Qualcomm® AI Hub
Qualcomm AI Hub 包含大量预训练的 AI 模型,这些模型经过优化,可在 Dragonwing 硬件NPU上运行。
查找支持的模型
AI Hub 中的模型按支持的 Qualcomm 芯片组进行分类。查看在您的开发套件上运行的模型:
1️⃣ 前往 model list。
2️⃣ 在“芯片组”下,选择:
- RB3 Gen 2 Vision Kit: 'Qualcomm QCS6490 (Proxy)'
- 魔方派 3: 'Qualcomm QCS6490 (Proxy)'
将模型部署到 NPU(Python)
以部署 Lightweight-Face-Detection 模型为示例。
运行示例代码库
所有 AI Hub 模型都附带一个示例代码库。这是理想的入门起点。代码库准确地展示了模型运行流程。它展示了网络输入的要求,以及如何解析输出(如,将输出张量映射到边界框)。示例代码库尚未支持 NPU 或 GPU 加速。在将此模型移至 NPU 之前,我们首先了解一下正确的输入/输出格式。
在 Lightweight-Face-Detection 的AI Hub页面上,点击“Model repository”,访问README文件。该文件包含运行示例代码库的具体说明。
如需部署此模型,请在开发板上打开终端或建立SSH会话,并执行以下操作:
1️⃣ 创建一个新的虚拟环境(venv)并安装一些基础包:
mkdir -p ~/aihub-demo
cd ~/aihub-demo
python3 -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate
pip3 install numpy setuptools Cython shapely
2️⃣ 将一张带有人脸的图像(640x480 分辨率,JPG 格式)下载到您的开发板上,例如:
wget https://cdn.edgeimpulse.com/qc-ai-docs/example-images/three-people-640-480.jpg

输入分辨率:AI Hub 模型对输入数据有尺寸要求。可以在“技术细节 > 输入分辨率”下找到所需的分辨率(高度 x 宽度,此处 480x640 => 640x480 为宽 x 高)。也可通过查看TFLite或ONNX文件中输入张量的尺寸获取该信息。
3️⃣ 按Facial Landmark Detection模型的“Example & Usage”章节下的说明进行操作:
# Install the example (add --no-build-isolation)
pip3 install --no-build-isolation "qai-hub-models[face-det-lite]"
# Run the example
# Use --help to see all options
python3 -m qai_hub_models.models.face_det_lite.demo --quantize w8a8 --image ./three-people-640-480.jpg --output-dir out/
在 out/FaceDetLitebNet_output.png 中找到输出图像。
如果通过 SSH 连接,则可以通过以下方式将输出图像复制回主机:
# Find IP via: ifconfig | grep -Eo 'inet (addr:)?([0-9]*\.){3}[0-9]*' | grep -Eo '([0-9]*\.){3}[0-9]*' | grep -v '127.0.0.1'
# Then: (replace 192.168.1.148 by the IP address of your development kit)
scp ubuntu@192.168.1.148:~/aihub-demo/out/FaceDetLitebNet_output.png ~/Downloads/FaceDetLitebNet_output.png
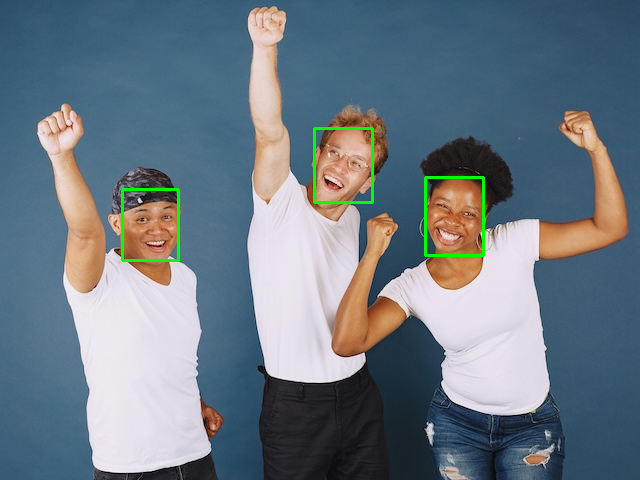

4️⃣ 好的,现在我们已经拥有了一个可运行的模型。例如,在 魔方派 3 上,运行此模型每次推理需要 189.7 毫秒。
将模型移植到NPU
至此,我们已获得一个可运行的参考模型,接下来将在NPU上运行该模型。您需要完成以下三个部分。
1️⃣ 对数据进行预处理,例如将图像转换为可以传递给神经网络的特征。
2️⃣ 将模型导出为 ONNX 或者 TFLite,并通过 LiteRT or ONNX Runtime 运行模型。
3️⃣ 对输出�进行后处理,例如将神经网络的输出转换为面部的边界框。
该模型较为直观,可通过 LiteRT 和 ONNX Runtime 进行了解。然而,数据预处理与输出后处理的代码可能并非如此简单。
预处理输入
