在软件中存在并具有 BlueZ 堆栈的已知行为。
列出当前通话
要列出当前通话,请从 ofono/test 菜单运行以下命令:
./list-calls
示例输出
sh-5.1# ./list-calls
[ /hfp/org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B ]
[ /hfp/org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/voicecall01 ]
State = incoming
LineIdentification = +917123456789
Name =
Multiparty = 0
RemoteHeld = 0
RemoteMultiparty = 0
Emergency = 0
拒绝或挂断电话
要拒绝或断开呼叫,请从 ofono/test 菜单运行以下命令:
./hangup-call <call_path>
参数
<call_path> 是当前呼叫的呼叫路径。
示例
要挂断路径 /hfp/org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/voicecall01 的呼叫,请运行以下命令:
./hangup-call /hfp/org/bluez/hci0/dev_F8_7D_76_9D_9B_6B/voicecall01
断开对端设备的连接
要断开远程设备的连接,请从 bluetoothctl 菜单运行以下命令:
disconnect <bt_address>
参数
<bt_address> 是远程设备的蓝牙地址。
示例
要断开与 <bt_address> F8:7D:76:9D:9B:6B 配对的远程设备,请运行以下命令:
disconnect F8:7D:76:9D:9B:6B
示例输出
[MyDeviceA]# disconnect
Attempting to disconnect from F8:7D:76:9D:9B:6B
[CHG] Device F8:7D:76:9D:9B:6B ServicesResolved: no
Successful disconnected
[CHG] Device F8:7D:76:9D:9B:6B Connected: no
[bluetooth]#
- 执行蓝牙 HFP 音频网关功能
用户可以使用 bluetoothctl 菜单和 paplay 命令执行 HFP 音频网关功能。
开始之前,请设置您的设备,并且配置 DUT 以实现 HFP 音频网关功能。
连接远程设备
要连接远程设备,请从 bluetoothctl 菜单运行以下命令:
connect <bt_address>
参数
<bt_address> 是远程设备的蓝牙地址。
示例
要使用 <bt_address> 20:19:D8:36:90:40 连接到已配对的远程设备,请运行以下命令:
connect 20:19:D8:36:90:40
示例输出
[Test]# connect 20:19:D8:36:90:40
Attempting to connect to 20:19:D8:36:90:40
[CHG] Device 20:19:D8:36:90:40 Connected: yes
[CHG] Device 20:19:D8:36:90:40 UUIDs: 00001108-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Device 20:19:D8:36:90:40 UUIDs: 0000110b-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Device 20:19:D8:36:90:40 UUIDs: 0000110c-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Device 20:19:D8:36:90:40 UUIDs: 0000110e-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Device 20:19:D8:36:90:40 UUIDs: 0000111e-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[CHG] Device 20:19:D8:36:90:40 ServicesResolved: yes
[CHG] Device 20:19:D8:36:90:40 Bonded: yes
[CHG] Device 20:19:D8:36:90:40 Paired: yes
[NEW] Endpoint /org/bluez/hci0/dev_20_19_D8_36_90_40/sep1
[NEW] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_20_19_D8_36_90_40/sep1/fd1
Connection successful
[CHG] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_20_19_D8_36_90_40/sep1/fdl State: active
[CHG] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_20_19_D8_36_90_40/sep1/fd1 Volume: 0x0068 (104)
[CHG] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_20_19_D8_36_90_40/sep1/fd1 State: idle
验证音频网关功能
要验证音频网关功能,请执行以下操作:
- 创建一个虚拟 SCO,如下所示:
- 运行 SSH。
- 通过运行以下命令播放 WAV 文件:
paplay <file.wav> -v
示例
要播放 AG_playback.wav 文件,请运行以下命令:
paplay AG_playback.wav -v
示例输出
sh-5.1# paplay AG_playback.wav -v
Opening a playback stream with sample specification 's16le 2ch 8000Hz' and channel map 'front-left,front-right'
Connection established.
Stream successfully created.
Buffer metrics: maxlength=4194304, tlength=64000, prebuf=63364, minreq=640
Using sample spec 's16le 2ch 8000Hz', channel map 'front-left,front-right'.
Connected to device bluez_sink.20_19_D8_36_90_40.handsfree_head_unit (index: 7, suspended: no).
Stream started.
Time: 2.003 sec; Latency: 2042009 usec.
- 通过运行以下命令从远程设备接收麦克风数据:
parec -v --rate=<rate> --format=<format> --channels=<channel_number> --file-format=<file_format audio_filepath> --device=<device_name>
参数
| 选项 | 参数 | 说明 | 关于 |
|---|---|---|---|
--rate | <rate> | 播放音频文件的特定采样率。 | 16000 |
--format | <format> | 播放音频文件的特定样本格式。 | s16le |
--channels | <channel_number> | 播放音频文件的具体通道数。 | 1 |
--file-format | <file_format audio_filepath> | 用于播放目录中的音频文件的文件格式。 | wav /data/rec1.wav |
--device | <device_name> | 播放音频文件的发送端或接收端的�设备名称。 | bluez_source.20_19_D8_36_90_40.handsfree_head_unit |
示例
要从远程设备接收表中列出的示例值的麦克风数据,请运行以下命令:
parec -v --rate=16000 --format=s16le --channels=1 --file-format=wav /data/rec1.wav --device=bluez_source.20_19_D8_36_90_40.handsfree_head_unit
- 播放录制的麦克风数据并验证音频是否清晰
断开对端设备的连接
要断开远程设备的连接,请从 bluetoothctl 菜单运行以下命令:
disconnect <bt_address>
参数
<bt_address> 是远程设备的蓝牙地址。
示例
要断开与 <bt_address> 20:19:D8:36:90:40 配对的远程设备,请运行以下命令:
disconnect 20:19:D8:36:90:40
示例输出
[MyHeadset]# disconnect 20:19:D8:36:90:40
Attempting to disconnect from 20:19:D8:36:90:40
[DEL] Transport /org/bluez/hci0/dev_20_19_D8_36_90_40/sep1/fd2
[DEL] Endpoint /org/bluez/hci0/dev_20_19_D8_36_90_40/sep1
[CHG] Device 20:19:D8:36:90:40 ServicesResolved: no
Successful disconnected
[CHG] Device 20:19:D8:36:90:40 Connected: no
对象推送配置文件
OPP 定义两个蓝牙设备如何交换对象,例如名片、图像、壁纸、铃声或视频。
要执行蓝牙 OPP 功能,用户必须首先完成以下过程中的步骤。
- 设置设备的��蓝牙 OPP 功能
前提条件
- 将 DUT 和远程设备放置在蓝牙附近。
通过运行以下命令打开蓝牙测试应用程序:
obexctl
要查看 OBEX 功能,请运行以下命令:
help
该命令提供 obexctl 的主菜单。要执行 OPP 服务器和客户端功能,请参阅执行蓝牙 OPP 服务器功能和执行蓝牙 OPP 客户端功能。
示例输出
sh-5.1# obexctl
[NEW] Client /org/bluez/obex
[obex]# help
Menu main:
Available commands:
-------------------
connect <dev> [uuid] [channel] Connect session
disconnect [session] Disconnect session
list List available sessions
show [session] Session information
select <session> Select default session
info <object> Object information
cancel <transfer> Cancel transfer
suspend <transfer> Suspend transfer
resume <transfer> Resume transfer
send <file> Send file
pull <file> Pull Vobject & stores in file
cd <path> Change current folder
ls <options> List current folder
cp <source file> <destination file> Copy source file to destination file
mv <source file> <destination file> Move source file to destination file
rm <file> Delete file
mkdir <folder> Create folder
version Display version
quit Quit program
exit Quit program
help Display help about this program
export Print environment variables
[obex]#
-
执行蓝牙 OPP 服务器功能 用户可以使用 obexctl 主菜单中提供的命令来验证蓝牙 OPP 服务器功能。
-
执行蓝牙 OPP 客户端功能 用户可以使用 obexctl 主菜单中提供的命令来验证蓝牙 OPP 客户端功能。
- 执行蓝牙 OPP 服务器功能
用户可以使用 obexctl 主菜单中提供的命令来验证蓝牙 OPP 服务器功能。
以服务器角色接收文件
要以服务器角色接收文件,执行以下操作:
- 配对 DUT 和远程设备。相关说明,可参见与远程蓝牙设备配对。
- 从远程设备启动到 DUT 的连接。
- 通过蓝牙共享将任何文件从远程设备发送到 DUT。 传输信息出现在 DUT 的 obexctl 屏幕中。文件将传输到 DUT 并存储在 /var/bluetooth 中。
示例输出
[NEW] Session /org/bluez/obex/server/session6
[NEW] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/server/session6/transfer5
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/server/session6/transfer5 Size: 36
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/server/session6/transfer5 Status: active
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/server/session6/transfer5 Transferred: 36 (@0KB/s 00:00)
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/server/session6/transfer5 Status: complete
[DEL] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/server/session6/transfer5
[DEL] Session /org/bluez/obex/server/session6
[22:22:75:C2:D2:72]#
- 执行蓝牙 OPP 客户端功能
用户可以使用 obexctl 主菜单中提供的命令来验证蓝牙 OPP 客户端功能。
以客户端角色发送文件
开始之前,请按照设置设备的蓝牙 OPP 功能中的说明设置设备。
以客户端角色发送文件,执行以下操作:
- 通过从 obexctl 菜单运行以下命令连接到远程设备:
connect <bt_address> <profile_name>
参数
bt_address 是远程设备的蓝牙地址。
profile_name 是 opp.
