LiteRT / TFLite
LiteRT, formerly known as TensorFlow Lite, is Google's high-performance runtime for on-device AI. You can run existing quantized LiteRT models (in Python or C++) on the NPU on Dragonwing devices with a single line of code using the LiteRT delegates that are part of AI Engine Direct.
Quantizing models
The NPU only supports uint8/int8 quantized models. Unsupported models, or unsupported layers will be automatically moved back to the CPU. You can use quantization-aware training or post-training quantization to quantize your LiteRT models. Make sure you follow the steps for "Full integer quantization".
Don't want to quantize yourself? You can download a range of pre-quantized models from Qualcomm AI Hub, or use Edge Impulse to quantize new or existing models.
Running a model on the NPU (Python)
To offload a model to the NPU, you just need to load the LiteRT delegate; and pass it into the interpreter. E.g.:
from ai_edge_litert.interpreter import Interpreter, load_delegate
qnn_delegate = load_delegate("libQnnTFLiteDelegate.so", options={"backend_type": "htp"})
interpreter = Interpreter(
model_path=...,
experimental_delegates=[qnn_delegate]
)
Running a model on the NPU (C++)
To offload a model to the NPU, you'll first need to add the following compile flags:
CFLAGS += -I${QNN_SDK_ROOT}/include
LDFLAGS += -L${QNN_SDK_ROOT}/lib/aarch64-ubuntu-gcc9.4 -lQnnTFLiteDelegate
Then, you instantiate the LiteRT delegate and pass it to the LiteRT interpreter:
// == Includes ==
#include "QNN/TFLiteDelegate/QnnTFLiteDelegate.h"
// == Application code ==
// Get your interpreter...
tflite::Interpreter *interpreter = ...;
// Create QNN Delegate options structure.
TfLiteQnnDelegateOptions options = TfLiteQnnDelegateOptionsDefault();
// Set the mandatory backend_type option. All other options have default values.
options.backend_type = kHtpBackend;
// Instantiate delegate. Must not be freed until interpreter is freed.
TfLiteDelegate* delegate = TfLiteQnnDelegateCreate(&options);
TfLiteStatus status = interpreter->ModifyGraphWithDelegate(delegate);
// Check that status == kTfLiteOk
Python Examples
Prerequisites
- Ubuntu OS should be flashed
- Terminal access with appropriate permissions
- If you haven’t previously installed the PPA packages, please run the following steps to install them.
git clone -b ubuntu_setup --single-branch https://github.com/rubikpi-ai/rubikpi-script.git
cd rubikpi-script
./install_ppa_pkgs.sh - Open the terminal on your development board, or an ssh session to your development board, and:
Create a new venv, and install the LiteRT runtime and Pillow:python3 -m venv .venv-litert-demo --system-site-packages
source .venv-litert-demo/bin/activate
pip3 install ai-edge-litert==1.3.0 Pillow
pip3 install opencv-python - Install necessary python3 and gtk packages.
sudo apt install python3-gi python3-gi-cairo gir1.2-gtk-3.0
sudo apt install python3-venv python3-full
sudo apt install -y pkg-config cmake libcairo2-dev
sudo apt install libgirepository1.0-dev gir1.2-glib-2.0
sudo apt install build-essential python3-dev python3-pip pkg-config meson
- Vision Transformers
- Image Classification
- Object Detection
Vision Transformers
Here's how you can run a Vision Transformer model (downloaded from AI Hub) on both the CPU and the NPU using the LiteRT delegates.
1️⃣ Create inference_vit.py and add following reference code:
import numpy as np
from ai_edge_litert.interpreter import Interpreter, load_delegate
from PIL import Image
import os, time, sys
import urllib.request
def curr_ms():
return round(time.time() * 1000)
use_npu = True if len(sys.argv) >= 2 and sys.argv[1] == '--use-npu' else False
# Path to your quantized TFLite model and test image (will be download automatically)
MODEL_PATH = "vit-vit-w8a8.tflite"
IMAGE_PATH = "boa-constrictor.jpg"
LABELS_PATH = "vit-vit-labels.txt"
if not os.path.exists(MODEL_PATH):
print("Downloading model...")
model_url = 'https://cdn.edgeimpulse.com/qc-ai-docs/models/vit-vit-w8a8.tflite'
urllib.request.urlretrieve(model_url, MODEL_PATH)
if not os.path.exists(LABELS_PATH):
print("Downloading labels...")
labels_url = 'https://cdn.edgeimpulse.com/qc-ai-docs/models/vit-vit-labels.txt'
urllib.request.urlretrieve(labels_url, LABELS_PATH)
if not os.path.exists(IMAGE_PATH):
print("Downloading image...")