对于图像模型,大多数AI Hub模型接受的输入矩阵格式为 (HEIGHT, WIDTH, CHANNELS) (LiteRT) 或 (CHANNELS, HEIGHT, WIDTH) (ONNX),且数值需归一化至0到1之间。若输入为单通道图像,需先将其转换为灰度图。若模型已量化(绝大多数情况如此),还需读取zero_point和scale,并对像素值进行相应缩放(在LiteRT中操作较为简便,因其内置量化参数,而ONNX则不包含这些参数)。通常量化模型的输入数据会线性缩放至0..255(uint8)或-128..127(int8)范围。这部分处理相对简单。下面示例代码中的(def load_image_litert)函数展示了完整的Python实现。
然而需要特别注意的是上述处理方式并非绝对通用,正因如此才需要参考AI Hub示例代码。每个示例都提供了精确的输入缩放实现代码。在我们当前的示例Lightweight-Face-Detection中,输入的张量维度为(480, 640, 1)。但值得注意的是,预处理代码并未将图像转换为灰度图,而是直接�提取了RGB图像的蓝色通道:
img_array = img_array.astype("float32") / 255.0
img_array = img_array[np.newaxis, ...]
img_tensor = torch.Tensor(img_array)
img_tensor = img_tensor[:, :, :, -1] # HERE WE TAKE BLUE CHANNEL, NOT CONVERT TO GRAYSCALE
这类细节极易出错。因此,当您发现自己的实现与AI Hub示例结果不一致时:请仔细阅读示例代码。对于非图像类输入(如音频数据),这一原则更为重要。请务必通过演示代码来理解模型真正的输入预期。
后处理输出
这同样适用于后处理。例如,将神经网络的输出映射到面部检测边界框并�不存在统一的方法。对于 Lightweight-Face-Detection,可以在face_det_lite/app.py#L77查看具体代码。
如果您的目标平台是 Python,那么最简单的方法是将后处理代码复制到您的应用程序中,因为 AI Hub 包含很多您可能不想要的依赖项。此外需要注意,AI Hub的后处理代码基于PyTorch张量运行,而您的推理环境是LiteRT或ONNX Runtime,因此需要对其中的部分细节进行调整。我们将在下面的端到端示例中具体演示这一点。
端到端示例(Python)
经过以上说明,接下来让我们查看具体代码实现。
1️⃣ 在开发板上打开一个终端,并设置此示例的基本环境:
# Create a new fresh directory
mkdir -p ~/aihub-npu
cd ~/aihub-npu
# Create a new venv
python3 -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate
# Install the LiteRT runtime (to run models) and Pillow (to parse images)
pip3 install ai-edge-litert==1.3.0 Pillow
# Download an example image
wget https://cdn.edgeimpulse.com/qc-ai-docs/example-images/three-people-640-480.jpg
2️⃣ NPU仅支持uint8/int8量化模型。值得庆幸的是,AI Hub 已提供预量化且优化过的模型。您可以:
-
下载本教程的模型(在 CDN 上镜像):
wget https://cdn.edgeimpulse.com/qc-ai-docs/models/face_det_lite-lightweight-face-detection-w8a8.tflite -
或通过以下步骤下载任意AI Hub模型并推送至开发板:
a. 访问Lightweight-Face-Detection。
b. 点击“Download model”。
c. 选择“TFLite”为运行时,“w8a8”为精度。
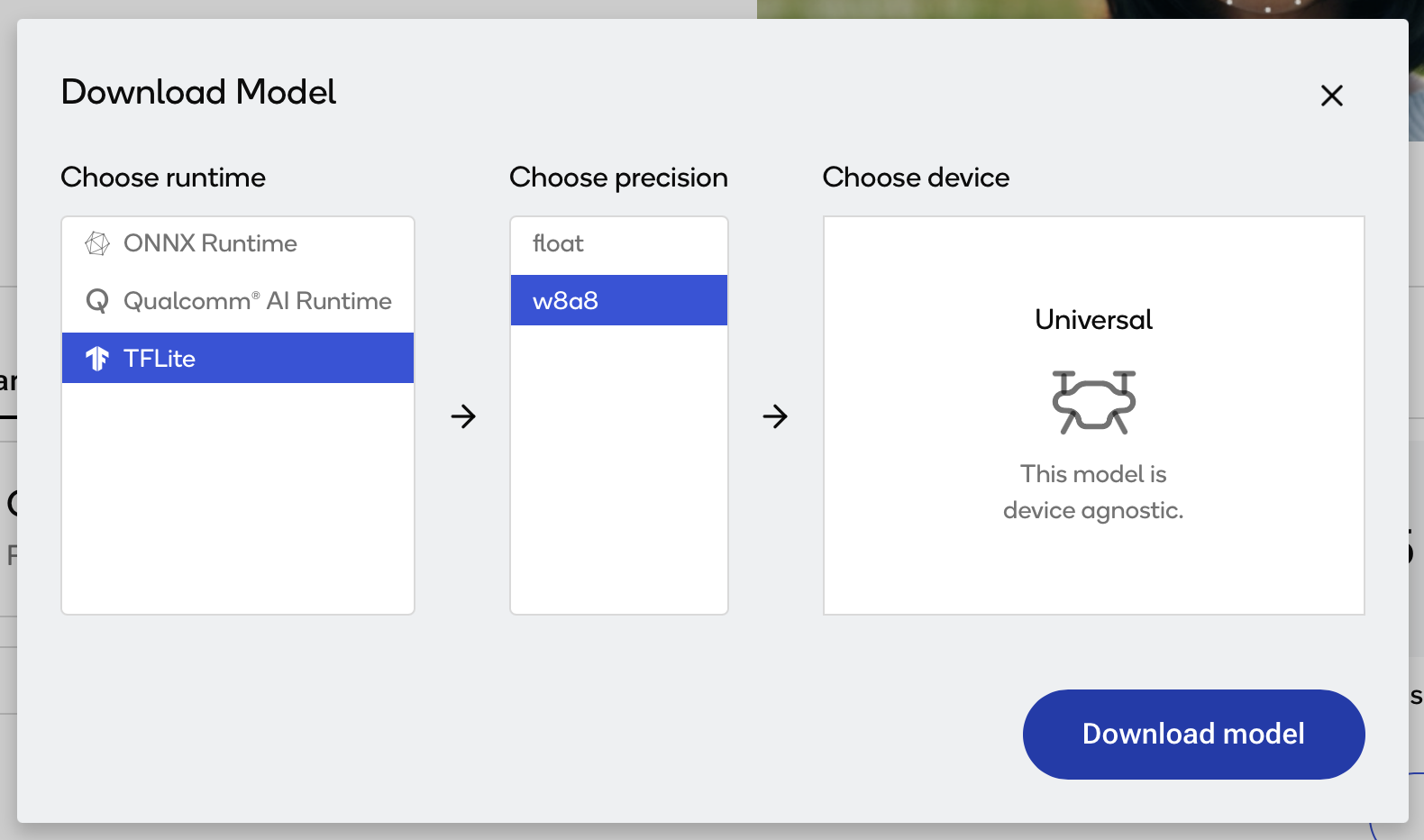
如果您的模型仅适用于 ONNX 格式,请从Run models using ONNX Runtime获取说明。原理与本教程相同。
d. 下载模型。
e. 如果您没有直接在 Dragonwing 开发板上下载模型,则需要通过 SSH 推送模型:
i. 找到开发板的 IP 地址。在您的开发板上运行:
ifconfig | grep -Eo 'inet (addr:)?([0-9]*\.){3}[0-9]*' | grep -Eo '([0-9]*\.){3}[0-9]*' | grep -v '127.0.0.1'