示例
要使用 <bt_address> 22:22:5A:A5:56:6B 连接到远程设备,请运行以下命令:
connect 22:22:5A:A5:56:6B opp
示例输出
[obex]# connect 22:22:5A:A5:56:6B opp
Attempting to connect to 22:22:5A:A5:56:6B
[NEW] Session /org/bluez/obex/client/session1 [default]
[NEW] ObjectPush /org/bluez/obex/client/session1
Connection successful
[22:22:5A:A5:56:6B]#
- 在 DUT 的本地目录中创建一个文本文件。
- 通过从
obexctl菜单:运行以下命令将此文本文件发送至远程设备
send <filepath>
参数
<filepath> 是文本文件的文件路径。
示例
要发送文本文件 temp.txt /local/mnt/workspace/,可运行以下命令:
send /local/mnt/workspace/temp.txt
示例输出
[22:22:5A:A5:56:6B]# send /local/mnt/workspace/temp.txt
Attempting to send /local/mnt/workspace/temp.txt to /org/bluez/obex/client/session1
[NEW] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session1/transfer1
Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session1/transfer1
Status: queued
Name: temp.txt
Size: 36
Filename: /local/mnt/workspace/temp.txt
Session: /org/bluez/obex/client/session1
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session1/transfer1 Status: complete
[DEL] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session1/transfer1
[22:22:5A:A5:56:6B]#
- 在远程设备上,接受提示以接收文件。
文件已成功发送至远程设备。
文件传输协议
FTP 定义了两个蓝牙设备之间交换文件的要求。
要执行蓝牙 FTP 功能,用户必须首先完成以下过程中的步骤。
- 设置设备的蓝牙 FTP 功能
前提条件
- 确保 DUT 和远程设备支持 BlueZ 堆栈。一台设备充当服务器,另一台设备充当客户端。
要测试或验证 FTP 服务器功能,无需测试应用程序。通过客户端连接来执行FTP功能。
-
配对 DUT 和远程设备。相关说明,可参见与远程蓝牙设备配对。
-
将 DUT 和远程设备放置在蓝牙附近。
步骤
- 通过运行以下命令打开蓝牙测试应用程序:
obexctl
要查看 OBEX 功能,请运行以下命令:
help
该命令提供 obexctl 的主菜单。
示例输出
sh-5.1# obexctl
[NEW] Client /org/bluez/obex
[obex]# help
Menu main:
Available commands:
-------------------
connect <dev> [uuid] [channel] Connect session
disconnect [session] Disconnect session
list List available sessions
show [session] Session information
select <session> Select default session
info <object> Object information
cancel <transfer> Cancel transfer
suspend <transfer> Suspend transfer
resume <transfer> Resume transfer
send <file> Send file
pull <file> Pull Vobject & stores in file
cd <path> Change current folder
ls <options> List current folder
cp <source file> <destination file> Copy source file to destination file
mv <source file> <destination file> Move source file to destination file
rm <file> Delete file
mkdir <folder> Create folder
version Display version
quit Quit program
exit Quit program
help Display help about this program
export Print environment variables
[obex]#
- 通过从
obexctl菜单运行以下命令连接到远程设备:
connect <bt_address> <profile_name>
参数
bt_address 是远程设备的蓝牙地址。
profile_name 是 ftp.
示例
要使用 <bt_address> E8:48:B8:C8:20:00 连接到远程设备,请运行以下命令:
connect E8:48:B8:C8:20:00 ftp
示例输出
[E8:48:B8:C8:20:00]# connect E8:48:B8:C8:20:00 ftp
Attempting to connect to E8:48:B8:C8:20:00
[NEW] Session /org/bluez/obex/client/session7
[NEW] FileTransfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session7
Connection successful
要执行 FTP 客户端功能,请参阅执行蓝牙 FTP 客户端功能。
- 执行蓝牙 FTP 客户端功能
用户可以使用 obexctl 主菜单中提供的命令验证蓝牙 FTP 客户端功能。
要测试或验证 FTP 服务器功能,无需测试应用程序。通过客户端连接来执行 FTP 功能。
开始之前,请按照设置设备的蓝牙 FTP 功能中的说明设置设备。
创建文件夹
要在远程设备上创建文件夹,请从 obexctl 菜单运行以下命令:
mkdir <folder_name>
用户可以验证服务器上 /var/bluetooth 目录中的文件夹创建情况。
参数
<folder_name> 是新文件夹名称。
示例
请运行以下命令,以便创建名为 new_dir 的文件夹:
mkdir new_dir
示例输出
#mkdir new_dir
Attempting to CreateFolder
CreateFolder successful
更改当前文件夹
要更改远程设备的当前文件夹,请从 obexctl 菜单运行以下命令:
cd <folder_path>
参数
<folder_path> 是您打算切换至的文件夹。
示例
要将当前文件夹更改为 new_dir,请运行以下命令:
cd new_dir
示例输出
#cd new_dir
Attempting to ChangeFolder to new_dir
ChangeFolder successful
获取当前文件夹信息
要获取有关当前文件夹的信息,请从 obexctl 菜单运行以下命令:
ls .
示例输出
# ls .
Attempting to ListFolder
[NEW] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session7/transfer4
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session7/transfer4 Size: 611
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session7/transfer4 Status: complete
Type: folder
Name: My_folder
User-perm: RWD
Group-perm: R
Other-perm:
Accessed: 20231214T123503Z
Modified: 20231214T123502Z
Created: 20231214T123502Z
Type: folder
Name: new_dir
User-perm: RWD
Group-perm: R
Other-perm:
Accessed: 20231215T093311Z
Modified: 20231215T093245Z
Created: 20231215T093245Z
将文件复制至远程设备
要将本地文件复制到远程设备,请从 obexctl 菜单运行以下命令:
cp :<source_file> <destination_file>
参数
-
<source_file>是本地文件。 -
<destination_file>是远程设备上的目标文件。
示例
要将 Documents/ftp_client.txt 处的本地文件复制到远程设备上的 ftp_client.txt,请运行以下命令:
cp :Documents/ftp_client.txt ftp_client.txt
示例输出
# cp :Documents/ftp_client.txt ftp_client.txt
Attempting to PutFile
[NEW] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session7/transfer5
Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session7/transfer5
Status: queued
Name: ftp_client.txt
Size: 10
Filename: Documents/ftp_client.txt
Session: /org/bluez/obex/client/session7
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session7/transfer5 Status: complete
[DEL] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session7/transfer5
从远程设备复制文件
开始之前,将当前文件夹更改为所需文件的文件夹。
要将文件从远程设备复制到本地目录,请从 obexctl 菜单运行以下命令:
cp <destination_file> :<source_file>
参数
-
<source_file>是远程设备上的文件。 -
<destination_file>是本地设备上的目标文件。
示例
��要将 ftp_client_2.txt 文件从远程设备复制到本地设备,请运行以下命令:
cp ftp_client_2.txt :ftp_client_2.txt
示例输出
# cp ftp_client_2.txt :ftp_client_2.txt
Attempting to GetFile
[NEW] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session7/transfer21
Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session7/transfer21
Status: queued
Name: ftp_client_2.txt
Size: 0
Filename: ftp_client_2.txt
Session: /org/bluez/obex/client/session7
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session7/transfer21 Size: 13
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session7/transfer21 Status: complete
[DEL] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session7/transfer21
在远程设备中复制文件
要将文件从远程设备上的一个目录复制到另一个目录,请从 obexctl 菜单运行以下命令:
cp <source_file> <destination_file>
参数
-
<source_file>是待复制的文件。 -
<destination_file>为目标位置。
示例
要将 ftp_client.txt 复制到 /new_dir_2/,请运行以下命令:
cp ftp_client.txt ../new_dir_2/ftp_client.txt
示例输出
# cp ftp_client.txt ../new_dir_2/ftp_client.txt
Attempting to CopyFile
CopyFile successful
移动文件
要将文件从一个文件夹移动到另一个文件夹,请从 obexctl 菜单运行以下命令:
mv <source_file> <destination_file>
参数
-
<source_file>是待移动的文件。 -
<destination_file>为目标位置。
示例
要将 ftp_client_2.txt 文件移动到 /new_dir_2/,请运行以下命令:
mv ftp_client_2.txt ../new_dir_2/ftp_client_2.txt
示例输出
#mv ftp_client_2.txt ../new_dir_2/ftp_client_2.txt
Attempting to MoveFile
MoveFile successful
删除文件
要删除文件,请从 obexctl 菜单运行以下命令:
rm <filename>
参数
<filename> 是待删除的文件。
示例
要删除 ftp_client.txt 文件,请运行以下命令:
rm ftp_client.txt
示例输出
# rm ftp_client.txt
Attempting to Delete
Delete successful
电话薄访问配置文件
PBAP 是一种蓝牙配置文件,支持在远程设备和本地设备之间交换电话簿对象。
要执行蓝牙 PBAP 功能,用户必须首先完成以下过程中的步骤。
- 设置设备的蓝牙 PBAP 功能
前提条件
-
配对 DUT 和远程设备。相关说明,可参见与远程蓝牙设备配对。
-
将 DUT 和远程设备放置在蓝牙附近。
通过运行以下命令打开蓝牙测试应用程序:
obexctl
要查看 OBEX 功能,请运行以下命令:
help
该命令提供 obexctl 的主菜单。要执行 PBAP 服务器和客户端功能,请参阅执行蓝牙 PBAP 服务器功能和执行蓝牙 PBAP 客户端功能。
示例输出
sh-5.1# obexctl
[NEW] Client /org/bluez/obex
[obex]# help
Menu main:
Available commands:
-------------------
connect <dev> [uuid] [channel] Connect session
disconnect [session] Disconnect session
list List available sessions
show [session] Session information
select <session> Select default session
info <object> Object information
cancel <transfer> Cancel transfer
suspend <transfer> Suspend transfer
resume <transfer> Resume transfer
send <file> Send file
pull <file> Pull Vobject & stores in file
cd <path> Change current folder
ls <options> List current folder
cp <source file> <destination file> Copy source file to destination file
mv <source file> <destination file> Move source file to destination file
rm <file> Delete file
mkdir <folder> Create folder
version Display version
quit Quit program
exit Quit program
help Display help about this program
export Print environment variables
[obex]#
执行蓝牙 PBAP 服务器功能 用户可以使用 obexctl 主菜单中提供的命令验证蓝牙 PBAP 服务器功能。
执行蓝牙 PBAP 客户端功能 用户可以使用 obexctl 主菜单中提供的命令验证蓝牙 PBAP 客户端功能。
- 执行蓝牙 PBAP 服务功能
用户可以使用 obexctl 主菜单中提供的命令验证蓝牙 PBAP 服务器功能。
从服务器拉取联系人
在开始之前,请执行以下操作:
-
配对 DUT 和远程设备。相关说明,可参见与远程蓝牙设备配对。
-
在服务器上创建 PBAP 目录。
在 BlueZ 堆栈中,无法直接测试或验证 PBAP 服务器功能,因为您无法在服务器上创建联系人。因此,您必须在 DUT 上创建 PBAP 目录。关于创建 PBAP 目录的更多信息,请参阅 PBAP 目录示例。
要从服务器中提取联系人,请执行以下操作:
-
从远程设备启动到 DUT 的连接。
-
接受 DUT 上的连接请求,如下所示:
- 在 DUT 上运行 SSH。
- 通过运行以下命令打开 bluetoothctl 应用程序:
bluetoothctl- 验证连接请求。
-
将预期联系人从服务器拉取至客户端。
-
在客户端上打开并验证检索到的联系人。
PBAP 目录示例
用户可以创建示例 PBAP 目录来验证 PBAP 服务器功能,如下所示:
- 运行 SSH。
- 通过运行以下命令,在 telecom 处为每个电话簿存储库创建一个 root 文件夹:
mkdir telecom
- 通过运行以下命令将当前目录更改为 telecom:
cd telecom
- 在 telecom 目录中,为不同的电话簿对象创建子文件夹。 请运行以下命令,以便在 telecom 处创建子文件夹:
mkdir <subfolder>
参数
subfolder 是子文件夹的名称。例如, pb。
对电话簿对象使用以下文件夹名称:
| 电话簿对象 | 文件夹名称 |
|---|---|
| 主电话簿 | pb |
| 来电历史记录 | ich |
| 拨出电话历史记录 | och |
| 未接来电记录 | mch |
| 合并通话记录 | cch |
| 快速拨号联系人 | spd |
| 收藏的联系人 | fav |
- 在每个子文件夹中,创建示例 VCF 文件。
下图展示了一个 PBAP 目录示例。它包含两个电话簿存储库的 telecom 目录。在 telecom 目录中,有不同电话簿对象的子文件夹。VCF 文件包含在这些子文件夹中。
- 执行蓝牙 PBAP 客户端功能
用户可以使用 obexctl 主菜单中提供的命令验证蓝牙 PBAP 客户端功能。
开始之前,请按�照设置设备的蓝牙 PBAP 功能中的说明设置设备。
连接远程设备
要在 PBAP 中连接远程设备,请从 obexctl 菜单运行以下命令:
connect <bt_address> <profile_name>
参数
-
<bt_address>是远程设备的蓝牙地址。 -
<profile_name>是pbap.