image_url = 'https://cdn.edgeimpulse.com/qc-ai-docs/examples/boa-constrictor.jpg'
urllib.request.urlretrieve(image_url, IMAGE_PATH)
with open(LABELS_PATH, 'r') as f:
labels = [line for line in f.read().splitlines() if line.strip()]
experimental_delegates = []
if use_npu:
experimental_delegates = [load_delegate("libQnnTFLiteDelegate.so", options={"backend_type": "htp"})]
# Load TFLite model and allocate tensors
interpreter = Interpreter(
model_path=MODEL_PATH,
experimental_delegates=experimental_delegates
)
interpreter.allocate_tensors()
# Get input and output tensor details
input_details = interpreter.get_input_details()
output_details = interpreter.get_output_details()
# Load and preprocess image
def load_image(path, input_shape):
# Expected input shape: [1, height, width, channels]
_, height, width, channels = input_shape
img = Image.open(path).convert("RGB").resize((width, height))
img_np = np.array(img, dtype=np.uint8) # quantized models expect uint8
img_np = np.expand_dims(img_np, axis=0)
return img_np
input_shape = input_details[0]['shape']
input_data = load_image(IMAGE_PATH, input_shape)
# Set tensor and run inference
interpreter.set_tensor(input_details[0]['index'], input_data)
# Run once to warmup
interpreter.invoke()
# Then run 10x
start = curr_ms()
for i in range(0, 10):
interpreter.invoke()
end = curr_ms()
# Get prediction
q_output = interpreter.get_tensor(output_details[0]['index'])
scale, zero_point = output_details[0]['quantization']
f_output = (q_output.astype(np.float32) - zero_point) * scale
# Image classification models in AI Hub miss a Softmax() layer at the end of the model, so add it manually
def softmax(x, axis=-1):
# subtract max for numerical stability
x_max = np.max(x, axis=axis, keepdims=True)
e_x = np.exp(x - x_max)
return e_x / np.sum(e_x, axis=axis, keepdims=True)
# show top-5 predictions
scores = softmax(f_output[0])
top_k = scores.argsort()[-5:][::-1]
print("\nTop-5 predictions:")
for i in top_k:
print(f"Class {labels[i]}: score={scores[i]}")
print('')
print(f'Inference took (on average): {(end - start) / 10}ms. per image')
2️⃣ Run the model on the CPU:
python3 inference_vit.py
# INFO: Created TensorFlow Lite XNNPACK delegate for CPU.
#
# Top-5 predictions:
# Class boa constrictor: score=0.6264431476593018
# Class rock python: score=0.047579940408468246
# Class night snake: score=0.006721484009176493
# Class mouse: score=0.0022421202156692743
# Class pick: score=0.001942973816767335
#
# Inference took (on average): 391.1ms. per image
3️⃣ Run the model on the NPU:
python3 inference_vit.py --use-npu
# INFO: TfLiteQnnDelegate delegate: 1382 nodes delegated out of 1633 nodes with 27 partitions.
#
# INFO: Created TensorFlow Lite XNNPACK delegate for CPU.
#
# Top-5 predictions:
# Class boa constrictor: score=0.6113042235374451
# Class rock python: score=0.038359832018613815
# Class night snake: score=0.011630792170763016
# Class mouse: score=0.002294909441843629
# Class lens cap: score=0.0018960189772769809
#
# Inference took (on average): 132.7ms. per image
As you can see this model runs significantly faster on NPU - but there's a slight change in the output of the model. You can also see that for this model not all layers can run on NPU ("1382 nodes delegated out of 1633 nodes with 27 partitions").
GTK-Based Image Classification App
Here's how you can use a GTK-based desktop application to run an image classification model—downloaded from (AI Hub) on both the CPU and NPU using LiteRT delegates from AI Engine Direct.
The GoogLeNet_w8a8.tflite model, sourced from AI-Hub, leverages TensorFlow Lite with QNN delegate acceleration to enable efficient on-device inference.
Now follow the steps to create Image classification application.
Summary
• Type: Desktop GUI application
• Functionality: Image classification using TFLite
• Modes: CPU and QNN delegate
• Interface: GTK-based GUI
• Output: Top predictions with confidence bars
Environment Setup & Imports
In the step the script sets up display-related environment variables (for Linux systems) and imports necessary libraries like OpenCV, NumPy, GTK, and TensorFlow Lite.
import cv2, numpy as np, os, time
from gi.repository import Gtk, GLib, GdkPixbuf
import ai_edge_litert.interpreter as tflite
• GTK is used for the GUI, OpenCV for image handling, and TensorFlow Lite for inference.
Configuration Constants
These constants define paths to the model, label file, and delegate library.
TF_MODEL = "/home/ubuntu/GoogLeNet_w8a8.tflite"
LABELS = "/etc/labels/imagenet_labels.txt"
DELEGATE_PATH = "libQnnTFLiteDelegate.so"
DEVICE_OS = "Ubuntu"
Download TFlite Model
This script checks if a TensorFlow Lite model file exists locally, and if not, downloads it from a specified Hugging Face URL.
import urllib.request
if not os.path.exists(TF_MODEL):
print("Downloading model...")
model_url = 'https://huggingface.co/qualcomm/GoogLeNet/resolve/main/GoogLeNet_w8a8.tflite'
urllib.request.urlretrieve(model_url, TF_MODEL)
Helper Functions
This step sets up the core logic and interface for image classification using LiteRT and GTK.
Softmax Calculation
Ensures numerical stability when converting logits to probabilities.
Pythondef stable_softmax(logits):
logits = logits.astype(np.float32)
shifted_logits = np.clip(logits - np.max(logits), -500, 500)
exp_scores = np.exp(shifted_logits)
return exp_scores / np.sum(exp_scores)
Label Loader
Loads class labels from a text file.
Pythondef load_labels(label_path):
with open(label_path, 'r') as f:
return [line.strip() for line in f.readlines()]
Image Preprocessing
Prepares the image for model input: resizing, color conversion, and reshaping.