# ... Example:
# 192.168.1.253ii.推送 .tflite 文件。从您的计算机运行:
scp face_det_lite-lightweight-face-detection-w8a8.tflite ubuntu@192.168.1.253:~/face_det_lite-lightweight-face-detection-w8a8.tflite
3️⃣ 创建一个新文件 face_detection.py。该文件包含模型调用,以及来自 AI Hub 示例的预处理和后处理代码(参见内联注释)。
import numpy as np
from ai_edge_litert.interpreter import Interpreter, load_delegate
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
import os, time, sys
def curr_ms():
return round(time.time() * 1000)
# Paths
IMAGE_IN = 'three-people-640-480.jpg'
IMAGE_OUT = 'three-people-640-480-overlay.jpg'
MODEL_PATH = 'face_det_lite-lightweight-face-detection-w8a8.tflite'
# If we pass in --use-qnn we offload to NPU
use_qnn = True if len(sys.argv) >= 2 and sys.argv[1] == '--use-qnn' else False
experimental_delegates = []
if use_qnn:
experimental_delegates = [load_delegate("libQnnTFLiteDelegate.so", options={"backend_type":"htp"})]
# Load TFLite model and allocate tensors
interpreter = Interpreter(
model_path=MODEL_PATH,
experimental_delegates=experimental_delegates
)
interpreter.allocate_tensors()
# Get input and output tensor details
input_details = interpreter.get_input_details()
output_details = interpreter.get_output_details()
# === BEGIN PREPROCESSING ===
# Load an image (using Pillow) and make it in the right format that the interpreter expects (e.g. quantize)
# All AI Hub image models use 0..1 inputs to start.
def load_image_litert(interpreter, path, single_channel_behavior: str = 'grayscale'):
d = interpreter.get_input_details()[0]
shape = [int(x) for x in d["shape"]] # e.g. [1, H, W, C] or [1, C, H, W]
dtype = d["dtype"]
scale, zp = d.get("quantization", (0.0, 0))
if len(shape) != 4 or shape[0] != 1:
raise ValueError(f"Unexpected input shape: {shape}")
# Detect layout
if shape[1] in (1, 3): # [1, C, H, W]
layout, C, H, W = "NCHW", shape[1], shape[2], shape[3]
elif shape[3] in (1, 3): # [1, H, W, C]
layout, C, H, W = "NHWC", shape[3], shape[1], shape[2]
else:
raise ValueError(f"Cannot infer layout from shape {shape}")
# Load & resize
img = Image.open(path).convert("RGB").resize((W, H), Image.BILINEAR)
arr = np.array(img)
if C == 1:
if single_channel_behavior == 'grayscale':
# Convert to luminance (H, W)
gray = np.asarray(Image.fromarray(arr).convert('L'))