示例
要使用 <bt_address> F8:7D:76:9D:9B:6B 连接到远程设备,请运行以下命令:
connect F8:7D:76:9D:9B:6B pbap
示例输出
[obex]# connect F8:7D:76:9D:9B:6B pbap
Attempting to connect to F8:7D:76:9D:9B:6B
[NEW] Session /org/bluez/obex/client/session1 [default]
[NEW] PhonebookAccess /org/bluez/obex/client/session1
Connection successful
[F8:7D:76:9D:9B:6B]#
选择电话簿对象
要选择电话簿对象,请从 obexctl 菜单运行以下命令:
cd <phonebook_object>
参数
<phonebook_object> 可以是:
-
pb用于电话簿。 -
ich是来电历史记录。 -
och是去电历史记录。 -
mch是未接来电历史记录。 -
cch是来电、去电和未接来电历史记录。 -
spd用于快速拨号联系人。 -
fav用于收藏的联系人。
示例
要选择整个电话簿,请从 obexctl 菜单运行以下命令:
cd pb
示例输出
[F8:7D:76:9D:9B:6B]# cd pb
Attempting to Select to pb
Select successful
[F8:7D:76:9D:9B:6B]#
提取电话簿
要提取电话簿,请执行以下操作:
- 连接 DUT 和远程设备。
- 选择所需的电话簿。
- 通过运行以下命令来提取所需的电话簿:
cp <source file> <destination file>
该文件存储在根目录或 /var/bluetooth/ 目录中。
参数
-
source file是被拉入的电话簿。 -
destination file是必须将电话簿拉入其中的文件。
示例
要将 *.vcf 拉至 contact.vcf,请运行以下命令:
cp *.vcf contact.vcf
示例输出
[F8:7D:76:9D:9B:6B]# cp *. vcf contact.vcf
Attempting to PullAll
[NEW] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session2/transfer22
PullAll successful
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session2/transfer22 Status: active
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session2/transfer22 Transferred: 23976 (@23KB/s)
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session2/transfer22 Transferred: 79920 (@55KB/s)
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session2/transfer22 Transferred: 130536 (@50KB/s)
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session2/transfer22 Transferred: 175824 (@45KB/s)
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session2/transfer22 Transferred: 229184 (@53KB/s)
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session2/transfer22 Transferred: 281052 (@51KB/s)
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session2/transfer22 Transferred: 336330 (@55KB/s)
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session2/transfer22 Transferred: 382284 (@45KB/s)
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session2/transfer22 Transferred: 478188 (095KB/s)
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session2/transfer22 Transferred: 615384 (@137KB/s)
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session2/transfer22 Transferred: 691974 (@76KB/s)
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session2/transfer22 Transferred: 740592 (@48KB/s)
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session2/transfer22 Transferred: 786546 (@45KB/s)
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session2/transfer22 Transferred: 829836 (@43KB/s)
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session2/transfer22 Transferred: 877122 (047KB/s)
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session2/transfer22 Transferred: 925074 (047KB/s)
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session2/transfer22 Transferred: 972360 (@47KB/s)
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session2/transfer22 Transferred: 1082250 (@109KB/s)
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session2/transfer22 Transferred: 1206126 (@123KB/s)
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session2/transfer22 Transferred: 1337328 (@131KB/s)
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session2/transfer22 Transferred: 1347984 (@10KB/s)
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session2/transfer22 Status: complete
[DEL] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session2/transfer22
[F8:7D:76:9D:9B:6B]#
- 打开并验证电话簿。
获取电话簿大小
要获取电话簿的大小,请执行以下操作:
- 连接 DUT 和远程设备。
- 选择所需的电话簿。
- 通过运行以下命令获取所需电话簿的大小:
ls -l
示例输出
Attempting to GetSize
[NEW] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session1/transfer4
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session1/transfer4 Status: complete
Size: 0x0006
Attempting to List
[DEL] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session1/transfer4
[NEW] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session1/transfer5
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session1/transfer5 Status: complete
0.vcf: MyContact1
1.vcf: MyContact2
2.vcf: MyContact3
3.vcf: MyContact4
4.vcf: MyContact5
5.vcf: MyContact6
[DEL] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session1/transfer5
搜索联系人
要按姓名或电话号码搜索联系人,请执行以下操作:
- 连接 DUT 和远程设备。
- 选择所需的电话簿。
- 通过运行以下命令搜索联系人:
ls <name_or_number>
出现联系人文件。
参数
<name_or_number> 是联系人姓名或电话号码。
示例
要在电话簿中搜索名为 BT 的联系人,请运行以下命令:
ls BT
示例输出
# ls BT
Attempting to Search
[NEW] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session1/transfer7
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session1/transfer7 Status: complete
4.vcf: MyContact5
[DEL] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session1/transfer7
消息访问配置文件
MAP 定义了交换消息对象的设备所使用的功能和过程。
要执行蓝牙 MAP 功能,用户必须首先完成以下过程中的步骤。
- 设置设备的蓝牙 MAP 功能
前提条件
-
配对 DUT 和远程设备。相关说明,可参见与远程蓝牙设备配对。
-
将 DUT 和远程设备放置在蓝牙附近。
通过运行以下命令打开蓝牙测试应用程序:
obexctl
要查看 OBEX 功能,请运行以下命令:
help
该命令提供 obexctl 的主菜单。要执行 MAP 服务器��和客户端功能,请参阅执行蓝牙 MAP 服务器功能和执行蓝牙 MAP 客户端功能。
示例输出
sh-5.1# obexctl
[NEW] Client /org/bluez/obex
[obex]# help
Menu main:
Available commands:
-------------------
connect <dev> [uuid] [channel] Connect session
disconnect [session] Disconnect session
list List available sessions
show [session] Session information
select <session> Select default session
info <object> Object information
cancel <transfer> Cancel transfer
suspend <transfer> Suspend transfer
resume <transfer> Resume transfer
send <file> Send file
pull <file> Pull Vobject & stores in file
cd <path> Change current folder
ls <options> List current folder
cp <source file> <destination file> Copy source file to destination file
mv <source file> <destination file> Move source file to destination file
rm <file> Delete file
mkdir <folder> Create folder
version Display version
quit Quit program
exit Quit program
help Display help about this program
export Print environment variables
[obex]#
-
执行蓝牙 MAP 服务器功能 用户可以使用 obexctl 主菜单中提供的命令验证蓝牙 MAP 服务器功能。
-
执行蓝牙 MAP 客户端功能 用户可以使用 obexctl 主菜单中提供的命令来验证蓝牙 MAP 客户端功能。
- 执行蓝牙 MAP 服务器功能
用户可以使用 obexctl 主菜单中提供的命令验证蓝牙 MAP 服务器功能。
拉取并阅读消息
在开始之前,请执行以下操作:
-
配对 DUT 和远程设备。相关说明,可参见与远程蓝牙设备配对。
-
在服务器上创建 MAP 目录。
在 BlueZ 堆栈中,无法直接测试或验证 MAP 服务器功能,因为您无法在设备上发送或接收蜂窝消息。因此,您必须在 DUT 上创建一个 MAP 目录。关于创建 MAP 目录的更多信息,请参阅示例 MAP 目录。
要从服务器拉取并读取消息,请执行以下操作:
- 从远程设备启动到 DUT 的连接。
- 接受 DUT 上的连接请求,如下所示:
- 在 DUT 上运行 SSH。
- 通过运行以下命令打开 bluetoothctl 应用程序:
bluetoothctl- 验证连接请求。
- 将预期的消息从服务器拉取至客户端。
- 在客户端打开并验证检索到的消息。
示例 MAP 目录
用户可以创建示例 MAP 目录来验证 MAP 服务器功能,如下所示:
- 运行 SSH。
- 通过按顺序运行以下命令创建消息目录 map-messages/telecom/msg:
mkdir map-messages
cd map-messages
mkdir telecom
cd map-messages/telecom
mkdir msg
cd telecom/msg
- 在 msg 目录中,创建以下子文件夹:
- inbox
- outbox
- sent
- deleted
- draft 要在 msg 处创建子文件夹,请运行以下命令:
mkdir <subfolder>
subfolder 是子文件夹的名称。例如, inbox。
- 在每个子文件夹中,创建消息文件。 下图展示了一个示例 MAP 目录�。在 /map-messages/telecom/msg/ 目录中,有用于不同类型消息的子文件夹。消息包含在这些子文件夹中。
- 执行蓝牙 MAP 客户端功能
用户可以使用 obexctl 主菜单中提供的命令来验证蓝牙 MAP 客户端功能。
开始之前,请按照设置设备的蓝牙 MAP 功能中的说明设置设备。
连接远程设备
要在 MAP 中连接远程设备,请从 obexctl 菜单运行以下命令:
connect <bt_address> <profile_name>
参数
-
<bt_address>是远程设备的蓝牙地址。 -
<profile_name>是map.