Pythondef preprocess_image(image_path, input_shape, input_dtype):
img = cv2.imread(image_path)
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img = cv2.resize(img, (input_shape[2], input_shape[1]))
img = img.astype(input_dtype)
return np.expand_dims(img, axis=0)
Inference Execution
This function will:
• Loads the model (with or without delegate)
• Prepares input
• Runs inference
• Applies softmax
• Returns top 4 predictions with confidence scores
def runInference(image, use_delegate):
if use_delegate:
try:
delegate = tflite.load_delegate(DELEGATE_PATH, {'backend_type': 'htp'})
model = tflite.Interpreter(model_path=TF_MODEL, experimental_delegates=[delegate])
except:
model = tflite.Interpreter(model_path=TF_MODEL)
else:
model = tflite.Interpreter(model_path=TF_MODEL)
model.allocate_tensors()
input_details = model.get_input_details()
input_data = preprocess_image(image, input_details[0]['shape'], input_details[0]['dtype'])
model.set_tensor(input_details[0]['index'], input_data)
start_time = time.time()
model.invoke()
inference_time = time.time() - start_time
output_data = model.get_tensor(model.get_output_details()[0]['index'])
probabilities = stable_softmax(output_data[0])
labels = load_labels(LABELS)
top_indices = np.argsort(probabilities)[::-1][:4]
results = [(labels[i], probabilities[i] * 100) for i in top_indices]
return results, inference_time
GTK GUI Components
File Browser Dialog
Allows users to select an image file.
class FileBrowser(Gtk.FileChooserDialog):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(title="Choose an image", action=Gtk.FileChooserAction.OPEN)
self.add_buttons(Gtk.STOCK_CANCEL, Gtk.ResponseType.CANCEL, Gtk.STOCK_OPEN, Gtk.ResponseType.OK)
def run_and_get_file(self):
if self.run() == Gtk.ResponseType.OK:
return self.get_filename()
self.destroy()
Main Window
The GUI includes:
• Image display area
• Radio buttons to choose CPU or delegate
• Buttons to select and reprocess image
• Result display with labels and progress bars
class MainWindow(Gtk.Window):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(title="Image Classification")
self.set_default_size(800, 600)
self.imageFilepath = ""
...
Image Processing and Display
This method:
• Resizes and displays the image
• Runs inference
• Displays results with progress bars and inference time
def process_file(self, filepath):
pixbuf = GdkPixbuf.Pixbuf.new_from_file(filepath)
new_width, new_height = resizeImage(pixbuf)
scaled_pixbuf = pixbuf.scale_simple(new_width, new_height, GdkPixbuf.InterpType.BILINEAR)
self.image.set_from_pixbuf(scaled_pixbuf)
results, inference_time = runInference(filepath, self.use_delegate())
...
Application Entry Point
Initializes and launches the GTK application.
def main():
app = MainWindow()
app.connect("destroy", Gtk.main_quit)
app.show_all()
Gtk.main()
if __name__ == "__main__":
success, _ = Gtk.init_check()
if not success:
print("GTK could not be initialized.")
exit(1)
main()
Reference Code
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
#
# Copyright (c) Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. and/or its subsidiaries.
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
#
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
import cv2
import gi
import numpy as np
import os