elif single_channel_behavior in ('red', 'green', 'blue'):
ch_idx = {'red': 0, 'green': 1, 'blue': 2}[single_channel_behavior]
gray = arr[:, :, ch_idx]
else:
raise ValueError(f"Invalid single_channel_behavior: {single_channel_behavior}")
# Keep shape as HWC with C=1
arr = gray[..., np.newaxis]
# HWC -> correct layout
if layout == "NCHW":
arr = np.transpose(arr, (2, 0, 1)) # (C,H,W)
# Scale 0..1 (all AI Hub image models use this)
arr = (arr / 255.0).astype(np.float32)
# Quantize if needed
if scale and float(scale) != 0.0:
q = np.rint(arr / float(scale) + int(zp))
if dtype == np.uint8:
arr = np.clip(q, 0, 255).astype(np.uint8)
else:
arr = np.clip(q, -128, 127).astype(np.int8)
return np.expand_dims(arr, 0) # add batch
# This model looks like grayscale, but AI Hub inference actually takes the BLUE channel
# see https://github.com/quic/ai-hub-models/blob/8cdeb11df6cc835b9b0b0cf9b602c7aa83ebfaf8/qai_hub_models/models/face_det_lite/app.py#L70
input_data = load_image_litert(interpreter, IMAGE_IN, single_channel_behavior='blue')
# === END PREPROCESSING (input_data contains right data) ===
# Set tensor and run inference
interpreter.set_tensor(input_details[0]['index'], input_data)
# Run once to warmup
interpreter.invoke()
# Then run 10x
start = curr_ms()
for i in range(0, 10):
interpreter.invoke()
end = curr_ms()
# === BEGIN POSTPROCESSING ===
# Grab 3 output tensors and dequantize
q_output_0 = interpreter.get_tensor(output_details[0]['index'])
scale_0, zero_point_0 = output_details[0]['quantization']
hm = ((q_output_0.astype(np.float32) - zero_point_0) * scale_0)[0]
q_output_1 = interpreter.get_tensor(output_details[1]['index'])
scale_1, zero_point_1 = output_details[1]['quantization']
box = ((q_output_1.astype(np.float32) - zero_point_1) * scale_1)[0]
q_output_2 = interpreter.get_tensor(output_details[2]['index'])
scale_2, zero_point_2 = output_details[2]['quantization']
landmark = ((q_output_2.astype(np.float32) - zero_point_2) * scale_2)[0]
# Taken from https://github.com/quic/ai-hub-models/blob/8cdeb11df6cc835b9b0b0cf9b602c7aa83ebfaf8/qai_hub_models/utils/bounding_box_processing.py#L369
def get_iou(boxA: np.ndarray, boxB: np.ndarray) -> float:
"""
Given two tensors of shape (4,) in xyxy format,
compute the iou between the two boxes.
"""
xA = max(boxA[0], boxB[0])
yA = max(boxA[1], boxB[1])
xB = min(boxA[2], boxB[2])
yB = min(boxA[3], boxB[3])
inter_area = max(0, xB - xA + 1) * max(0, yB - yA + 1)
boxA_area = (boxA[2] - boxA[0] + 1) * (boxA[3] - boxA[1] + 1)
boxB_area = (boxB[2] - boxB[0] + 1) * (boxB[3] - boxB[1] + 1)
return inter_area / float(boxA_area + boxB_area - inter_area)
# Taken from https://github.com/quic/ai-hub-models/blob/8cdeb11df6cc835b9b0b0cf9b602c7aa83ebfaf8/qai_hub_models/models/face_det_lite/utils.py
class BBox:
# Bounding Box
def __init__(
self,
label: str,
xyrb: list[int],
score: float = 0,
landmark: list | None = None,
rotate: bool = False,
):
"""
A bounding box plus landmarks structure to hold the hierarchical result.
parameters:
label:str the class label
xyrb: 4 list for bbox left, top, right bottom coordinates
score:the score of the detection
landmark: 10x2 the landmark of the joints [[x1,y1], [x2,y2]...]
"""
self.label = label
self.score = score
self.landmark = landmark
self.x, self.y, self.r, self.b = xyrb
self.rotate = rotate
minx = min(self.x, self.r)
maxx = max(self.x, self.r)
miny = min(self.y, self.b)
maxy = max(self.y, self.b)
self.x, self.y, self.r, self.b = minx, miny, maxx, maxy
@property
def width(self) -> int:
return self.r - self.x + 1
@property
def height(self) -> int:
return self.b - self.y + 1
@property
def box(self) -> list[int]:
return [self.x, self.y, self.r, self.b]
@box.setter
def box(self, newvalue: list[int]) -> None:
self.x, self.y, self.r, self.b = newvalue
@property
def haslandmark(self) -> bool:
return self.landmark is not None
@property
def xywh(self) -> list[int]:
return [self.x, self.y, self.width, self.height]
# Taken from https://github.com/quic/ai-hub-models/blob/8cdeb11df6cc835b9b0b0cf9b602c7aa83ebfaf8/qai_hub_models/models/face_det_lite/utils.py
def nms(objs: list[BBox], iou: float = 0.5) -> list[BBox]:
"""
nms function customized to work on the BBox objects list.
parameter:
objs: the list of the BBox objects.
return:
the rest of the BBox after nms operation.