示例
要使用 <bt_address> 22:22:23:DB:F2:4A 连接到远程设备,请运行以下命令:
connect 22:22:23:DB:F2:4A map
示例输出
#connect 22:22:23:DB:F2:4A map
Attempting to connect to 22:22:23:DB:F2:4A
[NEW] Session /org/bluez/obex/client/session23 [default]
[NEW] MessageAccess /org/bluez/obex/client/session23
[NEW] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session23/transfer149
Connection successful
列出文件夹中的邮件
要列出文件夹中的消息,请执行以下操作:
- 连接 DUT 和远程设备。
- 将当前目录更改为预期目录。
示例
如果消息文件夹位于 telecom/msg,请从 obexctl 菜单运行以下命令:
cd telecom/msg
- 通过运行以下命令列出目标文件夹中的消息:
ls <folder_name>
示例 要列出 inbox 消息,请运行以下命令:
ls inbox
示例输出
[22:22:23:DB:F2:4A]# ls inbox
Attempting to ListMessages
[NEW] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session22/transfer141
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session22/transfer141 Status: complete
[NEW] Message /org/bluez/obex/client/session22/message288230376151711846
[NEW] Message /org/bluez/obex/client/session22/message288230376151711844
[NEW] Message /org/bluez/obex/client/session22/message288230376151711842
发送消息
要发送消息,请执行以下操作:
- 连接 DUT 和远程设备。
- 将当前目录更改为发件箱目录。
示例
要将目录更改为 outbox,请从 obexctl 菜单运行以下命令:
cd outbox
- 确保该消息存在于 outbox 文件夹中。如果该消息不存在,请创建一条消息。
示例
可以创建一个名为 map_file.msg 的 BMSG 文件,其中包含以下内容:
BEGIN:BMSG
VERSION:1.0
STATUS:UNREAD
TYPE:SMS_GSM
FOLDER:outbox
NOTIFICATION:1
BEGIN:VCARD
VERSION:2.1
N:QCOM-BTD
END:VCARD
BEGIN:BENV
BEGIN:VCARD
VERSION:2.1
N:null;;;;
TEL:123-456-7890
END:VCARD
BEGIN:BBODY
CHARSET:UTF-8
LENGTH:50
BEGIN:MSG
Hello from client side
END:MSG
END:BBODY
END:BENV
END:BMSG
- 通过从 obexctl 菜单运行以下命令来发送消息:
send <message_filename>
参数
message_filename 是待发送消息的文件名。
示例 请运行以下命令,以便发送 map_file.msg:
send map_file.msg
示例输出
[22:22:23:DB:F2:4A]# send map_file.msg
Attempting to send map_file.msg to /org/bluez/obex/client/session22
[NEW] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session22/transfer147
Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session22/transfer147
Status: queued
Name :
Size: 322
Filename: map_file.msg
Session: /org/bluez/obex/client/session22
[CHG] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session22/transfer147 Status: complete
[DEL] Transfer /org/bluez/obex/client/session22/transfer147
BSA 协议栈
-
运行 app_manager 程序进行配对:
cd /usr/src/rubikpi-btapp/
./app_manager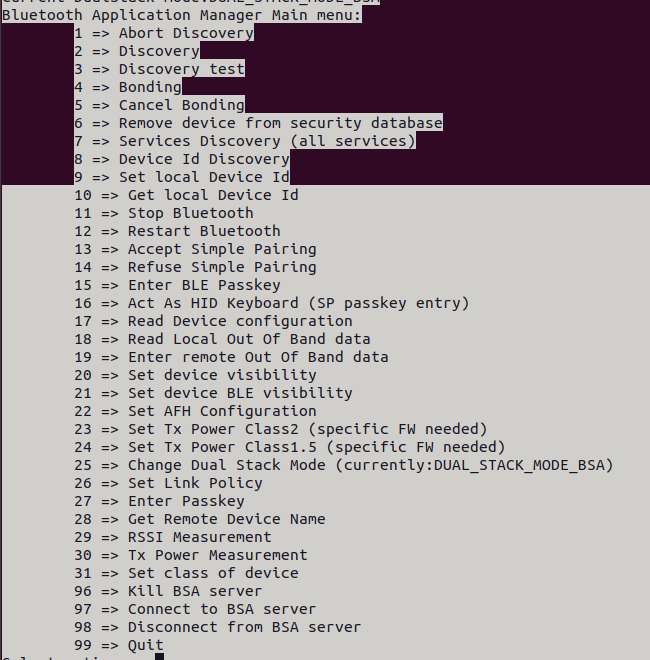
-
在终端输入 2 回车后等待蓝牙扫描结果。
-
在终端输入 4 回车后输入要配对的蓝牙设备 Dev 编号再次回车。
-
根据提示在终端输入 13 回车接受配对, 对端蓝牙设备同时也要接受配对请求。
app_manager 需要一直运行,下面步骤使用
adb shell命令创建新终端进行。 -
-
蓝牙发送
以发送文件为例:
cd /usr/src/rubikpi-btapp/
touch ./test_file.txt
echo RUBIKPi > test_file.txt
./app_opc
# 输入4回车
# 输入0回车
# 输入设备编号回车
# 手机接收文件
# 输入9回车退出 -
蓝牙接收:
cd /usr/src/rubikpi-btapp/
mkdir push
./app_ops
# 输入1回车
# 手机蓝牙发送文件
# 传输完成后,输入9回车退出, 在./push 文件夹中查看传输的文件 -
其他 Demo
在 魔方派 3 的 /usr/src/rubikpi-bt-demo/3rdparty/3rdparty/embedded/bsa_examples/linux 目录下,存放了所有 蓝牙 相关的源码,可以按需要进行编译和查看,编译方法如下:
cd /usr/src/rubikpi-bt-demo/3rdparty/3rdparty/embedded/bsa_examples/linux/<测试demo>/build/
export ARMGCC=gcc
make CPU=arm64
cp arm64/<demo可执行文件> /usr/src/rubikpi-btapp/
cd /usr/src/rubikpi-btapp/
# 运行demo程序
音频
魔方派 3 目前支持的音接口为:
-
3.5mm 耳机,下图4。
-
HDMI OUT, 下图9。
-
蓝牙
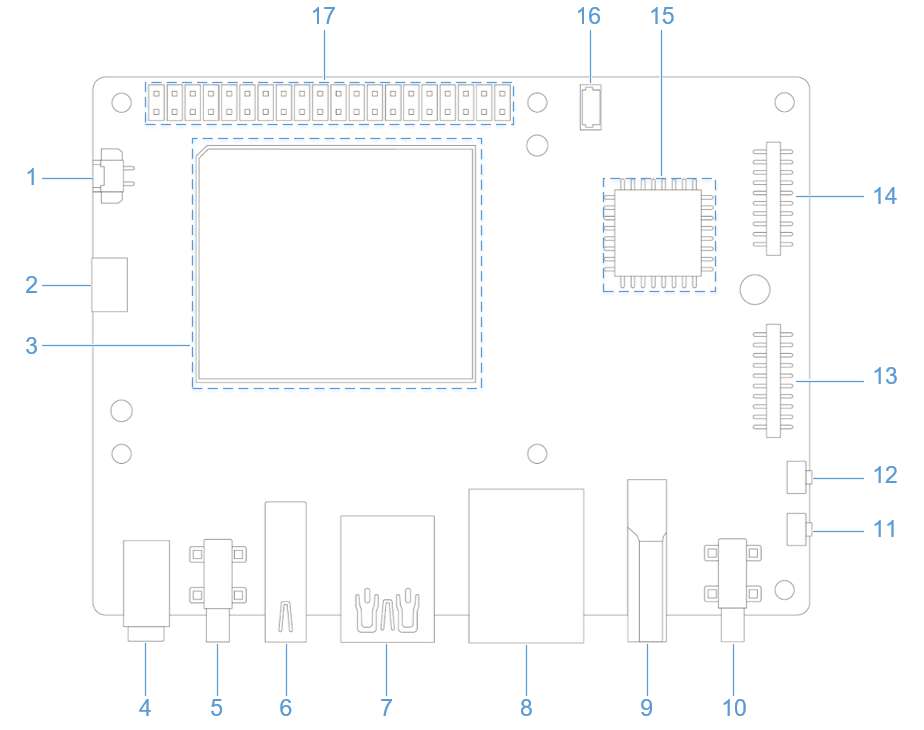
��查看声卡信息
-