os.environ['xDG_RUNTIME_DIR'] = '/run/user/1000/'
os.environ['WAYLAND_DISPLAY'] = 'wayland-1'
os.environ['DISPLAY'] = ':0'
import time
import urllib.request
gi.require_version("Gtk", "3.0")
from gi.repository import Gtk, GLib, GdkPixbuf
# ========= Constants =========
TF_MODEL = "/home/ubuntu/GoogLeNet_w8a8.tflite"
LABELS = "/etc/labels/imagenet_labels.txt"
DELEGATE_PATH = "libQnnTFLiteDelegate.so"
DEVICE_OS="Ubuntu"
UNAME = os.uname().nodename
import ai_edge_litert.interpreter as tflite
if not os.path.exists(TF_MODEL):
print("Downloading model...")
model_url = 'https://huggingface.co/qualcomm/GoogLeNet/resolve/main/GoogLeNet_w8a8.tflite'
urllib.request.urlretrieve(model_url, TF_MODEL)
# ========= Helper Functions =========
def stable_softmax(logits):
# Convert logits to float64 for higher precision
logits = logits.astype(np.float32)
# Subtract the maximum logit to prevent overflow
shifted_logits = logits - np.max(logits)
# Clip the shifted logits to a safe range to prevent overflow in exp
shifted_logits = np.clip(shifted_logits, -500, 500)
# Calculate the exponentials and normalize
exp_scores = np.exp(shifted_logits)
probabilities = exp_scores / np.sum(exp_scores)
return probabilities
# Load labels from file
def load_labels(label_path):
with open(label_path, 'r') as f:
return [line.strip() for line in f.readlines()]
def resizeImage(pixbuf):
original_width = pixbuf.get_width()
original_height = pixbuf.get_height()
# Target display size
max_width = 800
max_height = 600
# Calculate new size preserving aspect ratio
scale = min(max_width / original_width, max_height / original_height)
new_width = int(original_width * scale)
new_height = int(original_height * scale)
return new_width, new_height
# Load and preprocess input image
def preprocess_image(image_path, input_shape, input_dtype):
# Read the image using OpenCV
img = cv2.imread(image_path)
if img is None:
raise ValueError(f"Failed to load image at {image_path}")
# Convert BGR to RGB
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# Resize the image to the desired input shape
img = cv2.resize(img, (input_shape[2], input_shape[1]))
# Convert to the desired data type
img = img.astype(input_dtype)
# Add batch dimension
img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0)
return img
# ====== Inference Function ======
def runInference(image, use_delegate):
results = []
print(f"Running on {DEVICE_OS} using Delegate:{use_delegate}")
if use_delegate:
try:
# Load the QNN delegate library
delegate_options = { 'backend_type': 'htp' }
delegate = tflite.load_delegate(DELEGATE_PATH, delegate_options)
# Load the TFLite model
model = tflite.Interpreter(model_path=TF_MODEL, experimental_delegates=[delegate])
print("INFO: Loaded QNN delegate with HTP backend")
except Exception as e:
print(f"WARNING: Failed to load QNN delegate: {e}")
print("INFO: Continuing without QNN delegate")
model = tflite.Interpreter(model_path=TF_MODEL)
else:
model = tflite.Interpreter(model_path=TF_MODEL)
model.allocate_tensors()
# Get and Prepare input
input_details = model.get_input_details()
input_shape = input_details[0]['shape']
input_dtype = input_details[0]['dtype']
input_data = preprocess_image(image, input_shape, input_dtype)
# Load input data to input tensor
model.set_tensor(input_details[0]['index'], input_data)