"""
if objs is None or len(objs) <= 1:
return objs
objs = sorted(objs, key=lambda obj: obj.score, reverse=True)
keep = []
flags = [0] * len(objs)
for index, obj in enumerate(objs):
if flags[index] != 0:
continue
keep.append(obj)
for j in range(index + 1, len(objs)):
# if flags[j] == 0 and obj.iou(objs[j]) > iou:
if (
flags[j] == 0
and get_iou(np.array(obj.box), np.array(objs[j].box)) > iou
):
flags[j] = 1
return keep
# Ported from https://github.com/quic/ai-hub-models/blob/8cdeb11df6cc835b9b0b0cf9b602c7aa83ebfaf8/qai_hub_models/models/face_det_lite/utils.py#L110
# The original code uses torch.Tensor, this uses native numpy arrays
def detect(
hm: np.ndarray, # (H, W, 1), float32
box: np.ndarray, # (H, W, 4), float32
landmark: np.ndarray, # (H, W, 10), float32
threshold: float = 0.2,
nms_iou: float = 0.2,
stride: int = 8,
) -> list:
def _sigmoid(x: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
# stable-ish sigmoid
out = np.empty_like(x, dtype=np.float32)
np.negative(x, out=out)
np.exp(out, out=out)
out += 1.0
np.divide(1.0, out, out=out)
return out
def _maxpool3x3_same(x_hw: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
"""
x_hw: (H, W) single-channel array.
3x3 max pool, stride=1, padding=1 (same as PyTorch F.max_pool2d(kernel=3,stride=1,padding=1))
Pure NumPy using stride tricks.
"""
H, W = x_hw.shape
# pad with -inf so edges don't borrow smaller values
pad = 1
xpad = np.pad(x_hw, ((pad, pad), (pad, pad)), mode='constant', constant_values=-np.inf)
# build 3x3 sliding windows using as_strided
s0, s1 = xpad.strides
shape = (H, W, 3, 3)
strides = (s0, s1, s0, s1)
windows = np.lib.stride_tricks.as_strided(xpad, shape=shape, strides=strides, writeable=False)
# max over the 3x3 window
return windows.max(axis=(2, 3))
def _topk_desc(values_flat: np.ndarray, k: int):
"""Return (topk_values_sorted, topk_indices_sorted_desc)."""
if k <= 0:
return np.array([], dtype=values_flat.dtype), np.array([], dtype=np.int64)
k = min(k, values_flat.size)
# argpartition for top-k by value
idx_part = np.argpartition(-values_flat, k - 1)[:k]
# sort those k by value desc
order = np.argsort(-values_flat[idx_part])
idx_sorted = idx_part[order]
return values_flat[idx_sorted], idx_sorted
# 1) sigmoid heatmap
hm = _sigmoid(hm.astype(np.float32, copy=False))
# squeeze channel -> (H, W)
hm_hw = hm[..., 0]
# 2) 3x3 max-pool same
hm_pool = _maxpool3x3_same(hm_hw)
# 3) local maxima mask (keep equal to pooled)
# (like (hm == hm_pool).float() * hm in torch)
keep = (hm_hw >= hm_pool) # >= to keep plateaus, mirrors torch equality on floats closely enough
candidate_scores = np.where(keep, hm_hw, 0.0).ravel()
# 4) topk up to 2000
num_candidates = int(keep.sum())
k = min(num_candidates, 2000)
scores_k, flat_idx_k = _topk_desc(candidate_scores, k)
H, W = hm_hw.shape
ys = (flat_idx_k // W).astype(np.int32)
xs = (flat_idx_k % W).astype(np.int32)
# 5) gather boxes/landmarks and build outputs
objs = []
for cx, cy, score in zip(xs, ys, scores_k):
if score < threshold:
# because scores_k is sorted desc, we can break
break
# box offsets at (cy, cx): [x, y, r, b]
x, y, r, b = box[cy, cx].astype(np.float32, copy=False)