在 魔方派 3 中输入下面命令,查看声卡挂载情况:
cat /proc/asound/cards
-
在 魔方派 3 中输入下面命令,查看已分配的 PCM 流列表:
cat /proc/asound/pcm
设置输出源
在 魔方派 3 中输入下面命令,改变 gstreamer、paplay 等命令的音频输出源头:
-
设置输出接口为 3.5mm Headset
rubikpi_config audio output headset或
pactl set-sink-port low-latency0 headset -
设置输出接口为 HDMI OUT
rubikpi_config audio output hdmi或
pactl set-sink-port low-latency0 hdmi
播放
-
在 魔方派 3 中输入下面命令测试耳机播放。
备注运行命令前,务必将 MP3 测试文件 (
<FileName>.mp3) 推送到/opt/目录下。gst-launch-1.0 filesrc location=/opt/<FileName>.mp3 ! mpegaudioparse ! mpg123audiodec ! pulsesink -
在 魔方派 3 中输入下面命令测试 HDMI OUT 播放。
备注运行命令前,务必将 PCM 测试文件 (
<FileName>.wav) 推送到/opt/目录下。systemctl stop pulseaudio
agmplay /opt/<FileName>.wav -D 100 -d 100 -r 48000 -b 16 -c 2 -i MI2S-LPAIF_RXTX-RX-PRIMARY
systemctl start pulseaudio -
在 魔方派 3 中输入下面命令测试蓝牙设备播放,测试需要开启多个终端。
- 终端一:
cd /usr/src/rubikpi-btapp/
./app_manager
- 终端二:
cd /usr/src/rubikpi-btapp/
./app_av
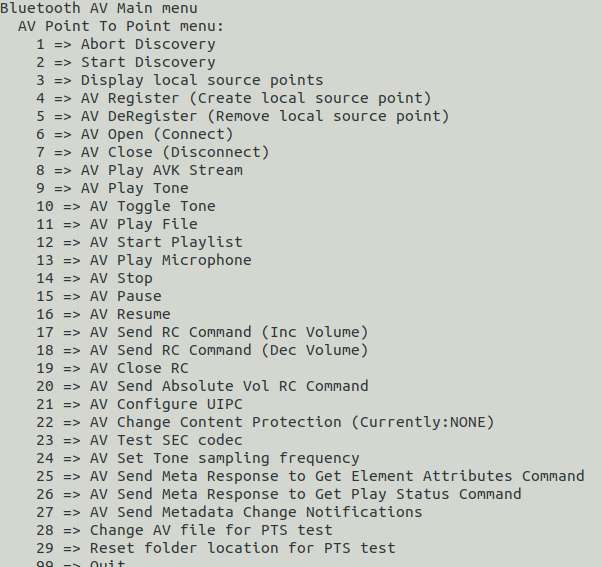
a. 输入 2 回车,等待发现蓝牙设备。
b. 输入 6 回车,开始建立连接。
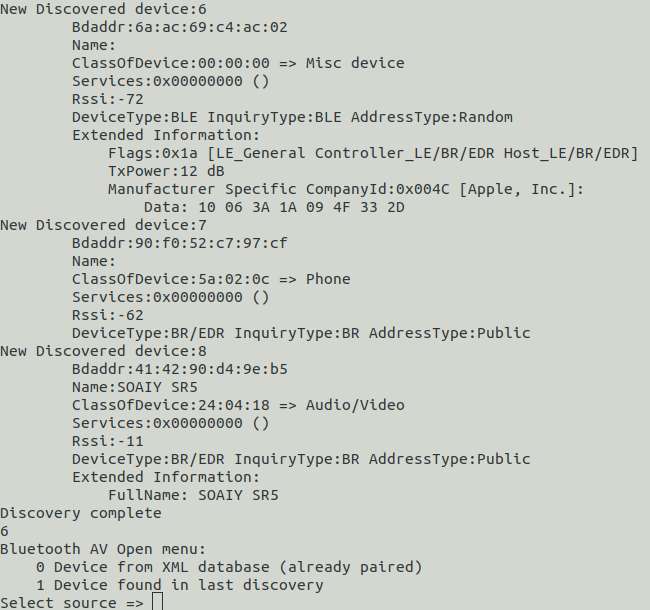
c. 输入 1 回车,从最近的扫描结果中连接。
d. 输入要连接蓝牙设备的 Dev 号。
-
返回终端一,输入 13 回车,接受配对。
-
返回终端二,输入 11 回车后选择要播放的音频编号回车播放。
录制
在 魔方派 3 中输入下面命令测试录音功能
-
耳机录制:
gst-launch-1.0 -v pulsesrc volume=10 ! audioconvert ! wavenc ! filesink location=/opt/test.wav -
蓝牙耳机录制,测试需要开启多个终端:
- 终端一:
cd /usr/src/rubikpi-btapp/
./app_manager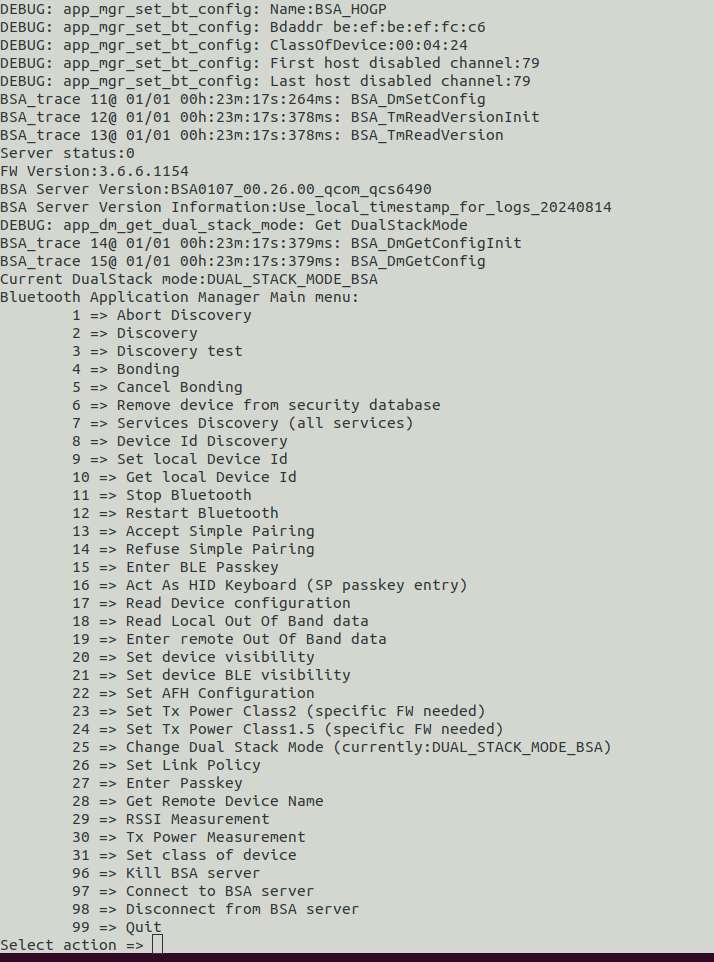
- 终端二:
cd /usr/src/rubikpi-btapp/
./app_ag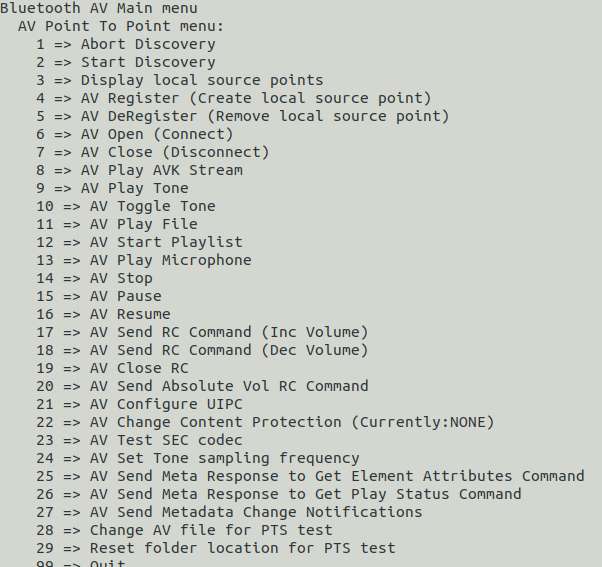
a. 输入 1 回车,等待发现蓝牙耳机。
b. 输入 6 回车,连接蓝牙耳机。
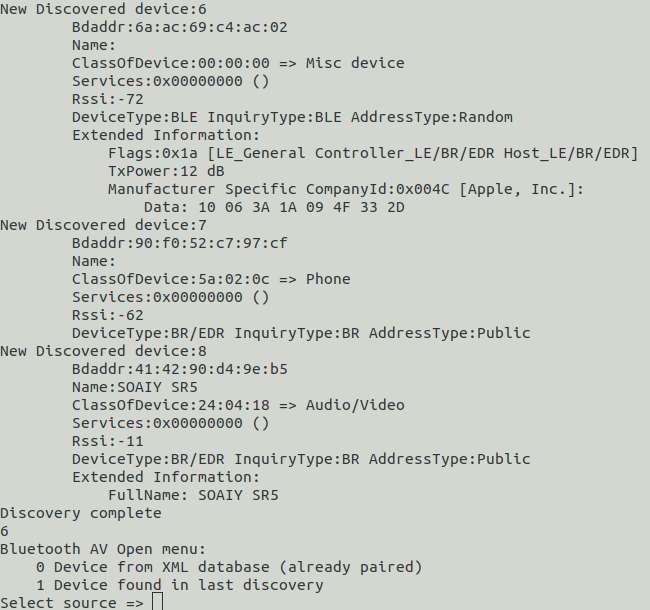
c. 输入 1 回车,从最近的扫描结果中连接。
d. 输入要连接蓝牙设备的Dev号。
e. 返回终端一,输入13 回车,接受配对。
f. 返回终端二,输入 8 回车,打开 SCO 链路。
- 终端三:
systemctl stop pulseaudio
#开始录制蓝牙耳机麦克风音频
agmcap /home/root/my.wav -D 100 -d 101 -r 16000 -b 16 -c 1 -i MI2S-LPAIF_VA-TX-PRIMARY -dkv 0xA3000003 -p 120 -n 2
#ctrl+c结束录制
systemctl start pulseaudio录制音频的保存路径为 /home/root/my.wav。
调节音量
-
耳机调节音量
可通过下面命令获取和设置音量:
tinymix get "DAC Playback Volume"
tinymix set "DAC Playback Volume" 192 192
-
蓝牙调节音量
在播放蓝牙音频时,可在终端二进行音量控制
-
输入 20
-
输入 0
-
输入音量(音量范围0到100)
-
抓取日志
-
用户空间日志
要抓取用户空间日志,请执行以下操作:
cat /var/log/user.log -
内核音频驱动程序日志
要抓取内核日志,请执行以下操作:
-
内核日志
dmesg -
禁用特定文件中的内核日志:
echo –n “file <filename> -p” > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control -
动态内核日志
默认情况下,动态日志处于禁用状态。要将其启用,请添加
CONFIG_DYNAMIC_DEBUG内核配置,重新编译并重新刷写设备。要启用音频动态内核日志,请执行以下操作:
ssh root@ip-addr
mount -o rw,remount /
mount -t debugfs none /sys/kernel/debug
echo –n “file <filename> +p” > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
-
分析抓取的日志
查看用户空间日志和内核音频驱动程序日志,了解播放和录制用例。
-
播放
以下日志片段描述了为播放用例收集的信息。
//Open Low latency Playback stream. Details of each stream type can be found at sources/audio/opensource/arpal-lx/inc/PalDefs.h
2022-04-28T18:02:08.748280+00:00 pulseaudio: pal_stream_open: 224: Enter, stream type:1
//Verify the backend device, sample rate, bitwidth, channels etc
2022-04-28T18:02:08.748627+00:00 pulseaudio: setDeviceMediaConfig: 1056: CODEC_DMA-LPAIF_WSA-RX-0 rate ch fmt data_fmt 48000 2 2 1
//Start playback stream
2022-04-28T18:02:08.751947+00:00 pulseaudio: pal_stream_start: 338: Enter. Stream handle 0xffff94001040K
//Map the metadata with kvh2xml.h file for playback usecase details.