model.get_signature_list()
# Run inference
try:
start_time = time.time()
model.invoke()
end_time = time.time()
print("Interpreter invoked successfully.")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error during model invocation: {e}")
return []
# Calculate and print duration
inference_time = end_time - start_time
# Prepare output tensor details
output_details = model.get_output_details()
# Load output data to output tensor
output_data = model.get_tensor(output_details[0]['index'])
# Load labels and get prediction
labels = load_labels(LABELS)
predicted_index = np.argmax(output_data)
predicted_label = labels[predicted_index]
print("Predicted index:", predicted_index)
print("Predicted label:", predicted_label)
# Add Softmax function
logits = output_data[0]
probabilities = stable_softmax(logits)
# Get top 4 predictions
top_k = 4
top_indices = np.argsort(probabilities)[::-1][:top_k]
for i in top_indices:
result = (labels[i], probabilities[i] * 100)
results.append(result)
return results, inference_time
# ====== GTK GUI Classes ======
class FileBrowser(Gtk.FileChooserDialog):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(title="Choose an image", action=Gtk.FileChooserAction.OPEN)
self.add_buttons(Gtk.STOCK_CANCEL, Gtk.ResponseType.CANCEL, Gtk.STOCK_OPEN, Gtk.ResponseType.OK)
def run_and_get_file(self):
response = super().run()
if response == Gtk.ResponseType.OK:
print("Selected file:", self.get_filename())
self.selected_file = self.get_filename()
self.destroy()
return self.selected_file
class MainWindow(Gtk.Window):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(title="Image Classification")
self.set_default_size(800, 600)
self.imageFilepath = ""
# Main layout
self.mainBox = Gtk.Box(orientation=Gtk.Orientation.HORIZONTAL, spacing=10)
self.mainBox.set_margin_top(10)
self.mainBox.set_margin_bottom(10)
self.mainBox.set_margin_start(10)
self.mainBox.set_margin_end(10)
self.add(self.mainBox)
# Main Window Image setup with fallback
self.image = Gtk.Image()
try:
MAIN_IMAGE = "MainWindowPic.jpg"
self.image.set_from_file(MAIN_IMAGE)
except Exception as e:
print("Error loading main image:", e)
self.image.set_from_icon_name("image-missing", Gtk.IconSize.DIALOG)
self.mainBox.pack_start(self.image, True, True, 0)
# Set up a new box to add results and and file button
self.infoBox = Gtk.Box(orientation=Gtk.Orientation.VERTICAL, spacing=10)
# Radio button to select Delegate
delegate_label = Gtk.Label(label="Select Inference Mode:")
self.infoBox.pack_start(delegate_label, False, False, 10)
self.cpu_radio = Gtk.RadioButton.new_with_label_from_widget(None, "CPU")
self.delegate_radio = Gtk.RadioButton.new_with_label_from_widget(self.cpu_radio, "Delegate")
self.infoBox.pack_start(self.cpu_radio, False, False, 0)
self.infoBox.pack_start(self.delegate_radio, False, False, 0)
# Radio button signal
self.cpu_radio.connect("toggled", self.on_radio_toggled)
self.delegate_radio.connect("toggled", self.on_radio_toggled)
# Open file button
open_button = Gtk.Button(label="Select Image")
open_button.connect("clicked", self.on_open_file_clicked)
self.infoBox.pack_start(open_button, False, True, 10)
# Reprocess Image
reprocess_button = Gtk.Button(label="Reprocess Image")
reprocess_button.connect("clicked", self.on_reprocess_image_clicked)