# convert to absolute xyrb in pixels (same math as torch code)
cxcycxcy = np.array([cx, cy, cx, cy], dtype=np.float32)
xyrb = (cxcycxcy + np.array([-x, -y, r, b], dtype=np.float32)) * float(stride)
xyrb = xyrb.astype(np.int32, copy=False).tolist()
# landmarks: first 5 x, next 5 y
x5y5 = landmark[cy, cx].astype(np.float32, copy=False)
x5y5 = x5y5 + np.array([cx]*5 + [cy]*5, dtype=np.float32)
x5y5 *= float(stride)
box_landmark = list(zip(x5y5[:5].tolist(), x5y5[5:].tolist()))
objs.append(BBox("0", xyrb=xyrb, score=float(score), landmark=box_landmark))
if nms_iou != -1:
return nms(objs, iou=nms_iou)
return objs
# Detection code from https://github.com/quic/ai-hub-models/blob/8cdeb11df6cc835b9b0b0cf9b602c7aa83ebfaf8/qai_hub_models/models/face_det_lite/app.py#L77
dets = detect(hm, box, landmark, threshold=0.55, nms_iou=-1, stride=8)
res = []
for n in range(0, len(dets)):
xmin, ymin, w, h = dets[n].xywh
score = dets[n].score
L = int(xmin)
R = int(xmin + w)
T = int(ymin)
B = int(ymin + h)
W = int(w)
H = int(h)
if L < 0 or T < 0 or R >= 640 or B >= 480:
if L < 0:
L = 0
if T < 0:
T = 0
if R >= 640:
R = 640 - 1
if B >= 480:
B = 480 - 1
# Enlarge bounding box to cover more face area
b_Left = L - int(W * 0.05)
b_Top = T - int(H * 0.05)
b_Width = int(W * 1.1)
b_Height = int(H * 1.1)
if (
b_Left >= 0
and b_Top >= 0
and b_Width - 1 + b_Left < 640
and b_Height - 1 + b_Top < 480
):
L = b_Left
T = b_Top
W = b_Width
H = b_Height
R = W - 1 + L
B = H - 1 + T
print(f'Found face: x={L}, y={T}, w={W}, h={H}, score={score}')
res.append([L, T, W, H, score])
# === END POSTPROCESSING ===
# Create new PIL image from the input data, stripping off the batch dim
input_reshaped = input_data.reshape(input_data.shape[1:])
if input_reshaped.shape[2] == 1:
input_reshaped = np.squeeze(input_reshaped, axis=-1) # strip off the last dim if grayscale
# And write to output image so we can debug
img_out = Image.fromarray(input_reshaped).convert("RGB")
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img_out)
for bb in res:
L, T, W, H, score = bb
draw.rectangle([L, T, L + w, T + H], outline="#00FF00", width=3)
img_out.save(IMAGE_OUT)
print('')
print(f'Inference took (on average): {(end - start) / 10}ms. per image')
4️⃣ 在 CPU 上运行模型:
python3 face_detection.py
# INFO: Created TensorFlow Lite XNNPACK delegate for CPU.
# Found face: x=120, y=186, w=62, h=79, score=0.8306506276130676
# Found face: x=311, y=125, w=66, h=81, score=0.8148472309112549
# Found face: x=424, y=173, w=64, h=86, score=0.8093323111534119
#
# Inference took (on average): 35.6ms. per image
至此,我们每次推理的时间从 189.7 毫秒缩短到 35.6 毫秒。
5️⃣ 在 NPU 上运行模型:
python3 face_detection.py --use-qnn
# INFO: TfLiteQnnDelegate delegate: 1382 nodes delegated out of 1633 nodes with 27 partitions.
#
# Found face: x=120, y=186, w=62, h=78, score=0.8255056142807007
# Found face: x=311, y=125, w=66, h=81, score=0.8148472309112549
# Found face: x=421, y=173, w=67, h=86, score=0.8093323111534119
#
# Inference took (on average): 2.4ms. per image
至此已完成优化。通过量化该模型并将其移植到 NPU,我们将模型速度提高了 79 倍。相信您对 AI Hub 的资源价值以及 NPU 和 AI Engine Direct SDK 的潜在功能有充分的了解。您也不局限于使用 Python。例如, LiteRT 也提供了C++的调用示例。
将模型部署到 NPU(Edge Impulse)
可以通过 Edge Impulse 部署图像分类、视觉回归和某些对象检测模型。