2022-04-28T18:02:08.853157+00:00 pulseaudio: metadata_print: 82 key:0xa1000000, value:0xa100000e//PCM_LL_PLAYBACK
2022-04-28T18:02:08.853395+00:00 pulseaudio: metadata_print: 82 key:0xab000000, value:0x1
2022-04-28T18:02:08.853660+00:00 pulseaudio: metadata_print: 82 key:0xa2000000, value:0xa2000001//Speaker
2022-04-28T18:02:08.853881+00:00 pulseaudio: metadata_print: 82 key:0xac000000, value:0xac000002//DEVICEPP_RX_AUDIO_MBDRC
//Verify the graph opened for playback usecase
2022-04-28T18:02:08.856934+00:00 pulseaudio: print_graph_alias: 2334 GKV Alias 142 | StreamRX_PCM_LL_Playback_DeviceRX_Speaker_Instance_Instance_1_DevicePP_Rx_Audio_MBDRC
//graph_open called
2022-04-28T18:02:08.859509+00:00 pulseaudio: graph_open: 709 graph_handle 0x47534c
//Configure hardware endpoint module
2022-04-28T18:02:08.864386+00:00 pulseaudio: configure_hw_ep_media_config: 636 entry mod tag c0000004 miid 43b1 mid 7001023
2022-04-28T18:02:08.864495+00:00 pulseaudio: configure_hw_ep_media_config: 664 rate 48000 bw 16 ch 2, data_fmt 1
2022-04-28T18:02:08.864603+00:00 pulseaudio: configure_hw_ep_media_config: 676 exit, ret 0
//graph_start entry
2022-04-28T18:02:08.867234+00:00 pulseaudio: graph_start: 899 entry graph_handle 0x47534c
//Stream started
2022-04-28T18:02:08.867864+00:00 pulseaudio: pal_stream_start: 387: Exit. status 0
//graph_stop entry
2022-04-28T18:02:25.037338+00:00 pulseaudio: graph_stop: 928 entry graph_handle 0x47534c
//Stop the PAL stream once playback completes
2022-04-28T18:02:25.039923+00:00 pulseaudio: pal_stream_stop: 441: Exit. status 0
//graph_close entry
2022-04-28T18:02:25.050944+00:00 pulseaudio: graph_close: 762 entry handle 0x47534c
//Close the PAL stream
2022-04-28T18:02:25.054510+00:00 pulseaudio: pal_stream_close: 322: Exit. status 0 -
录制
以下日志片段描述了为录制用例收集的信息。
//Open Recording stream for PAL_STREAM_RAW. Details of stream type can be found at sources/audio/opensource/arpal-lx/inc/PalDefs.h
Apr 29 09:23:11 pulseaudio[862]: pal_stream_open: 224: Enter, stream type:9
//Verify the backend device, sample rate, bitwidth, channels etc
Apr 29 09:23:11 pulseaudio[862]: setDeviceMediaConfig: 1056: CODEC_DMA-LPAIF_VA-TX-0 rate ch fmt data_fmt 48000 1 2 1
//Start recording stream
Apr 29 09:23:11 pulseaudio[862]: pal_stream_start: 338: Enter. Stream handle 0xffff6c001040K
//graph_open entry
Apr 29 09:23:11 pulseaudio[862]: graph_open: 709 graph_handle 0x47534c
//Metadata details to identify the usecase
Apr 29 09:23:11 pulseaudio[862]: metadata_print: 82 key:0xb1000000, value:0xb1000009//RAW_RECORD
Apr 29 09:23:11 pulseaudio[862]: metadata_print: 82 key:0xa3000000, value:0xa3000004//HANDSETMIC
//Verify the graph opened for recording usecase
Apr 29 09:23:11 pulseaudio[862]: print_graph_alias: 2334 GKV Alias 29 | DeviceTX_Handset_Mic_StreamTX_RAW_Record