self.infoBox.pack_start(reprocess_button, False, True, 10)
# Classification results
self.results = Gtk.Box(orientation=Gtk.Orientation.VERTICAL, spacing=10)
self.infoBox.pack_start(self.results, True, True, 0)
self.mainBox.pack_start(self.infoBox, True, True, 0)
def use_delegate(self):
return self.delegate_radio.get_active()
def on_radio_toggled(self, button):
if button.get_active():
print(f"Selected option: {button.get_label()}")
def process_file(self, filepath):
try:
# Resize Image
pixbuf = GdkPixbuf.Pixbuf.new_from_file(filepath)
new_width, new_height = resizeImage(pixbuf)
scaled_pixbuf = pixbuf.scale_simple(new_width, new_height, GdkPixbuf.InterpType.BILINEAR)
# Replace the image with new image
self.image.set_from_pixbuf(scaled_pixbuf)
# Run Inference
use_delegate = self.use_delegate()
print("delegate: " , use_delegate)
options, inference_time = runInference(filepath, use_delegate)
# Clear result box
for child in self.results.get_children():
self.results.remove(child)
# Set up predictions
for label, percent in options:
textBox = Gtk.Box(orientation=Gtk.Orientation.HORIZONTAL, spacing=10)
barBox = Gtk.Box(orientation=Gtk.Orientation.HORIZONTAL, spacing=10)
text = Gtk.Label(label=label, xalign=0)
text.set_size_request(100, -1)
bar = Gtk.ProgressBar()
bar.set_fraction(percent / 100.0)
bar.set_text(f"{percent:.2f}%")
bar.set_show_text(True)
textBox.pack_start(text, False, False, 0)
barBox.pack_start(bar, True, True, 0)
self.results.pack_start(textBox, False, False, 0)
self.results.pack_start(barBox, False, False, 0)
self.results.show_all()
# Add inference time label
time_label = Gtk.Label(label=f"Inference Time : {inference_time * 1000:.2f} ms")
self.results.pack_start(time_label, False, False, 50)
self.results.show_all()
except Exception as e:
print("Error reading file:", e)
def on_open_file_clicked(self, widget):
dialog = FileBrowser()
selected_file = dialog.run_and_get_file()
self.imageFilepath = selected_file
if selected_file:
self.process_file(selected_file)
def on_reprocess_image_clicked(self, widget):
self.process_file(self.imageFilepath)
def on_destroy(self, widget):
Gtk.main_quit()
# === Main Entry Point ===
def main():
app = MainWindow()
app.connect("destroy", Gtk.main_quit)
app.show_all()
Gtk.main()
if __name__ == "__main__":
success, _ = Gtk.init_check()
if not success:
print("GTK could not be initialized. Check environmental variables")
exit(1)
main()
Now you're set up to run the application on either CPU/delegate using the command below:
python3 classification.py
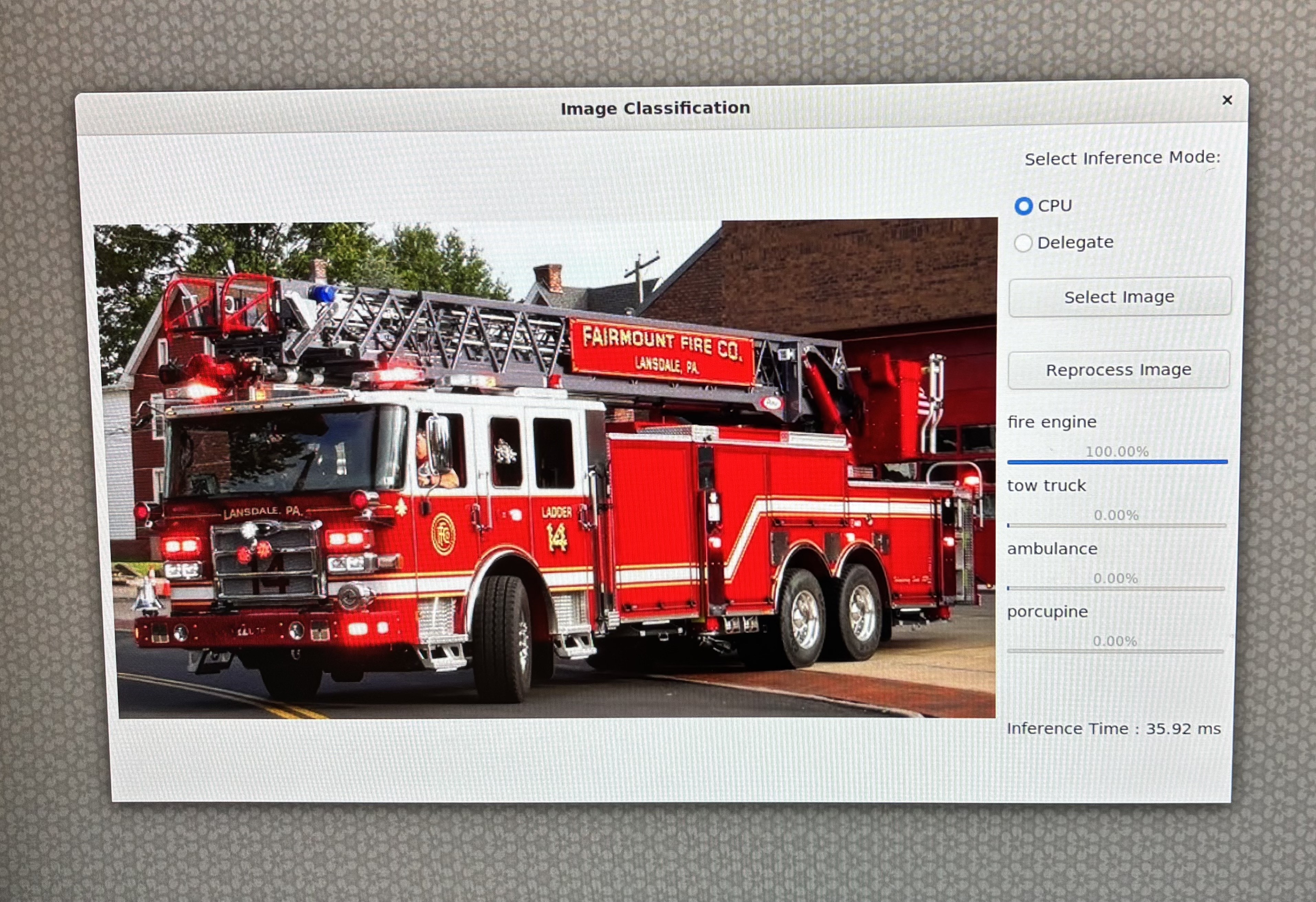
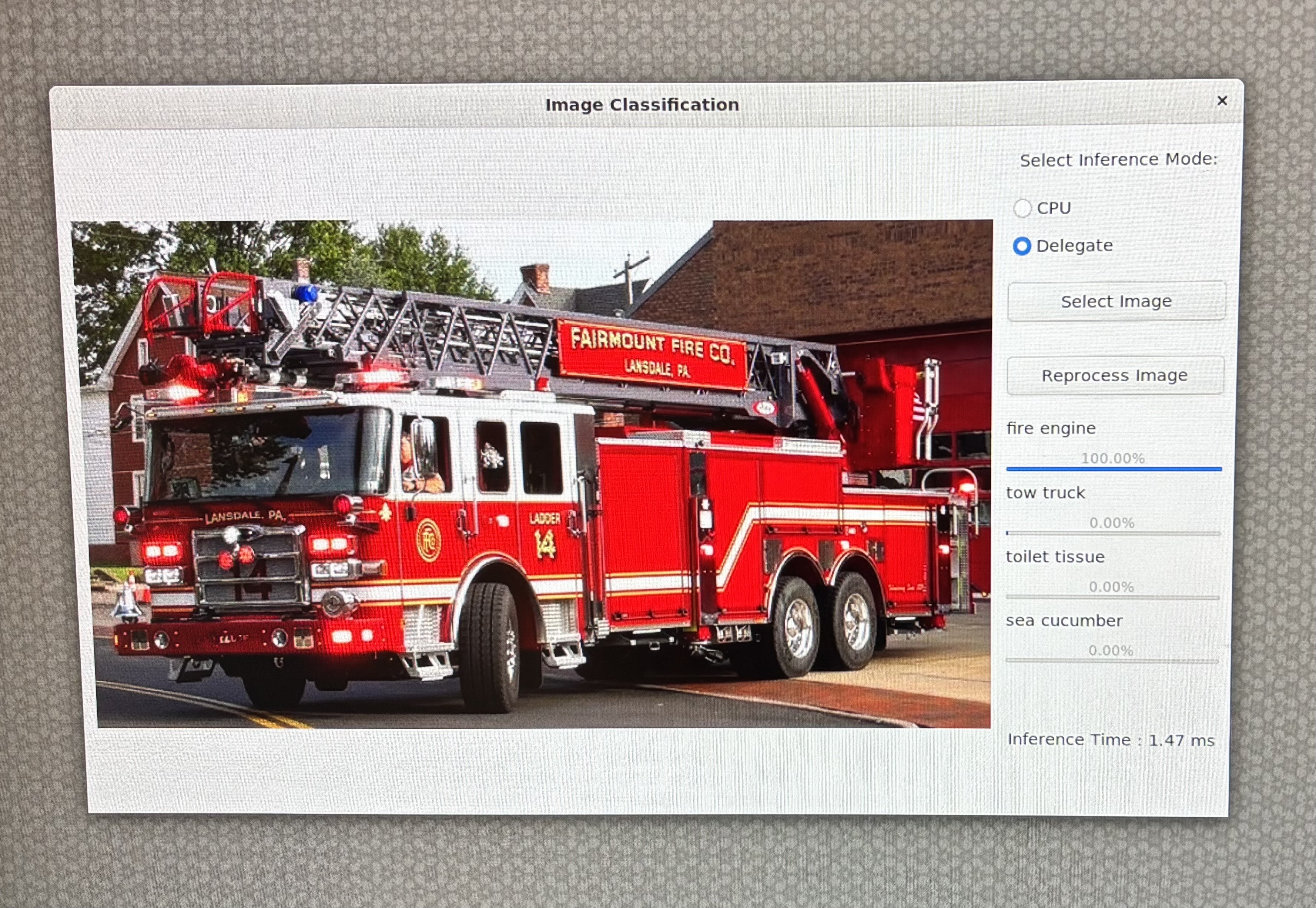
Download any image from internet. In this example we used firetruck image. Through scp command copy image onto the device.
scp xxx.jpg ubuntu@IP_address:/home/ubuntu/
Select CPU as your runtime option on the GUI:
Select delegate as your runtime option on the GUI:
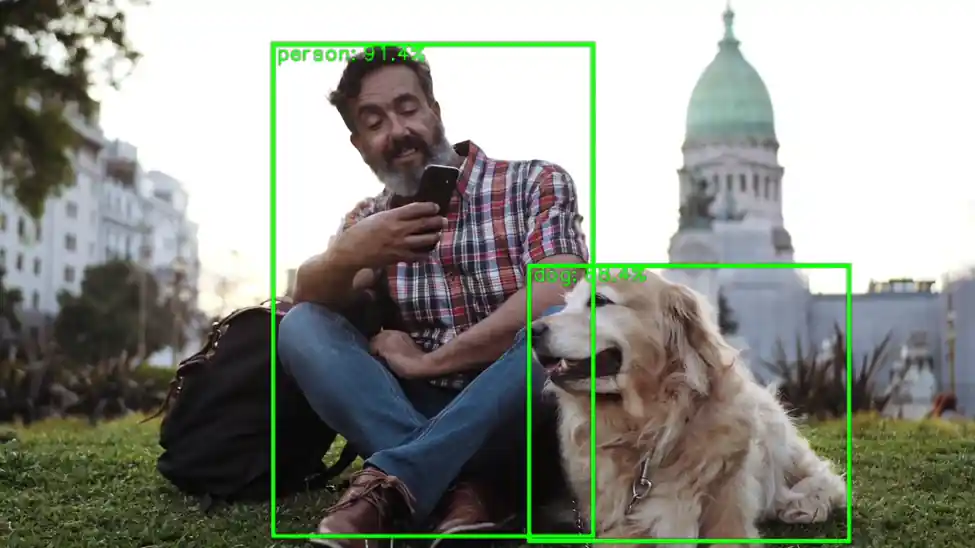
Object Detection with OpenCV & Wayland Display
This Python script performs real-time object detection on a video file using a quantized YOLOv8 TensorFlow Lite model and displays the annotated frames via GStreamer on a Wayland display. It is optimized for edge AI scenarios using hardware acceleration through the QNN TFLite delegate.