//Configure hardware endpoint module
Apr 29 09:23:11 pulseaudio[862]: configure_hw_ep_media_config: 636 entry mod tag c0000005 miid 43af mid 7001024
Apr 29 09:23:11 pulseaudio[862]: configure_hw_ep_media_config: 664 rate 48000 bw 16 ch 1, data_fmt 1
Apr 29 09:23:11 pulseaudio[862]: configure_hw_ep_media_config: 676 exit, ret 0
//graph_start entry
Apr 29 09:23:11 pulseaudio[862]: graph_start: 899 entry graph_handle 0x47534c
//Stream recording started
Apr 29 09:23:11 pulseaudio[862]: pal_stream_start: 387: Exit. status 0
//graph_stop entry
Apr 29 09:23:26 pulseaudio[862]: graph_stop: 928 entry graph_handle 0x47534c
//Stop the PAL stream once user stops recording
Apr 29 09:23:26 pulseaudio[862]: D: [regular2] pal-source.c: pal_stream_stop returned 0
//Close the PAL stream
Apr 29 09:23:26 pulseaudio[862]: pal_stream_close: 284: Enter. Stream handle :0xffff6c001040K
//graph_close entry
Apr 29 09:23:26 pulseaudio[862]: graph_close: 762 entry handle 0x47534c
//Close the PAL stream
Apr 29 09:23:26 pulseaudio[862]: pal_stream_close: 322: Exit. status 0
风扇
魔方派 3 兼容树莓派 5 的散热套件:
在一些高负载或高性能的场景下使用 魔方派 3 ,需要使用散热措施来保证设备性能稳定,否则会因为 CPU 温度过高而带来降频等性能影响。
风扇安装
- 将散热器背面所有导热硅脂移除,将下图标记的两块硅脂按 魔方派 3 的 SoC 及 uMCP 的形状裁下。
两块的表面尺寸约为14*12mm和13*11.5mm。
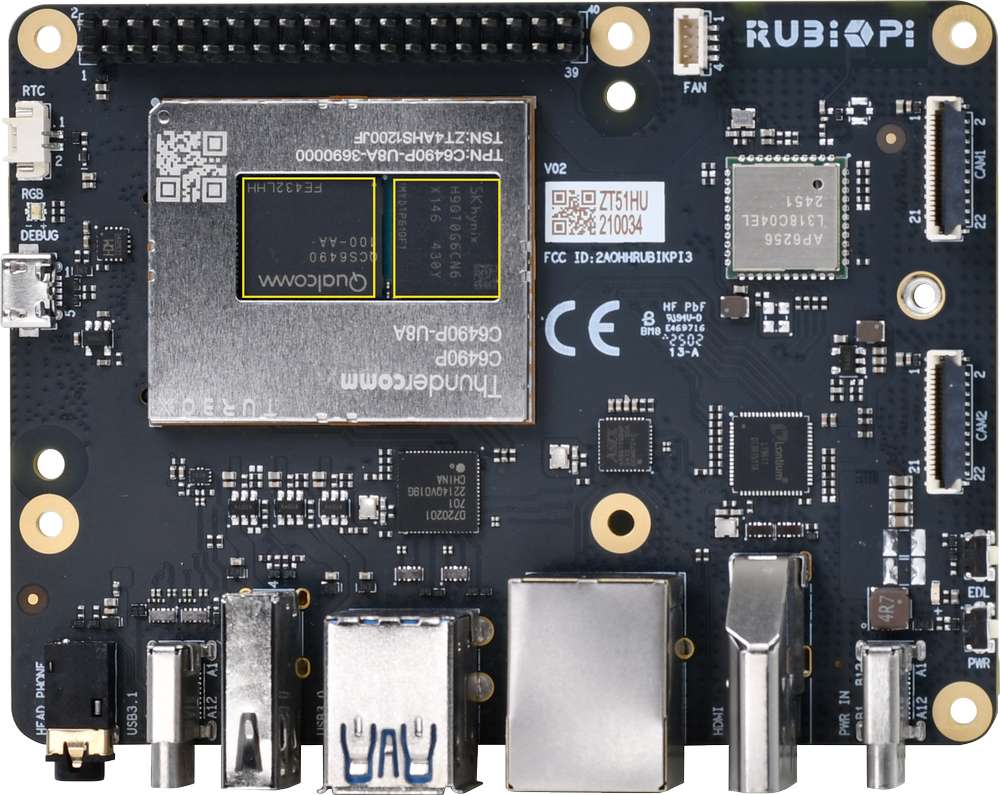
- 将裁剪好的两块导热硅脂贴在 魔方派 3 上对应位置。

- 安装散热器,连接风扇排线。
建议将风扇安装到 魔方派 3 上后不要将其取下。拆卸会导致风扇的推针和散热垫退化,并可能导致产品损坏。如果推针损坏或变形,或无法牢固夹住,请停止使用风扇。
风扇控制方法
魔方派 3 风扇会根据当前的 CPU 温度自动调整转速,同时也可在 魔方派 3 中使用下面命令进行手动控制转速,0 和 255 分别表示风扇的最低和最高速度。
rubikpi_config fan speed 100
rubikpi_config fan speed 255
rubikpi_config fan speed 0
或
echo 100 > /sys/class/hwmon/hwmon29/pwm1
echo 255 > /sys/class/hwmon/hwmon29/pwm1
echo 0 > /sys/class/hwmon/hwmon29/pwm1
在将风扇转速设置为一个固定值前时,需要使用 rubikpi_config thermal disable 命令将 CPU 热管理关掉。
LED
魔方派 3 上有一个由 PMIC (Power Management IC) 驱动的 RGB 的三色灯,默认情况下其中的绿色灯被设置为�了心跳灯用来反馈系统的运行情况和 CPU 负载情况)。
如下是 LED 灯不同状态时,所指示的状态:
-
蓝灯长亮:fastboot 模式
-
绿色心跳:正常工作
-
红色心跳:低功耗电源插入(小于 12V 2.25A)
-
快速心跳: CPU 高负荷工作
-
停止心跳:
-
系统死机
-
进入睡眠
-
正在开机中
-
可使用如下命令,操作 LED 灯:
-
关闭心跳灯
rubikpi_config led heartbeat off或
echo none > /sys/class/leds/green/trigger -
开启心跳灯
rubikpi_config led heartbeat on或
echo heartbeat > /sys/class/leds/green/trigger -
设置绿灯的亮度(亮度 0 - 511,如下为设置亮度为100)
rubikpi_config led green 100或
echo 100 > /sys/class/leds/green/brightness -
设置红灯的亮度(亮度 0 - 511,如下为设置亮度为100)
rubikpi_config led red 100或
echo 100 > /sys/class/leds/red/brightness -
设置蓝灯的亮度(亮度 0 - 511,如下为设置亮度为100)
rubikpi_config led blue 100或
echo 100 > /sys/class/leds/blue/brightness
以太网
以太网技术旨在使用有线技术以不同的链路速度传输数据。它使用线缆在网络模型(例如��局域网 (LAN) 和广域网 (WAN))中传输数据,实现可靠、安全和更出色的网络连接。
以太网连接集成到 IoT 设备和传感器,使它们能够将数据传输到网络。它根据 IEEE 802.3 标准定义,可为这些设备提供用于与网关通信的标准化接口。
以太网接口为下图 8, 魔方派 3 支持千兆以太网:
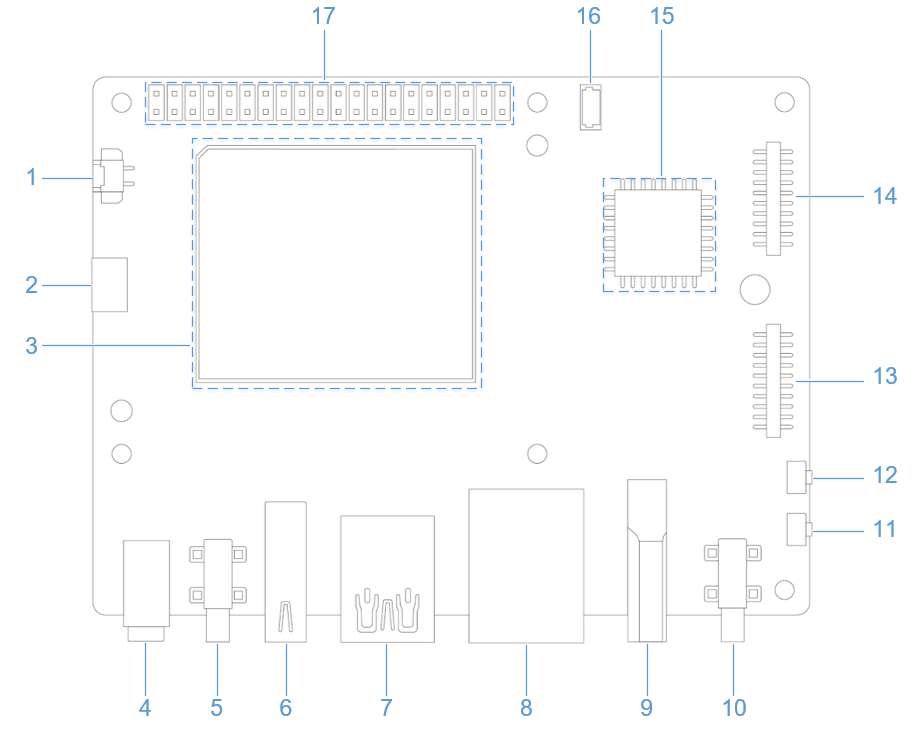
接入网线,如下图所示:
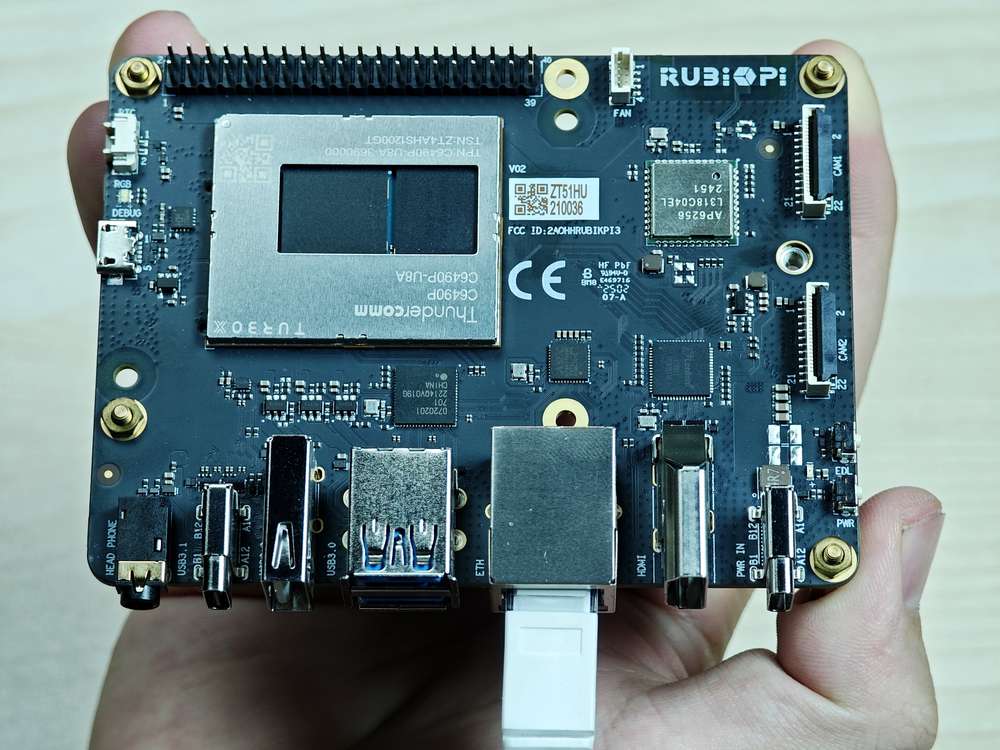

可在 魔方派 3 中使用下面命令查看网络连接情况,如下图所示,已经成功分配 IP,说明网络连接成功:
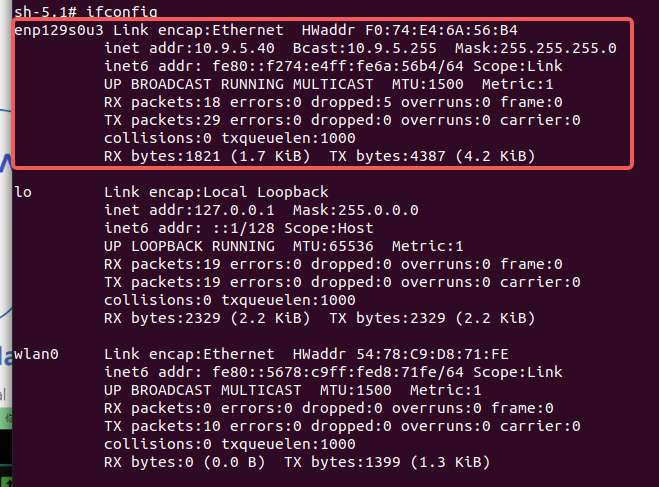
调试以太网
可以使用以下日志类型来记录和调试与以太网有关的问题。
-
dmesg:调试与内核驱动程序相关的问题 -
tcpdump: 验证数据包传输
要调试在以太网调通期间可能出现的问题,请执行以下操作:
-
要收集
dmesg日志并调试与内核驱动程序有关的问题,请运行以下命令:dmesg > /var/log/dmesg_logs.txt -
要收集
tcpdump日志并验证数据包传输,请运行以下命令。tcpdump -i any -s 0 -w /var/log/tcpdump.pcap -
收集来自
ethtool、ifconfig、netstat和 IP 路由表的输出以进行调试。
RTC 电池接口
RTC (Real-time Clock) 电池接口为下图 1。
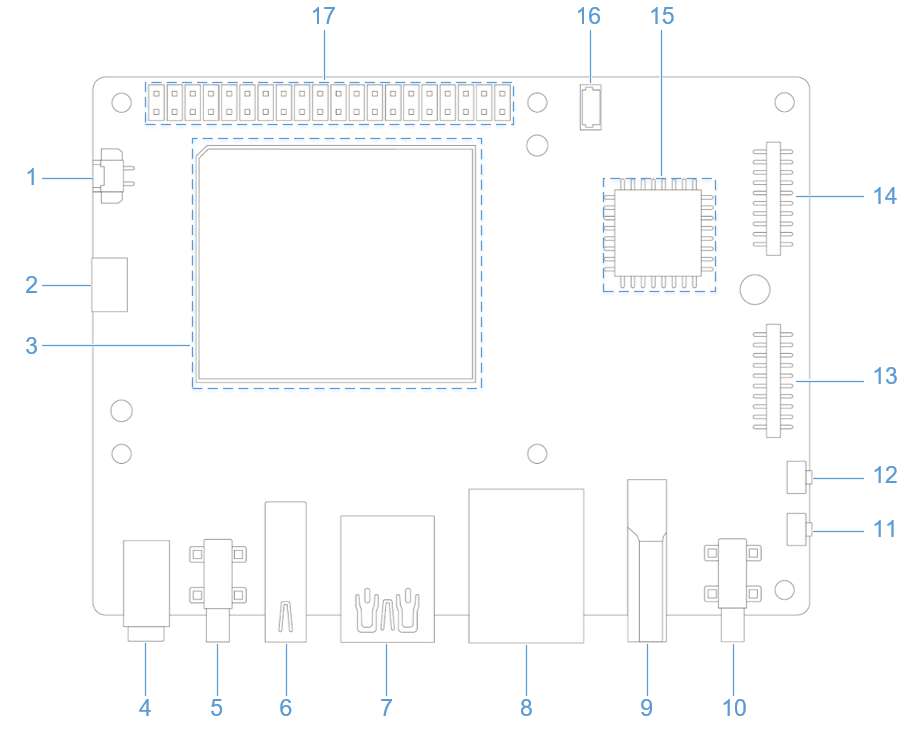
接入 RTC 电池, 如下图所示,并将时间写入 魔方派 3 的系统硬件时钟,可在 魔方派 3 完全断电后,仍对 魔方派 3 的系统时间进行保存。
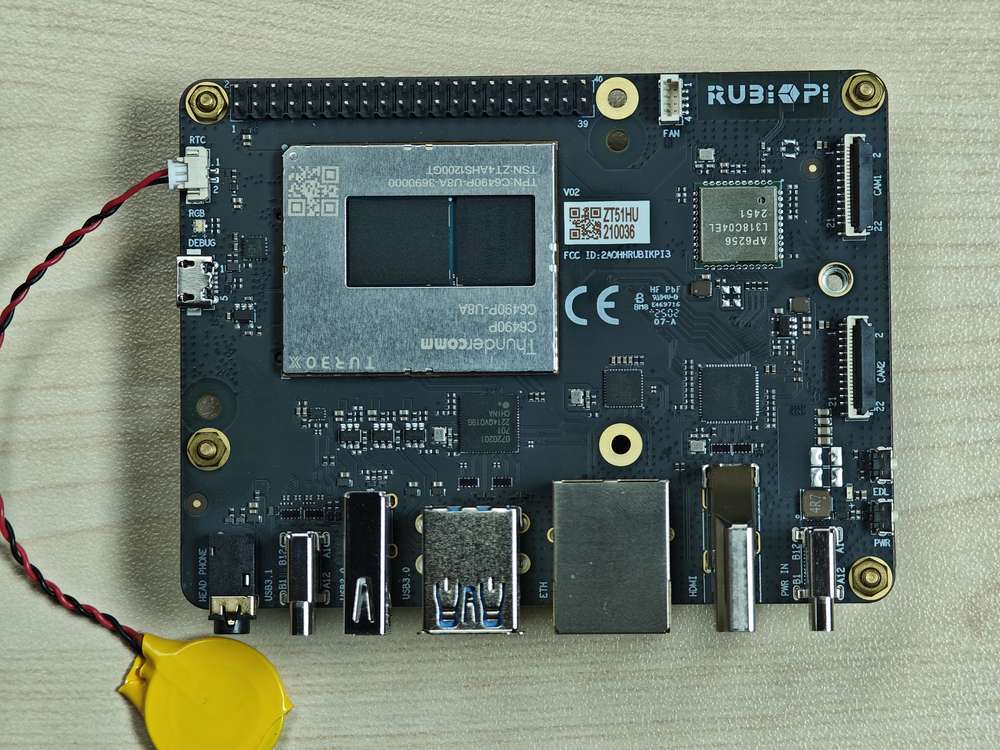

在 魔方派 3 中将系统时间写入系统硬件时钟方法如下:
date -s "08:00:00 20241201" # 将系统时间设置为2024年12月1日8时0分
hwclock -w # 将系统时间写入系统硬件时钟
M.2 Key M 接口
魔方派 3 提供一个标准 M.2 插槽,用于连接 NVMe 存储,可安装 2280 规格(22*80mm)M.2 SSD 硬盘。M.2 插槽最大支持 PCIe Gen 3 x 2。M.2 接口最大对外输出能力为 3.3V 2A,可单独控制开关。
M.2 Key M 接口使用了 QCS6490 的 PCIe1 总线,设备路径为:/sys/bus/pci/devices/0001:00:00.0
M.2 Key M 接口为下图 18:
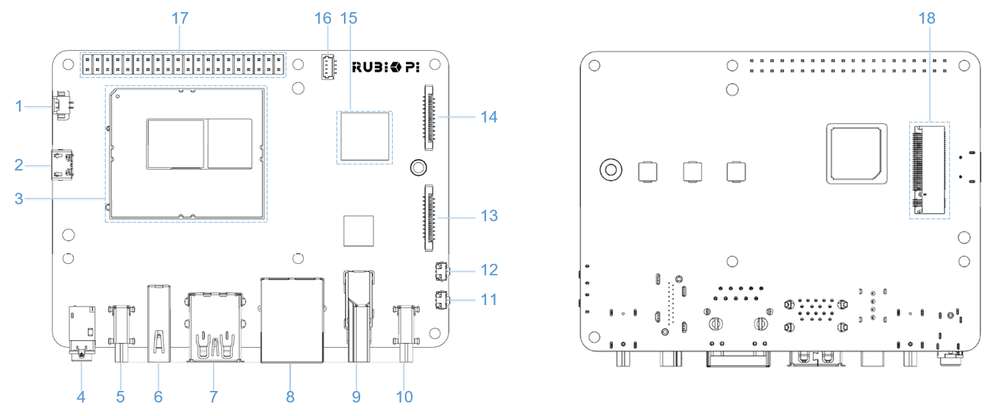
M.2 Key M 接口可以接入规格为2280的固态硬盘,如下图所示:

目前 魔方派 3 暂未支持固态硬盘的自动挂载,可在 魔方派 3 中执行下面命令对固态硬盘手动挂载:
mkdir /opt/ssd
mount /dev/nvme0n1 /opt/ssd
PCIe 功耗优化
PCIe 定义了两种功耗管理方法。
-
功耗管理软件,用于确定每个设备的功耗管理功能并分别对各个设备进行管理
-
不需要软件干预的系统,例如主动状态功耗管理 (ASPM)
当链路上未传输任何数据包时,设备会将链路置于节能状态。
PCIe L0 链路状态
PCIe 功耗管理定义下了 L0 链路状态:
-
L0:工作状态
-
L0s:具有低恢复延迟的 ASPM 状态(节能待机状态)
PCIe 设备状态
PCIe 功耗管理定义了以下设备状态:
-
D0(必选): 设备处于完全 ON 状态,此时存在两个子状态
-
D0(uninitialized):当设备退出复位状态后等待枚举和配置时,该功能处于 D0(uninitialized) 状态
-
D0(active)
-
当完成枚举和配置过程后,该功能处于 D0(active) 状态
-
当系统软件启用一个或多个(任意组合)功能参数(如内存空间启用、I/O 空间启用、总线主启用(BME)位)时,该功能进入 D0(active) 状态
-
-
-
D1(可选):轻度休眠状态
-
该功能只能发出 PME 消息,无法发出其他 TLP
-
该功能只能充当配置事务的目标,无法充当其他事务的目标
-
该功能通过发出设定 PM 控制和状态寄存器的软件命令来进入 D1 状态
-
-
D2(可选):深度休眠状态
-
该功能只能发出 PME 消息,无法发出其他 TLP
-
该功能只能充当配置事务的目标,无法充当其他事务的目标
-
该功能通过发出设定 PM 控制和状态寄存器的软件命令来进入 D2 状态
-
-
D3(必选):设备处于最低功耗状态,此时该功能必须支持两种 D3 状态
-
D3(hot)
-
该功能只能发出 PME 消息,无法发出其他 TLP
-
该功能只能充当配置事务的目标,无法充当其他事务的目标
-
该功能通过设定功耗状态位域发出软件命令来进入 D3(hot) 状态
-
-
D3(cold):设备进入 D3(cold) 状态并断电;当恢复供电时,设备进入 D0(uninitialized) 状态
PCIe 调试
M.2 Key M 接口使用了 QCS6490 的 PCIe1 总线,设备路径为:/sys/bus/pci/devices/0001:00:00.0。
lspci 和 setpci 命令为 Linux 发行版的本机命令。这两条命令提供多种级别的输出,并且还可用于在某个时间点查看 PCI 总线上训练的不同组件的功能和状态。这些功能大多反映的是 PCIe 基本规范所需的配置空间寄存器。更多详细信息,可访问 https://pcisig.com/specifications
如需查看使用说明,可运行以下命令。
lspci --help
以下功能有助于解决 PCIe 问题。
-
显示设备信息
lspci示例输出
0000:00:00.0 PCI bridge: Qualcomm Device 010b
0000:01:00.0 USB controller: Renesas Technology Corp. uPD720201 USB 3.0 Host Controller (rev 03)
0001:00:00.0 PCI bridge: Qualcomm Device 010b -
显示设备控制寄存器中的 PCIe 设备和厂商 ID。
lspci -nvmm示例输出
Slot: 00:00.0
Class: 0604
Vendor: 17cb
Device: 010b
IOMMUGroup: 6
Slot: 01:00.0
Class: 0c03
Vendor: 1912
Device: 0014
Rev: 03
ProgIf: 30
IOMMUGroup: 6
Slot: 0001:00:00.0
Class: 0604
Vendor: 17cb
Device: 010b
DTNode: /sys/firmware/devicetree/base/soc@0/pci@1c08000/pcie@1
IOMMUGroup: 7