The YOLOv8 model isn't available by default. Please follow the Step-6 from Qualcomm Intelligent Multimedia SDK to export YoloV8 quantized model.
The next step is to push the model on to the target device Through scp command copy the model onto the device.
scp xxxx.tflite ubuntu@IP_address:/home/ubuntu/
Initialization and Configuration
• Paths for the model, labels, input video, and delegate are defined.
• Constants like frame dimensions, FPS, confidence threshold, and scaling factors are set for preprocessing and postprocessing.
MODEL_PATH = "yolov8_det_quantized.tflite"
LABEL_PATH = "coco_labels.txt"
VIDEO_IN = "video.mp4"
DELEGATE_PATH = "libQnnTFLiteDelegate.so"
Use a video file that works well with object detection models.
For best results, choose videos with clear subjects, good lighting, and minimal motion blur.
Examples:
• A street scene with vehicles and pedestrians
• A warehouse or factory floor with visible objects
• A static camera feed showing people or products
Model Loading and Delegate Setup
• Loads the hardware delegate for accelerated inference.
• Initializes the TensorFlow Lite interpreter with the quantized YOLOv8 model.
delegate_options = { 'backend_type': 'htp' }
delegate = tflite.load_delegate(DELEGATE_PATH, delegate_options)
interpreter = tflite.Interpreter(model_path=MODEL_PATH, experimental_delegates=[delegate])
interpreter.allocate_tensors()
Label Loading
• Loads COCO dataset labels for object annotation.
labels = [l.strip() for l in open(LABEL_PATH)]
GStreamer Pipeline Setup
• Creates a GStreamer pipeline using appsrc to stream frames to a Wayland sink.
• Enables real-time display of processed frames.
pipeline = Gst.parse_launch(
'appsrc name=src is-live=true block=true format=time caps=video/x-raw,format=BGR,width=1600,height=900,framerate=30/1 ! videoconvert ! waylandsink')
Video Capture and Frame Processing
• Opens the video file using OpenCV.
• Each frame is resized and preprocessed to match the model’s input dimensions.
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(VIDEO_IN)
Inference and Post-processing
• Runs inference on each frame.
• Dequantizes the model outputs using predefined scales and zero-points.
interpreter.set_tensor(in_det[0]['index'], input_tensor)
interpreter.invoke()
boxes_q = interpreter.get_tensor(out_det[0]['index'])[0]
scores_q = interpreter.get_tensor(out_det[1]['index'])[0]
classes_q = interpreter.get_tensor(out_det[2]['index'])[0]
• Applies a confidence threshold to filter low-probability detections. • Uses Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) to remove overlapping boxes.
mask = scores >= CONF_THRES
boxes_f = boxes[mask]
scores_f = scores[mask]
classes_f = classes[mask]
Annotation and Display
• Draws bounding boxes and labels on the frame using OpenCV. • Logs the highest detection score every 100 frames.
cv2.rectangle(frame_rs, (x1i, y1i), (x2i, y2i), (0,255,0), 2)
cv2.putText(frame_rs, f"{lab} {sc:.2f}", (x1i, max(10,y1i-5)), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0,255,0), 2)
Streaming to Wayland Display
Converts frames to GStreamer buffers and pushes them to the pipeline with timestamps for smooth playback.
buf = Gst.Buffer.new_allocate(None, len(data), None)
buf.fill(0, data)
buf.duration = Gst.util_uint64_scale_int(1, Gst.SECOND, FPS_OUT)
timestamp = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_POS_MSEC) * Gst.MSECOND
buf.pts = buf.dts = int(timestamp)
appsrc.emit('push-buffer', buf)
Completion
Gracefully shuts down the pipeline after processing all frames.
appsrc.emit('end-of-stream')
pipeline.set_state(Gst.State.NULL)
cap.release()
Use Cases
This script is ideal for:
• Smart cameras
• Robotics
• Embedded systems with Wayland-based GUIs
• Real-time monitoring in edge AI deployments
Reference Code
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
#
# Copyright (c) Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. and/or its subsidiaries.
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
#
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Import necessary libraries
import cv2
import numpy as np
import gi
gi.require_version('Gst', '1.0')
from gi.repository import Gst
import ai_edge_litert.interpreter as tflite
# Initialize GStreamer
Gst.init(None)
# -------------------- Parameters --------------------
MODEL_PATH = "/home/ubuntu/yolov8_det_quantized.tflite" # Path to TFLite model
LABEL_PATH = "/etc/labels/coco_labels.txt" # Path to label file # Path to label file
VIDEO_IN = "/etc/media/video.mp4" # Input video file
DELEGATE_PATH = "libQnnTFLiteDelegate.so" # Delegate for hardware acceleration
# Frame and model parameters
FRAME_W, FRAME_H = 1600, 900
FPS_OUT = 30
CONF_THRES = 0.25
NMS_IOU_THRES = 0.50
BOX_SCALE = 3.2108588218688965
BOX_ZP = 31.0
SCORE_SCALE = 0.0038042240776121616
# -------------------- Load Model --------------------
# Load delegate for hardware acceleration
delegate_options = { 'backend_type': 'htp' }
delegate = tflite.load_delegate(DELEGATE_PATH, delegate_options)
# Load and allocate TFLite interpreter
interpreter = tflite.Interpreter(model_path=MODEL_PATH, experimental_delegates=[delegate])
interpreter.allocate_tensors()
# Get input/output tensor details
in_det = interpreter.get_input_details()
out_det = interpreter.get_output_details()
in_h, in_w = in_det[0]["shape"][1:3]
# -------------------- Load Labels --------------------
labels = [l.strip() for l in open(LABEL_PATH)]
# -------------------- GStreamer Pipeline --------------------
# Create GStreamer pipeline to display video via Wayland
pipeline = Gst.parse_launch(
'appsrc name=src is-live=true block=true format=time caps=video/x-raw,format=BGR,width=1600,height=900,framerate=30/1 ! videoconvert ! waylandsink'
)
appsrc = pipeline.get_by_name('src')
pipeline.set_state(Gst.State.PLAYING)
# -------------------- Video Input --------------------
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(VIDEO_IN)
# Scaling factors for bounding box adjustment
sx, sy = FRAME_W / in_w, FRAME_H / in_h
# Preallocate frame buffers
frame_rs = np.empty((FRAME_H, FRAME_W, 3), np.uint8)
input_tensor = np.empty((1, in_h, in_w, 3), np.uint8)
frame_cnt = 0
# -------------------- Main Loop --------------------
while True:
ok, frame = cap.read()
if not ok:
break
frame_cnt += 1
# ---------- Preprocessing ----------
# Resize frame to display resolution
cv2.resize(frame, (FRAME_W, FRAME_H), dst=frame_rs)
# Resize again to model input resolution
cv2.resize(frame_rs, (in_w, in_h), dst=input_tensor[0])
# ---------- Inference ----------
# Set input tensor and run inference
interpreter.set_tensor(in_det[0]['index'], input_tensor)
interpreter.invoke()
# ---------- Postprocessing ----------
# Get raw output tensors
boxes_q = interpreter.get_tensor(out_det[0]['index'])[0]
scores_q = interpreter.get_tensor(out_det[1]['index'])[0]
classes_q = interpreter.get_tensor(out_det[2]['index'])[0]
# Dequantize outputs
boxes = BOX_SCALE * (boxes_q.astype(np.float32) - BOX_ZP)
scores = SCORE_SCALE * scores_q.astype(np.float32)
classes = classes_q.astype(np.int32)
# Filter by confidence threshold
mask = scores >= CONF_THRES
if np.any(mask):
boxes_f = boxes[mask]
scores_f = scores[mask]
classes_f = classes[mask]
# Convert boxes to OpenCV format
x1, y1, x2, y2 = boxes_f.T
boxes_cv2 = np.column_stack((x1, y1, x2 - x1, y2 - y1))
# Apply Non-Maximum Suppression
idx_cv2 = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(
bboxes=boxes_cv2.tolist(),
scores=scores_f.tolist(),
score_threshold=CONF_THRES,
nms_threshold=NMS_IOU_THRES
)
if len(idx_cv2):
idx = idx_cv2.flatten()
sel_boxes = boxes_f[idx]
sel_scores = scores_f[idx]
sel_classes = classes_f[idx]
# Debug print every 100 frames
if frame_cnt % 100 == 0:
print(f"[{frame_cnt:4d}] max score = {sel_scores.max():.3f}")
# Rescale boxes to display resolution
sel_boxes[:, [0,2]] *= sx
sel_boxes[:, [1,3]] *= sy
sel_boxes = sel_boxes.astype(np.int32)
# Clip boxes to frame boundaries
sel_boxes[:, [0,2]] = np.clip(sel_boxes[:, [0,2]], 0, FRAME_W-1)
sel_boxes[:, [1,3]] = np.clip(sel_boxes[:, [1,3]], 0, FRAME_H-1)
# Draw boxes and labels
for (x1i, y1i, x2i, y2i), sc, cl in zip(sel_boxes, sel_scores, sel_classes):
cv2.rectangle(frame_rs, (x1i, y1i), (x2i, y2i), (0,255,0), 2)
lab = labels[cl] if cl < len(labels) else str(cl)
cv2.putText(frame_rs, f"{lab} {sc:.2f}", (x1i, max(10,y1i-5)),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0,255,0), 2)
# ---------- Video Output ----------
# Convert frame to bytes and push to GStreamer pipeline
data = frame_rs.tobytes()
buf = Gst.Buffer.new_allocate(None, len(data), None)
buf.fill(0, data)
buf.duration = Gst.util_uint64_scale_int(1, Gst.SECOND, FPS_OUT)
timestamp = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_POS_MSEC) * Gst.MSECOND
buf.pts = buf.dts = int(timestamp)
appsrc.emit('push-buffer', buf)
# -------------------- Finish --------------------
appsrc.emit('end-of-stream')
pipeline.set_state(Gst.State.NULL)
cap.release()
print("Done – video streamed to Wayland sink")
Now you're set up to run the application on NPU(delegate) using the command below:
python3 ObjectDetection.py